Are you wondering, “Can I Get An Iv At Urgent Care?” and seeking fast relief from dehydration? CARS.EDU.VN clarifies how urgent care facilities offer vital intravenous (IV) hydration and treatments, swiftly addressing dehydration and related health concerns. Explore alternative options for rapid rehydration, discover which solution suits you best, and receive comprehensive care recommendations that prioritize your well-being.
1. Understanding Dehydration: Causes, Symptoms, and the Need for IV Fluids
Dehydration occurs when your body loses more fluids than it takes in, disrupting normal bodily functions. Considering that the human body is approximately 60% water, maintaining hydration is essential for overall health. Let’s dive into the causes and symptoms of dehydration, highlighting when IV fluids become a necessary intervention.
1.1. Primary Causes of Dehydration
Dehydration primarily stems from inadequate fluid intake to compensate for daily water loss. Common causes include:
- Insufficient Water Consumption: Simply not drinking enough water.
- Excessive Sweating: Due to physical activity, high temperatures, or fever.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Vomiting and diarrhea lead to rapid fluid loss.
- Certain Medications: Diuretics can increase urination, contributing to dehydration.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Diabetes can cause frequent urination and dehydration.
1.2. Recognizing the Symptoms of Dehydration
Identifying dehydration early can prevent severe complications. Symptoms vary based on the severity of fluid loss.
| Symptom | Mild to Moderate Dehydration | Severe Dehydration |
|---|---|---|
| Thirst | Increased thirst | Extreme thirst |
| Mouth & Tongue | Dry mouth or swollen tongue | Very dry mouth |
| Urination | Infrequent urination, dark-colored urine | Minimal or no urination |
| Skin | Dry skin | Poor skin elasticity (skin stays folded when pinched) |
| Heart Rate | Normal to slightly elevated | Rapid heartbeat |
| Blood Pressure | Normal | Low blood pressure |
| Eyes | Normal | Sunken eyes |
| Other Symptoms | Headache, muscle cramps | Dizziness, confusion, lethargy, fainting |



1.3. When to Consider IV Fluids
While mild dehydration can be managed by drinking water and electrolyte solutions, severe cases require immediate medical intervention, often through IV fluids. Consider IV fluids if you experience:
- Inability to Keep Fluids Down: Persistent vomiting makes oral rehydration impossible.
- Severe Symptoms: Confusion, dizziness, or fainting indicate critical dehydration.
- Underlying Conditions: Individuals with chronic illnesses may need IV fluids to manage dehydration effectively.
Alt text: A man experiencing dehydration symptoms, highlighting the importance of recognizing signs of dehydration and seeking timely treatment.
2. Urgent Care Centers: Your Immediate Solution for Dehydration
Urgent care centers bridge the gap between primary care physicians and emergency rooms, offering accessible and timely treatment for various medical conditions, including dehydration. Understanding the role of urgent care can help you make informed decisions about your healthcare needs.
2.1. What is Urgent Care?
Urgent care centers provide medical care for illnesses and injuries that require prompt attention but are not life-threatening. They offer a convenient and cost-effective alternative to emergency rooms for non-critical conditions.
2.2. Services Offered at Urgent Care Centers
Urgent care centers offer a range of services, including:
- Treatment for Acute Illnesses: Colds, flu, infections, and dehydration.
- Minor Injury Care: Wound care, sprains, and fractures.
- Diagnostic Services: X-rays, lab tests, and EKGs.
- Preventive Care: Vaccinations and physical exams.
- IV Hydration: Administration of intravenous fluids for dehydration.
2.3. Can You Get IV Fluids at Urgent Care?
Yes, most urgent care centers are equipped to administer IV fluids for dehydration. This treatment is particularly effective for individuals who cannot tolerate oral rehydration due to vomiting or severe symptoms. IV fluids can quickly restore hydration levels and alleviate symptoms.
2.4. Benefits of Choosing Urgent Care for Dehydration
- Accessibility: Urgent care centers are typically open extended hours and on weekends, providing care when primary care physicians are unavailable.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Urgent care visits are generally less expensive than emergency room visits.
- Timeliness: Urgent care centers offer shorter wait times compared to emergency rooms.
- Expert Care: Trained medical professionals at urgent care centers can accurately assess your condition and provide appropriate treatment.
