Car Air Conditioners are essential for comfortable driving, especially during hot weather. At CARS.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of a properly functioning AC system. This guide offers a comprehensive look at car AC systems, from basic operations to maintenance tips, helping you keep your vehicle cool and comfortable. Let’s explore automotive climate control, AC repair, and car cooling systems.
1. Understanding the Core Functions of Your Car Air Conditioner
The primary function of a car air conditioner is to cool the air inside the vehicle’s cabin. It does this by removing heat and humidity from the air, providing a more comfortable environment for the driver and passengers. This process relies on the principles of thermodynamics and the properties of refrigerants. A well-maintained AC system also contributes to driver alertness and focus by preventing overheating and discomfort.
1.1 How Car AC Systems Work: A Step-by-Step Explanation
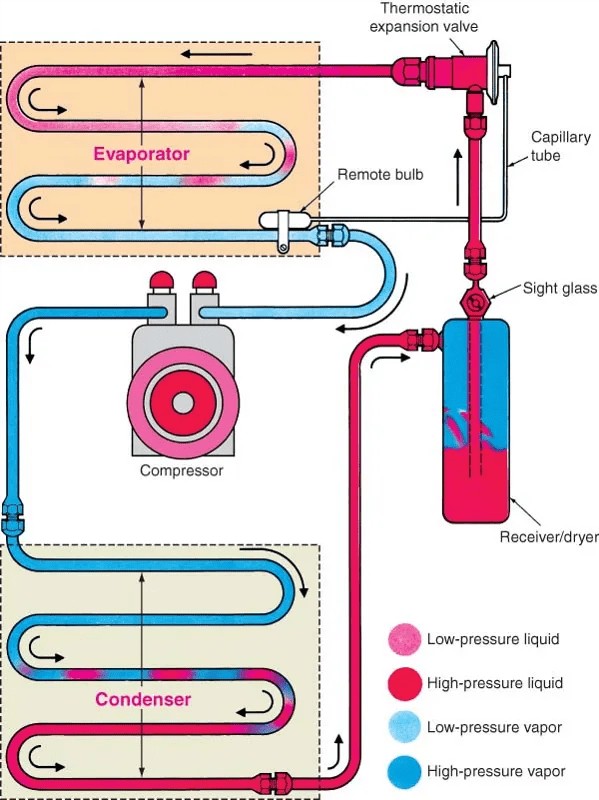
Car AC systems operate on a cycle involving several key components and a refrigerant. The process can be broken down into the following steps:
- Compression: The compressor, driven by the engine, compresses the refrigerant gas, increasing its temperature and pressure.
- Condensation: The high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant gas flows into the condenser, where it releases heat to the outside air and turns into a high-pressure liquid.
- Expansion: The high-pressure liquid refrigerant passes through an expansion valve or orifice tube, which reduces its pressure and temperature.
- Evaporation: The low-pressure, low-temperature refrigerant enters the evaporator, located inside the vehicle’s cabin. Here, it absorbs heat from the air blowing across the evaporator fins, turning back into a gas and cooling the air.
- Cycle Repeat: The low-pressure refrigerant gas returns to the compressor, and the cycle begins again.
1.2 The Role of Refrigerant in Car AC Systems
Refrigerant is the lifeblood of your car’s AC system. It’s a special fluid that absorbs and releases heat as it changes between liquid and gaseous states. The type of refrigerant used in car AC systems has evolved over time due to environmental concerns.
- R-12 (Freon): An older, CFC-based refrigerant that was phased out due to its ozone-depleting properties.
- R-134a: A more environmentally friendly HFC-based refrigerant that replaced R-12.
- R-1234yf: The newest refrigerant, with a significantly lower global warming potential compared to R-134a.
It’s crucial to use the correct type of refrigerant for your vehicle’s AC system. Mixing refrigerants can damage the system and reduce its efficiency.
2. Essential Components of a Car Air Conditioner
A car AC system consists of several interconnected components, each playing a vital role in the cooling process. Understanding these components can help you diagnose potential issues and ensure proper maintenance.
2.1 The Compressor: Powering the Cooling Process
The compressor is the heart of the AC system, responsible for compressing the refrigerant gas and circulating it throughout the system. It’s driven by the engine via a belt and pulley system.
