Does urgent care administer IV fluids? Absolutely. At CARS.EDU.VN, we understand the critical role of intravenous (IV) fluids in treating dehydration and other medical conditions. This comprehensive guide explores when and why IV fluids are necessary, whether urgent care centers offer this service, and what you should know to make informed decisions about your health, including electrolyte balance. Discover expert insights and practical advice, and consider consulting CARS.EDU.VN for further information on automotive care.
1. Understanding Dehydration: A Comprehensive Overview
Dehydration occurs when your body loses more fluids than it takes in, disrupting the normal balance of minerals and salts, or electrolytes. This imbalance can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe health complications. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments for dehydration is essential for maintaining your health and well-being. It’s also vital for understanding the demands on your car’s cooling system, much like how your body needs fluids, your vehicle needs proper maintenance which you can learn about on CARS.EDU.VN.
1.1. Common Causes of Dehydration
Dehydration can stem from various factors, including inadequate fluid intake, intense physical activity, exposure to high temperatures, and certain medical conditions. Identifying these causes can help you take preventive measures and stay hydrated.
- Insufficient Fluid Intake: Not drinking enough water is the primary cause of dehydration.
- Physical Exertion: Sweating during exercise or strenuous activities leads to fluid loss.
- Environmental Factors: Hot and humid weather increases sweat production, leading to dehydration.
- Illness: Conditions like vomiting and diarrhea cause rapid fluid loss. According to the Mayo Clinic, adults can experience a fever caused by dehydration.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as diuretics, can increase urination and contribute to dehydration.
1.2. Recognizing the Symptoms of Dehydration
Recognizing the symptoms of dehydration early can help you take prompt action and prevent the condition from worsening. Symptoms range from mild to severe and can vary depending on the level of fluid loss.
- Mild to Moderate Symptoms:
- Thirst
- Dry mouth
- Dark urine
- Decreased urination
- Headache
- Muscle cramps
- Severe Symptoms:
- Extreme thirst
- Very dark urine
- Dizziness
- Confusion
- Rapid heartbeat
- Sunken eyes
- Lack of sweating
- Poor skin elasticity
1.3. Effective Treatment Strategies for Dehydration
The treatment for dehydration varies depending on the severity of the condition. Mild to moderate dehydration can often be treated at home, while severe dehydration requires medical intervention.
- Home Remedies:
- Drink Water: Sip water slowly to rehydrate the body gradually.
- Electrolyte Solutions: Consume sports drinks or electrolyte solutions to replenish lost minerals and salts.
- Avoid Caffeine and Alcohol: These substances can further dehydrate the body.
- Medical Treatments:
- IV Fluids: In cases of severe dehydration, intravenous fluids are administered to quickly restore fluid levels.
- Medical Supervision: Healthcare professionals monitor vital signs and adjust treatment as needed.
2. The Role of Urgent Care Centers in Treating Dehydration
Urgent care centers play a vital role in providing timely and accessible medical care for various conditions, including dehydration. These centers bridge the gap between primary care physicians and emergency rooms, offering convenient treatment options for non-life-threatening conditions.
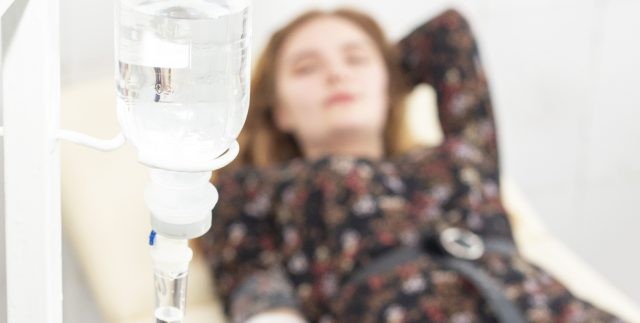
2.1. Can Urgent Care Centers Administer IV Fluids?
Yes, urgent care centers can administer IV fluids to treat dehydration. IV fluids are an effective way to quickly rehydrate the body and restore electrolyte balance. Urgent care facilities are equipped to handle cases of moderate to severe dehydration, providing timely and efficient treatment.
2.2. Benefits of Choosing Urgent Care for Dehydration Treatment
Opting for urgent care for dehydration treatment offers several advantages, including accessibility, cost-effectiveness, and reduced wait times compared to emergency rooms.