2.5. Finding a Reputable Urgent Care Center
When seeking urgent care for dehydration, consider the following:
- Check for Accreditation: Ensure the center is accredited by reputable organizations like the Urgent Care Association (UCA).
- Read Reviews: Look for patient reviews and testimonials to gauge the quality of care.
- Verify Insurance Acceptance: Confirm that the center accepts your insurance plan.
- Assess Cleanliness and Organization: A well-maintained facility indicates a commitment to patient safety.
3. The IV Hydration Process at Urgent Care Centers
Understanding what to expect during IV hydration at an urgent care center can ease anxiety and ensure a smooth treatment experience.
3.1. Initial Assessment
Upon arrival, a healthcare professional will evaluate your condition by:
- Reviewing Your Medical History: Identifying any underlying health conditions or medications.
- Assessing Your Symptoms: Determining the severity of dehydration.
- Checking Vital Signs: Monitoring heart rate, blood pressure, and temperature.
3.2. Preparing for IV Hydration
The healthcare provider will explain the IV hydration process and answer any questions. Preparation includes:
- Cleaning the Insertion Site: Using an antiseptic to prevent infection.
- Inserting the IV Catheter: A small needle is inserted into a vein, typically in the arm.
- Securing the IV Line: The catheter is secured with a bandage to prevent movement.
3.3. Administering IV Fluids
The IV bag contains a sterile solution of electrolytes and fluids, which is administered directly into your bloodstream. The healthcare provider will monitor the flow rate and your response to the treatment.
3.4. Types of IV Fluids Used
Common types of IV fluids include:
- Normal Saline: A solution of sodium chloride and water, used to restore fluid balance.
- Lactated Ringer’s Solution: Contains electrolytes similar to those found in blood, ideal for severe dehydration.
- Dextrose Solutions: Used to provide calories and energy, particularly for individuals with low blood sugar.
3.5. Monitoring and Aftercare
During IV hydration, healthcare providers will monitor your vital signs and symptoms. After the treatment, they will:
- Remove the IV Catheter: Once you are adequately hydrated.
- Apply a Bandage: To prevent bleeding and infection.
- Provide Aftercare Instructions: Including advice on maintaining hydration and recognizing potential complications.
Alt text: A woman rehydrating with a water bottle, demonstrating the importance of timely fluid replacement in preventing dehydration complications.
4. The Benefits of IV Hydration: More Than Just Rehydration
IV hydration offers several advantages beyond simply replenishing fluids, making it a valuable treatment option for various conditions.
4.1. Rapid Rehydration
IV fluids are delivered directly into the bloodstream, providing immediate rehydration compared to oral fluids, which must be absorbed through the digestive system.
4.2. Electrolyte Balance
IV solutions contain essential electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and magnesium, which help regulate bodily functions and maintain fluid balance.
4.3. Medication Administration
IV drips can be used to administer medications directly into the bloodstream, ensuring rapid and effective delivery.
4.4. Vitamin and Nutrient Boost
Some IV drips contain vitamins and nutrients that can boost energy levels, support immune function, and improve overall well-being.
4.5. Treatment for Nausea and Vomiting
IV hydration can alleviate nausea and vomiting by restoring fluid balance and administering anti-nausea medications.
5. Comparing Urgent Care to Other Options: ERs and Home Remedies
When faced with dehydration, understanding the available treatment options is crucial. Here’s a comparison of urgent care, emergency rooms, and home remedies.
5.1. Urgent Care vs. Emergency Room (ER)
| Feature | Urgent Care | Emergency Room (ER) |
|---|---|---|
| Severity of Condition | Non-life-threatening conditions | Life-threatening conditions |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Wait Time | Shorter wait times | Longer wait times |
| Services | Treatment for acute illnesses, minor injuries | Treatment for severe illnesses, major injuries |
| Availability | Extended hours, weekends | 24/7 availability |
5.2. When to Choose Urgent Care
Choose urgent care for:
- Moderate to severe dehydration without life-threatening symptoms.
- Inability to keep fluids down.
- Need for rapid rehydration and electrolyte balance.
5.3. When to Choose the Emergency Room
Choose the emergency room for:
- Severe dehydration with life-threatening symptoms (e.g., confusion, fainting).