- Function: Increases the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant gas.
- Location: Typically mounted on the front of the engine.
- Common Issues: Compressor failure can result from leaks, lack of lubrication, or internal damage.
2.2 The Condenser: Dissipating Heat
The condenser is similar to the engine radiator and is responsible for dissipating heat from the refrigerant.
- Function: Cools the high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant gas, turning it into a liquid.
- Location: Usually mounted in front of the engine radiator.
- Common Issues: Blockage from debris, corrosion, or damage to the fins can reduce its efficiency.
 Car AC Condenser
Car AC Condenser
2.3 The Evaporator: Absorbing Heat Inside the Cabin
The evaporator is located inside the vehicle’s cabin and is responsible for absorbing heat from the air.
- Function: Cools the air blowing across it as the refrigerant evaporates from a liquid to a gas.
- Location: Typically located behind the dashboard.
- Common Issues: Leaks, corrosion, or blockage can reduce its cooling capacity.
2.4 The Expansion Valve or Orifice Tube: Regulating Refrigerant Flow
The expansion valve or orifice tube controls the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator.
- Function: Reduces the pressure of the refrigerant, causing it to cool rapidly before entering the evaporator.
- Location: Located between the condenser and the evaporator.
- Common Issues: Blockage or malfunction can disrupt refrigerant flow and reduce cooling efficiency.
2.5 The Receiver-Drier or Accumulator: Filtering and Drying Refrigerant
The receiver-drier (used in systems with an expansion valve) or accumulator (used in systems with an orifice tube) filters and removes moisture from the refrigerant.
- Function: Removes moisture and contaminants from the refrigerant to protect the AC system.
- Location: Typically located in the high-pressure side of the system.
- Common Issues: Saturation with moisture, which can lead to corrosion and system damage.
3. Common Problems with Car Air Conditioners
Several issues can affect the performance of your car’s AC system. Recognizing these problems early can help you address them before they cause significant damage.
3.1 Refrigerant Leaks: Causes and Detection
Refrigerant leaks are one of the most common AC problems. Because automotive air conditioning systems operate under pressure, they need to remain completely sealed from the surrounding environment.
- Causes: Leaks can occur at any of the AC system’s connections, hoses, or components due to corrosion, damage, or loose fittings.
- Detection: Signs of a refrigerant leak include reduced cooling performance, oily residue around AC components, or the presence of a refrigerant leak detection dye.
3.2 Compressor Issues: Failure and Prevention
The compressor is a critical component and can be expensive to replace.
- Causes: Compressor failure can result from leaks, lack of lubrication, internal damage, or excessive wear.
- Prevention: Regular maintenance, such as checking refrigerant levels and belt condition, can help prevent compressor failure.
3.3 Clogged Condenser or Evaporator: Reduced Airflow
A clogged condenser or evaporator can restrict airflow and reduce cooling efficiency.
- Causes: Road debris, dirt, leaves, and other contaminants can accumulate on the fins of the condenser and evaporator.
- Prevention: Regularly cleaning the condenser and evaporator can help maintain proper airflow.
3.4 Electrical Problems: Faulty Wiring and Components
Electrical issues can also affect AC system performance.
- Causes: Faulty wiring, relays, switches, or sensors can disrupt the operation of the AC system.
- Diagnosis: Electrical problems may require diagnostic tools and expertise to identify and repair.
4. Car AC Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance
Regular maintenance is essential for keeping your car’s AC system in top condition. Here are some tips to help you maintain your AC system:
4.1 Regular AC System Inspections
Regular inspections can help identify potential problems early.
- Frequency: Inspect the AC system at least once a year, or more frequently if you notice any issues.
- Check: Inspect the compressor belt, hoses, connections, and refrigerant level.
4.2 Cleaning the Condenser and Evaporator
Keeping the condenser and evaporator clean is crucial for maintaining proper airflow.
- Procedure: Use a soft brush or vacuum to remove debris from the fins of the condenser and evaporator.
- Frequency: Clean the condenser and evaporator at least once a year, or more frequently if you drive in dusty or dirty conditions.