- Accessibility: Urgent care centers are often open during extended hours, including evenings and weekends, making them a convenient option for immediate medical attention.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Treatment at an urgent care center is typically less expensive than a visit to the emergency room.
- Reduced Wait Times: Urgent care centers generally have shorter wait times compared to emergency rooms, allowing you to receive treatment more quickly.
- Comprehensive Care: Urgent care centers offer a range of services, including physical exams, diagnostic tests, and IV fluid administration, ensuring comprehensive care for dehydration.
2.3. What to Expect During an Urgent Care Visit for Dehydration
When you visit an urgent care center for dehydration treatment, you can expect a thorough evaluation, personalized care, and clear communication from healthcare professionals.
- Initial Assessment: A healthcare provider will review your medical history, assess your symptoms, and perform a physical exam to determine the severity of dehydration.
- Diagnostic Tests: Depending on your condition, diagnostic tests such as blood tests and urine tests may be conducted to evaluate electrolyte levels and kidney function.
- IV Fluid Administration: If necessary, IV fluids will be administered to rehydrate your body and restore electrolyte balance. The type and amount of fluid will be determined based on your individual needs.
- Medication and Monitoring: Healthcare providers may prescribe medications to manage symptoms such as nausea or vomiting. Vital signs will be monitored to ensure you respond well to treatment.
3. Understanding IV Fluids: Types and Administration
IV fluids are a critical component of medical treatment for dehydration and various other conditions. Understanding the different types of IV fluids and the administration process can help you feel more informed and prepared during medical care.
3.1. Types of IV Fluids Used in Urgent Care
Urgent care centers use different types of IV fluids to address specific medical needs. The choice of fluid depends on the patient’s condition, electrolyte levels, and overall health status.
- Normal Saline: A solution of sodium chloride in water, used to increase fluid volume and treat dehydration.
- Lactated Ringer’s Solution: Contains electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, calcium, and chloride, used to restore electrolyte balance and treat dehydration.
- Dextrose Solutions: Contains glucose, used to provide calories and treat low blood sugar in addition to dehydration.
3.2. The IV Fluid Administration Process
The administration of IV fluids involves several steps to ensure patient safety and treatment effectiveness. Healthcare professionals follow strict protocols to monitor fluid levels and prevent complications.
- Preparation: The healthcare provider will explain the procedure, answer any questions, and prepare the IV equipment.
- Insertion: A small catheter is inserted into a vein, usually in the arm, to allow access for fluid administration.
- Fluid Administration: The IV fluid is connected to the catheter and allowed to flow into the bloodstream at a controlled rate.
- Monitoring: The healthcare provider monitors vital signs, fluid levels, and the patient’s response to treatment throughout the process.
3.3. Potential Risks and Side Effects of IV Fluid Therapy
While IV fluid therapy is generally safe, there are potential risks and side effects to be aware of. Healthcare providers take precautions to minimize these risks and ensure patient safety.
- Infection: There is a risk of infection at the IV insertion site.
- Fluid Overload: Administering too much fluid can lead to fluid overload, causing swelling and breathing difficulties.
- Electrolyte Imbalance: Improper fluid selection can disrupt electrolyte balance.
- Allergic Reaction: Rarely, patients may experience an allergic reaction to the IV fluid or equipment.
4. Emergency Room vs. Urgent Care for Dehydration
When facing dehydration, knowing whether to visit an emergency room (ER) or an urgent care center is crucial. Both offer treatments, but they cater to different levels of severity. This comparison helps you make an informed decision based on your symptoms and needs. Keep in mind, just like your body needs fluids, so does your vehicle. Neglecting to address issues can lead to bigger problems down the road, so check out CARS.EDU.VN for more information.
4.1. Key Differences in Services and Capabilities
Emergency rooms are equipped to handle life-threatening conditions, while urgent care centers focus on illnesses and injuries that are not severe enough for an ER visit.
| Feature | Emergency Room (ER) | Urgent Care Center |
|---|---|---|
| Severity | Life-threatening conditions | Non-life-threatening illnesses and injuries |
| Services | Advanced diagnostics, surgery, critical care | Basic diagnostics, IV fluids, minor procedures |
| Equipment | Extensive medical equipment | Limited medical equipment |
| Staffing | Specialists, surgeons, nurses | Physicians, nurses, medical assistants |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Wait Times | Can be long, depending on the severity of cases | Generally shorter |
| Hours | 24/7 | Extended hours, but not always 24/7 |


4.2. When to Choose an Emergency Room for Dehydration
Choose an emergency room if you or someone you know is experiencing severe dehydration symptoms that indicate a life-threatening condition.