- Underlying conditions requiring immediate medical attention.
- Trauma or injuries associated with dehydration.
5.4. Home Remedies for Mild Dehydration
For mild dehydration, try:
- Drinking water slowly.
- Consuming electrolyte-rich beverages like sports drinks or coconut water.
- Eating hydrating foods like fruits and vegetables.
- Avoiding caffeine and alcohol.
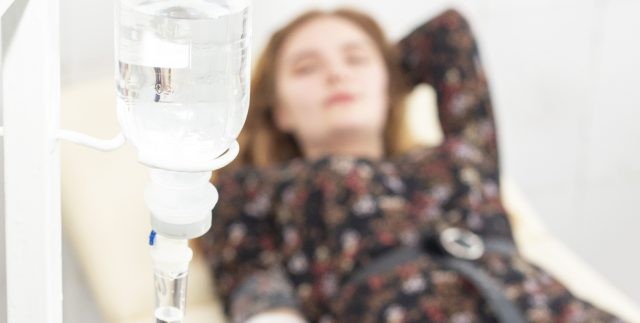
Alt text: A woman receiving IV hydration treatment, highlighting the effectiveness of IV fluids in rapidly restoring hydration and alleviating dehydration symptoms.
6. Potential Risks and Side Effects of IV Hydration
While IV hydration is generally safe, it’s essential to be aware of potential risks and side effects.
6.1. Common Side Effects
- Pain or Bruising at the Insertion Site: Mild discomfort is common and usually resolves quickly.
- Infection: Rare, but possible if the insertion site is not properly cleaned.
- Fluid Overload: Excessive fluid administration can lead to swelling and shortness of breath.
6.2. Rare but Serious Risks
- Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may be allergic to the IV solution or medications.
- Air Embolism: Air entering the bloodstream can cause serious complications.
- Blood Clots: Prolonged IV catheter use can increase the risk of blood clots.
6.3. How to Minimize Risks
- Choose a Reputable Facility: Ensure the urgent care center is accredited and staffed by trained professionals.
- Inform Your Healthcare Provider: Disclose any allergies, medical conditions, or medications.
- Monitor for Symptoms: Report any unusual symptoms during or after IV hydration.
7. Preventing Dehydration: Daily Habits and Special Considerations
Prevention is always better than cure. Adopting healthy habits can significantly reduce your risk of dehydration.
7.1. Daily Hydration Tips
- Drink Water Regularly: Aim for at least eight glasses of water per day.
- Carry a Water Bottle: Keep water accessible throughout the day.
- Eat Hydrating Foods: Include fruits and vegetables with high water content in your diet.
- Monitor Urine Color: Pale yellow urine indicates good hydration.
7.2. Hydration During Exercise
- Drink Before, During, and After Exercise: Replenish fluids lost through sweat.
- Consider Electrolyte Drinks: Especially for prolonged or intense workouts.
7.3. Hydration in Hot Weather
- Avoid Peak Heat Hours: Limit outdoor activities during the hottest parts of the day.
- Wear Light-Colored Clothing: Reflects heat and reduces sweating.
- Stay in Shaded Areas: Minimizes sun exposure and heat absorption.
7.4. Special Considerations for Vulnerable Groups
- Infants and Young Children: Offer frequent sips of water or electrolyte solutions.
- Older Adults: Encourage regular fluid intake, as thirst sensation may decrease with age.
- Individuals with Chronic Illnesses: Follow healthcare provider’s recommendations for fluid management.
8. Debunking Common Myths About Dehydration
Separating fact from fiction can help you make informed decisions about hydration.
8.1. Myth: You Only Need to Drink When You’re Thirsty
Fact: Thirst is a late indicator of dehydration. By the time you feel thirsty, you’re already experiencing fluid loss.
8.2. Myth: All Fluids are Equally Hydrating
Fact: Water is the best choice for hydration. Sugary drinks and alcohol can dehydrate you further.
8.3. Myth: You Can’t Overhydrate
Fact: Overhydration, or hyponatremia, can occur when you drink too much water, diluting electrolytes.
8.4. Myth: Dehydration Only Occurs in Hot Weather
Fact: Dehydration can occur in any climate, especially with physical activity or illness.