4.3 Checking and Replacing the Cabin Air Filter
The cabin air filter filters the air entering the vehicle’s cabin and can become clogged over time.
- Function: Filters dust, pollen, and other contaminants from the air.
- Frequency: Check and replace the cabin air filter every 12,000 to 15,000 miles, or more frequently if you drive in dusty or polluted areas.
4.4 Refrigerant Recharge: When and How
If your AC system is not cooling as well as it used to, it may need a refrigerant recharge.
- When: Recharge the system if you notice reduced cooling performance or if the refrigerant level is low.
- How: It’s best to have a qualified technician recharge the system to ensure proper refrigerant levels and avoid overcharging.
4.5 Professional AC Service: When to Seek Expert Help
Some AC problems require professional diagnosis and repair.
- When: Seek expert help if you notice refrigerant leaks, compressor failure, electrical problems, or other complex issues.
- Benefits: Professional AC service can ensure proper diagnosis, repair, and maintenance of your AC system.
5. Upgrading Your Car’s AC System for Enhanced Cooling
If you’re looking to improve the cooling performance of your car’s AC system, several upgrade options are available.
5.1 High-Performance Compressors
High-performance compressors can provide improved cooling capacity and efficiency.
- Benefits: Enhanced cooling performance, improved efficiency, and increased durability.
- Considerations: High-performance compressors may be more expensive than standard compressors.
5.2 Enhanced Condensers and Evaporators
Upgrading to enhanced condensers and evaporators can improve heat transfer and cooling capacity.
- Benefits: Improved heat transfer, increased cooling capacity, and reduced system pressure.
- Considerations: Enhanced condensers and evaporators may require modifications to the AC system.
5.3 Electronic Expansion Valves
Electronic expansion valves offer more precise control over refrigerant flow.
- Benefits: Improved cooling performance, enhanced efficiency, and optimized system control.
- Considerations: Electronic expansion valves may require specialized installation and programming.
5.4 Thermal Barrier Coatings
Applying thermal barrier coatings to AC components can reduce heat absorption and improve cooling efficiency.
- Benefits: Reduced heat absorption, improved cooling efficiency, and enhanced system performance.
- Considerations: Thermal barrier coatings may require specialized application techniques.
6. Understanding Car AC System Costs
The cost of maintaining and repairing your car’s AC system can vary depending on the type of problem, the parts needed, and the labor involved.
6.1 Average Repair Costs for Common AC Issues
Here are some average repair costs for common AC issues:
| Issue | Average Cost |
|---|---|
| Refrigerant Leak Repair | $150 – $800 |
| Compressor Replacement | $400 – $1200 |
| Condenser Replacement | $300 – $700 |
| Evaporator Replacement | $600 – $1500 |
| Cabin Air Filter Replacement | $30 – $70 |
6.2 Factors Affecting AC Repair Costs
Several factors can affect AC repair costs:
- Vehicle Make and Model: The make and model of your vehicle can affect the cost of parts and labor.
- Type of Repair: Complex repairs, such as compressor or evaporator replacement, will typically cost more than simple repairs, such as refrigerant recharge.
- Location: Labor costs can vary depending on your location.
6.3 DIY vs. Professional AC Service Costs
DIY AC service can save you money on labor costs, but it’s essential to have the necessary knowledge and tools.
- DIY: DIY AC service may be suitable for simple tasks, such as cleaning the condenser or replacing the cabin air filter.
- Professional: Professional AC service is recommended for complex repairs, such as refrigerant leaks, compressor failure, or electrical problems.
7. Car Air Conditioner System Innovations
The future of car AC systems is focused on improving energy efficiency, reducing environmental impact, and enhancing comfort.
7.1 Electric Compressors
Electric compressors are becoming increasingly common in hybrid and electric vehicles.
- Benefits: Improved energy efficiency, reduced emissions, and quieter operation.
- Technology: Electric compressors are powered by the vehicle’s battery and can operate independently of the engine.
7.2 CO2 Refrigerant Systems
CO2 refrigerant systems are an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional refrigerants.
- Benefits: Reduced global warming potential and improved energy efficiency.
- Technology: CO2 refrigerant systems use carbon dioxide as the refrigerant, which has a significantly lower environmental impact than traditional refrigerants.