- Severe Symptoms:
- Rapid heartbeat
- Confusion or disorientation
- Fainting or loss of consciousness
- Seizures
- High fever with dehydration
- Underlying Conditions:
- Infants and young children with severe dehydration
- Elderly individuals with chronic health issues
- Patients with conditions like diabetes, heart disease, or kidney problems
4.3. When to Opt for Urgent Care for Dehydration
Urgent care centers are appropriate for treating moderate dehydration symptoms that do not pose an immediate threat to life.
- Moderate Symptoms:
- Extreme thirst
- Dark urine
- Dizziness
- Muscle cramps
- Weakness
- Accessibility:
- When your primary care physician’s office is closed
- For quicker treatment compared to an emergency room wait
- When the symptoms are not life-threatening
5. Preventive Measures to Avoid Dehydration
Preventing dehydration involves adopting proactive habits to maintain adequate fluid levels. Simple lifestyle adjustments can significantly reduce your risk and promote overall health. Just like your car needs regular check-ups, your body requires consistent hydration. And for all your car care needs, remember to visit CARS.EDU.VN.
5.1. Daily Hydration Tips
Incorporate these tips into your daily routine to ensure you stay adequately hydrated:
- Drink Water Regularly:
- Carry a water bottle and sip throughout the day.
- Set reminders to drink water, especially during busy periods.
- Consume Hydrating Foods:
- Eat fruits and vegetables with high water content, such as watermelon, cucumbers, and oranges.
- Include soups and broths in your diet.
- Avoid Excessive Caffeine and Alcohol:
- Limit intake of coffee, tea, and alcoholic beverages, as they can dehydrate you.
- If consuming these, balance with extra water.
5.2. Staying Hydrated During Physical Activity
Physical activity increases fluid loss through sweat, making hydration even more critical.
- Pre-Hydration:
- Drink water or a sports drink before starting any physical activity.
- During Activity:
- Take frequent water breaks to replenish fluids.
- For intense workouts, choose sports drinks with electrolytes.
- Post-Hydration:
- Continue to drink water after exercise to replace lost fluids.
- Monitor urine color to ensure you are adequately rehydrated (light yellow is ideal).
5.3. Recognizing High-Risk Groups and Special Considerations
Certain groups are more susceptible to dehydration and require extra attention to their fluid intake.
- Infants and Children:
- Offer frequent sips of water or diluted juice.
- Monitor for signs of dehydration, such as fewer wet diapers or dry mouth.
- Older Adults:
- Encourage regular fluid intake, even if they don’t feel thirsty.
- Be aware that certain medications can increase dehydration risk.
- Individuals with Chronic Illnesses:
- Consult with a healthcare provider to determine appropriate fluid intake levels.
- Manage underlying conditions that can contribute to dehydration, such as diabetes or kidney disease.
6. The Cost of IV Fluids at Urgent Care
Understanding the costs associated with IV fluid treatment at urgent care centers can help you plan for medical expenses. The price can vary based on several factors, making it important to inquire about costs upfront.
6.1. Factors Influencing the Cost
Several elements can influence the overall cost of receiving IV fluids at an urgent care center.
- Location:
- Urban areas or regions with higher living costs may have higher prices.
- Rural areas might offer more affordable rates due to lower overhead costs.
- Urgent Care Center Policies:
- Each center sets its own pricing structure, which can vary widely.
- Some centers may offer package deals or discounts.
- Type of IV Fluid:
- Basic saline solutions are generally less expensive.
- Specialized fluids with added vitamins or medications will increase the cost.
- Additional Services:
- The cost of the initial consultation and examination.
- Any diagnostic tests, such as blood work, will add to the total bill.
6.2. Average Cost Range
While the cost can vary, understanding the average range can provide a general idea of what to expect.
- Basic IV Hydration:
- The average cost for a basic IV hydration package ranges from $100 to $300.