8.5. Myth: Sports Drinks are Always Necessary for Hydration
Fact: Sports drinks are beneficial for prolonged or intense exercise, but water is sufficient for moderate activity.
9. New Technologies and Innovations in Hydration Therapy
Advancements in hydration therapy continue to improve treatment outcomes and patient comfort.
9.1. Portable IV Devices
These compact devices allow for convenient IV hydration in various settings, including homes and offices.
9.2. Wearable Hydration Sensors
These sensors monitor hydration levels in real-time, providing personalized hydration recommendations.
9.3. Advanced Electrolyte Formulas
New electrolyte solutions are designed to optimize fluid balance and enhance athletic performance.
9.4. Telehydration Services
Telemedicine platforms offer virtual consultations and remote monitoring for individuals receiving IV hydration at home.
10. CARS.EDU.VN: Your Trusted Source for Automotive and Health Information
At CARS.EDU.VN, we’re committed to providing you with reliable and comprehensive information on automotive care and health-related topics. Our goal is to empower you with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions about your well-being.
10.1. Comprehensive Automotive Services at CARS.EDU.VN
Facing car troubles? CARS.EDU.VN offers detailed insights into automotive services, including repair options, maintenance schedules, and expert advice to keep your vehicle running smoothly. Whether it’s routine maintenance or complex repairs, we provide the information you need to make informed decisions.
10.2. Expert Health Information at Your Fingertips
In addition to automotive expertise, CARS.EDU.VN provides valuable health information, including articles on preventive care, common medical conditions, and tips for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Our health content is designed to help you stay informed and proactive about your well-being.
10.3. Connect with Us
Stay updated with the latest automotive and health insights by visiting CARS.EDU.VN. For immediate assistance, contact us at 456 Auto Drive, Anytown, CA 90210, United States. Reach us via WhatsApp at +1 555-123-4567 or visit our website at CARS.EDU.VN.
Alt text: A healthcare professional preparing an IV drip, illustrating the medical care and expertise involved in administering IV hydration to treat dehydration.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About IV Hydration and Urgent Care
1. Can any urgent care administer IV fluids?
Most urgent care centers can administer IV fluids, but it’s best to call ahead and confirm.
2. How long does IV hydration take at an urgent care center?
IV hydration typically takes 30 to 60 minutes, depending on the severity of dehydration and the type of fluids administered.
3. How much does IV hydration cost at urgent care?
The cost of IV hydration varies, but it’s generally less expensive than emergency room treatment. Contact the urgent care center for specific pricing.
4. What are the common ingredients in IV hydration solutions?
Common ingredients include normal saline, lactated Ringer’s solution, electrolytes, and vitamins.
5. Is IV hydration safe for everyone?
IV hydration is generally safe, but individuals with certain medical conditions, such as heart or kidney problems, should consult their healthcare provider before undergoing treatment.
6. What should I do if I experience side effects during IV hydration?
Report any unusual symptoms to the healthcare provider immediately.
7. Can IV hydration help with hangovers?
IV hydration can alleviate hangover symptoms by replenishing fluids and electrolytes lost due to alcohol consumption.
8. Are there alternatives to IV hydration for dehydration?
Yes, oral rehydration with water and electrolyte solutions can be effective for mild to moderate dehydration.
9. How can I tell if I’m adequately hydrated after IV hydration?
Signs of adequate hydration include improved energy levels, reduced thirst, and pale yellow urine.
10. Where can I find more information about dehydration and IV hydration?
Visit CARS.EDU.VN for comprehensive articles and resources on dehydration, IV hydration, and related health topics.
Conclusion: Stay Informed and Take Action
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for dehydration is crucial for maintaining your health and well-being. Whether you choose urgent care, emergency room treatment, or home remedies, timely intervention can prevent serious complications.
Ready to Learn More?
Do you want to explore more in-depth information about automotive care or health-related topics? Visit CARS.EDU.VN today for a wealth of resources, expert advice, and the latest insights to keep you informed and empowered. Don’t wait—discover the knowledge you need to stay healthy and maintain your vehicle with confidence. Visit cars.edu.vn now and take control of your well-being and automotive care! For immediate assistance, contact us at 456 Auto Drive, Anytown, CA 90210, United States. Reach us via WhatsApp at +1 555-123-4567.