7.3 Smart Climate Control Systems
Smart climate control systems use sensors and algorithms to optimize AC system performance and enhance comfort.
- Benefits: Improved comfort, enhanced energy efficiency, and personalized climate control.
- Technology: Smart climate control systems can adjust the AC system based on factors such as vehicle occupancy, ambient temperature, and driver preferences.
7.4 Solar-Powered AC Systems
Solar-powered AC systems use solar panels to generate electricity and power the AC system.
- Benefits: Reduced energy consumption, lower emissions, and improved sustainability.
- Technology: Solar panels can be integrated into the vehicle’s roof or hood to capture sunlight and generate electricity.
8. Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing AC Problems
If your car’s AC system is not working correctly, you can follow these steps to diagnose the problem:
- Check the Basics: Make sure the AC system is turned on, the blower fan is working, and the temperature is set to the coldest setting.
- Inspect the Compressor: Check the compressor belt for damage or wear. Make sure the compressor is engaging when the AC is turned on.
- Check Refrigerant Level: Use a refrigerant gauge to check the refrigerant level. If the level is low, there may be a leak in the system.
- Inspect the Condenser and Evaporator: Check the condenser and evaporator for blockage or damage. Clean the fins if necessary.
- Check Electrical Components: Use a multimeter to check the wiring, relays, switches, and sensors for continuity and voltage.
- Seek Professional Help: If you’re unable to diagnose the problem, seek professional help from a qualified technician.
9. Choosing the Right AC Repair Shop
Selecting a reputable AC repair shop is crucial for ensuring quality service and fair pricing.
9.1 Checking for Certifications and Accreditation
Look for repair shops with certifications from organizations such as the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE).
- Benefits: ASE certification indicates that the technicians have the knowledge and skills to properly diagnose and repair AC systems.
- Accreditation: Accreditation from organizations such as the Better Business Bureau (BBB) can provide additional assurance of quality and professionalism.
9.2 Reading Online Reviews and Testimonials
Online reviews and testimonials can provide valuable insights into the quality of service and customer satisfaction.
- Sources: Check reviews on websites such as Google, Yelp, and the BBB.
- Considerations: Read reviews carefully and consider both positive and negative feedback.
9.3 Asking for Estimates and Warranties
Always ask for a written estimate before authorizing any AC repairs.
- Estimates: The estimate should include a detailed breakdown of the costs for parts and labor.
- Warranties: Ask about warranties on parts and labor to protect yourself against future problems.
9.4 Verifying Experience and Expertise
Choose a repair shop with experience and expertise in AC system diagnosis and repair.
- Questions: Ask the technicians about their experience with AC systems and the types of training they have received.
- Specialization: Consider choosing a repair shop that specializes in AC systems or specific vehicle makes and models.
10. Maintaining a Healthy Car Cabin Environment
Maintaining a healthy car cabin environment is essential for your health and well-being.
10.1 Using AC Systems Effectively
Use your car’s AC system effectively to maintain a comfortable and healthy cabin environment.
- Settings: Adjust the temperature and fan speed to your desired comfort level.
- Recirculation: Use the recirculation mode to prevent outside air from entering the cabin.
10.2 Controlling Humidity and Air Quality
Control humidity and air quality inside your car to prevent the growth of mold and bacteria.
- Dehumidifying: Use the AC system to dehumidify the air and reduce moisture levels.
- Air Purifiers: Consider using a car air purifier to remove dust, pollen, and other contaminants from the air.
10.3 Preventing Mold and Bacteria Growth
Prevent mold and bacteria growth inside your car by keeping the cabin clean and dry.
- Cleaning: Regularly clean the interior of your car, including the dashboard, seats, and carpets.
- Ventilation: Ventilate the car by opening the windows or using the AC system to circulate fresh air.
10.4 Addressing Odors and Allergens
Address odors and allergens inside your car to improve air quality and prevent allergic reactions.
- Odor Removal: Use odor eliminators or baking soda to remove unpleasant odors from the cabin.
- Allergen Control: Use allergen-reducing air filters to remove pollen, dust mites, and other allergens from the air.
11. Environmental Impact of Car AC Systems
Car AC systems can have a significant impact on the environment due to refrigerant emissions and energy consumption.