- This typically includes saline solution and basic electrolytes.
- Advanced IV Therapy:
- Advanced therapies with added vitamins, antioxidants, or medications can range from $300 to $700 or more.
- These may be marketed as “wellness” or “detox” packages.
- Consultation and Additional Fees:
- The initial consultation can cost between $50 and $150.
- Additional tests or medications can add another $50 to $200.
6.3. Insurance Coverage and Payment Options
Navigating insurance coverage and understanding payment options can ease the financial burden of IV fluid treatment.
- Insurance Coverage:
- Contact your insurance provider to understand your coverage for urgent care services.
- Some plans may require a co-pay or deductible for urgent care visits.
- Inquire whether the specific urgent care center is in your insurance network.
- Payment Options:
- Many urgent care centers accept cash, credit cards, and health savings accounts (HSA).
- Some centers may offer payment plans or financing options.
- Ask about discounts for paying in cash or at the time of service.
7. Understanding Electrolyte Balance and IV Fluids
Electrolytes are essential minerals that play a critical role in maintaining bodily functions. When dehydration occurs, electrolyte imbalances can arise, necessitating IV fluid treatment to restore equilibrium. Understanding this balance is crucial for effective hydration and overall health. Remember, just like your car needs the right fluids, so does your body.
7.1. The Importance of Electrolytes
Electrolytes are minerals that carry an electrical charge when dissolved in bodily fluids such as blood, plasma, and intracellular fluid. They regulate nerve and muscle function, hydrate the body, balance blood acidity and pressure, and help rebuild damaged tissue.
- Key Electrolytes:
- Sodium: Maintains fluid balance and nerve function.
- Potassium: Essential for heart and muscle function.
- Calcium: Important for bone health, muscle contraction, and nerve signaling.
- Magnesium: Involved in muscle and nerve function, blood sugar control, and blood pressure regulation.
- Chloride: Helps maintain fluid balance.
7.2. How Dehydration Affects Electrolyte Levels
Dehydration can disrupt the delicate balance of electrolytes in the body. When you lose fluids through sweating, vomiting, or diarrhea, you also lose electrolytes. This imbalance can lead to various health issues.
- Common Imbalances:
- Hyponatremia: Low sodium levels, which can cause confusion, seizures, and coma.
- Hypokalemia: Low potassium levels, leading to muscle weakness, heart arrhythmias, and fatigue.
- Hypocalcemia: Low calcium levels, resulting in muscle cramps, spasms, and numbness.
- Symptoms of Electrolyte Imbalance:
- Muscle weakness
- Muscle cramps or spasms
- Irregular heartbeat
- Confusion or disorientation
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue
7.3. Restoring Electrolyte Balance with IV Fluids
IV fluids are often used to restore electrolyte balance in cases of dehydration. These fluids contain specific concentrations of electrolytes tailored to the patient’s needs.
- Types of IV Fluids for Electrolyte Restoration:
- Lactated Ringer’s Solution: Contains sodium, potassium, calcium, and chloride, closely resembling the electrolyte composition of blood plasma.
- Normal Saline with Electrolytes: Normal saline can be supplemented with specific electrolytes based on the patient’s deficiencies.
- Monitoring Electrolyte Levels:
- Healthcare providers monitor electrolyte levels through blood tests to ensure proper balance is restored.
- Adjustments to IV fluid composition may be made based on test results.
8. Special Considerations for Children and the Elderly
Dehydration can pose significant risks to both children and the elderly. Understanding the unique challenges and considerations for these age groups is crucial for effective prevention and treatment. Just as your car needs specific care for different seasons, these age groups require tailored hydration strategies.
8.1. Dehydration Risks in Children
Children are more vulnerable to dehydration due to their higher metabolic rate and smaller body size. They also lose fluids more quickly than adults, making them susceptible to dehydration from common illnesses and activities.
- Increased Risk Factors:
- Higher metabolic rate leads to increased fluid turnover.
- Smaller body size means less fluid reserve.
- Inability to communicate thirst effectively, especially in younger children.
- Vomiting and diarrhea from common childhood illnesses.
- Recognizing Dehydration in Children:
- Fewer wet diapers than usual.
- Dry mouth and tongue.
- Sunken eyes and cheeks.