11.1 Refrigerant Emissions and Global Warming
Refrigerant emissions contribute to global warming and ozone depletion.
- Regulations: Regulations such as the Montreal Protocol have been implemented to phase out ozone-depleting refrigerants.
- Alternatives: Environmentally friendly refrigerants such as R-1234yf and CO2 are being developed and used in car AC systems.
11.2 Energy Consumption and Fuel Efficiency
Car AC systems consume energy and reduce fuel efficiency.
- Impact: AC systems can reduce fuel efficiency by up to 20%, depending on the vehicle and driving conditions.
- Optimization: Efficient AC systems, such as those with electric compressors and smart climate control, can help reduce energy consumption and improve fuel efficiency.
11.3 Sustainable AC System Practices
Sustainable AC system practices can help reduce the environmental impact of car AC systems.
- Refrigerant Recovery: Properly recover and recycle refrigerant during AC service to prevent emissions.
- Energy Efficiency: Choose energy-efficient AC systems and use them effectively to reduce energy consumption.
11.4 Responsible Refrigerant Disposal
Dispose of refrigerant responsibly to prevent environmental damage.
- Regulations: Regulations such as the Clean Air Act require proper handling and disposal of refrigerant.
- Professional Disposal: Use a qualified technician to recover and dispose of refrigerant safely and responsibly.
12. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Car Air Conditioners
Here are some frequently asked questions about car air conditioners:
Q1: How often should I recharge my car’s AC system?
A: It depends on how often you use it and if there are any leaks. Generally, every 2-3 years is a good guideline, but if you notice the cooling isn’t as effective, get it checked sooner.
Q2: Can I recharge my car’s AC system myself?
A: While DIY kits are available, it’s best to have a professional do it. They can ensure the correct refrigerant level and check for leaks.
Q3: What causes a car AC to stop working?
A: Common causes include refrigerant leaks, compressor failure, clogged condenser or evaporator, and electrical problems.
Q4: How much does it cost to fix a car AC?
A: The cost can vary depending on the problem. Simple repairs like a refrigerant recharge can cost $100 – $200, while more complex repairs like compressor replacement can cost $400 – $1200.
Q5: How can I improve my car’s AC efficiency?
A: Regular maintenance, such as cleaning the condenser and replacing the cabin air filter, can improve AC efficiency. Also, consider upgrading to a high-performance compressor or electronic expansion valve.
Q6: Is it safe to use aftermarket AC additives?
A: It’s generally not recommended to use aftermarket AC additives, as they can damage the system and void the warranty.
Q7: What is the difference between R-134a and R-1234yf refrigerant?
A: R-1234yf is a newer refrigerant with a significantly lower global warming potential compared to R-134a.
Q8: How do I know if my car’s AC system has a leak?
A: Signs of a refrigerant leak include reduced cooling performance, oily residue around AC components, or the presence of a refrigerant leak detection dye.
Q9: Can I convert my car’s AC system from R-12 to R-134a?
A: Yes, it’s possible to convert a car’s AC system from R-12 to R-134a, but it requires modifications to the system and is best done by a professional.
Q10: How can I find a reputable AC repair shop?
A: Look for repair shops with certifications, read online reviews, ask for estimates and warranties, and verify experience and expertise.
Conclusion
Maintaining a properly functioning car air conditioner is essential for comfortable and safe driving. By understanding the components, common problems, and maintenance tips outlined in this guide, you can keep your AC system in top condition. Remember to seek professional help when needed and follow sustainable practices to minimize the environmental impact of your AC system.
If you’re experiencing issues with your car’s AC system or want to learn more about car maintenance, visit CARS.EDU.VN. Our team of experts can help you diagnose problems, find reliable repair shops, and provide valuable maintenance tips. Contact us today at 456 Auto Drive, Anytown, CA 90210, United States, Whatsapp: +1 555-123-4567, or visit our website at CARS.EDU.VN for more information. Let CARS.EDU.VN help you stay cool and comfortable on the road!
Explore cars.edu.vn today for expert advice on automotive climate control, AC repair services, and maintaining your car’s cooling system. Discover more valuable insights and solutions to keep your vehicle running smoothly.