- Lack of tears when crying.
- Lethargy or irritability.
8.2. Dehydration Risks in the Elderly
Older adults are also at higher risk of dehydration due to several age-related factors. These include decreased thirst sensation, reduced kidney function, and chronic medical conditions.
- Increased Risk Factors:
- Decreased thirst sensation leads to reduced fluid intake.
- Reduced kidney function impairs the ability to conserve water.
- Chronic medical conditions like diabetes and heart failure increase fluid loss.
- Medications such as diuretics can contribute to dehydration.
- Recognizing Dehydration in the Elderly:
- Confusion or disorientation.
- Dark urine.
- Dry mouth and skin.
- Muscle weakness or cramps.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness.
8.3. Tailored Hydration Strategies
Effective hydration strategies should be tailored to the specific needs of children and the elderly.
- For Children:
- Offer frequent sips of water or diluted juice throughout the day.
- Encourage fluid intake during and after physical activity.
- Monitor urine output to ensure adequate hydration.
- Consult a pediatrician for guidance on appropriate fluid intake.
- For the Elderly:
- Encourage regular fluid intake, even when not thirsty.
- Offer hydrating foods like fruits, vegetables, and soups.
- Monitor for signs of dehydration and seek medical attention promptly.
- Work with healthcare providers to manage chronic conditions and medications that can contribute to dehydration.
9. Real-Life Scenarios: When IV Fluids Are Essential
Understanding when IV fluids are essential can help you make informed decisions about seeking medical care. Several real-life scenarios highlight the critical role of IV fluids in treating dehydration and other conditions.
9.1. Case Studies of Successful IV Fluid Treatment
Examining case studies can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of IV fluid treatment in various situations.
- Case Study 1: Severe Dehydration from Gastroenteritis:
- A 30-year-old adult experienced severe vomiting and diarrhea due to gastroenteritis, leading to significant dehydration.
- Symptoms included extreme thirst, dizziness, and decreased urination.
- IV fluids were administered at an urgent care center, resulting in rapid rehydration and symptom relief.
- The patient was able to return home within a few hours after stabilization.
- Case Study 2: Dehydration in an Elderly Patient with Pneumonia:
- An 80-year-old patient with pneumonia developed dehydration due to fever and decreased fluid intake.
- Symptoms included confusion, dry mouth, and dark urine.
- IV fluids were administered in the hospital, along with antibiotics to treat the pneumonia.
- The patient’s condition improved significantly within 24 hours, and they were able to resume oral hydration.
- Case Study 3: Athlete with Heatstroke:
- A 22-year-old athlete collapsed during a marathon due to heatstroke and severe dehydration.
- Symptoms included rapid heartbeat, confusion, and loss of consciousness.
- Emergency medical personnel administered IV fluids on-site, stabilizing the athlete before transport to the hospital.
- The athlete made a full recovery after receiving continued IV fluid therapy and medical care.
9.2. Conditions That May Require IV Fluids
Certain medical conditions can increase the risk of dehydration and may require IV fluid treatment.
- Gastrointestinal Illnesses:
- Vomiting and diarrhea can lead to rapid fluid loss.
- IV fluids help restore hydration and electrolyte balance.
- Heat-Related Illnesses:
- Heatstroke and heat exhaustion cause excessive sweating and dehydration.
- IV fluids cool the body and replenish lost fluids.
- Chronic Medical Conditions:
- Diabetes, kidney disease, and heart failure can affect fluid balance.
- IV fluids help manage dehydration and prevent complications.
- Surgical Procedures:
- Patients may require IV fluids before, during, or after surgery.
- IV fluids maintain hydration and electrolyte balance during the perioperative period.
9.3. Recognizing the Signs and Acting Quickly
Recognizing the signs of dehydration and acting quickly can prevent serious complications and improve outcomes.
- Key Indicators of Dehydration:
- Extreme thirst
- Dark urine
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Confusion
- Rapid heartbeat
- Decreased urination
- When to Seek Medical Attention:
- If symptoms are severe or do not improve with oral hydration.
- In cases of underlying medical conditions that increase dehydration risk.
- For infants, children, and the elderly showing signs of dehydration.
10. CARS.EDU.VN: Your Resource for Automotive Care
Just as your body needs fluids, your car needs the right maintenance to perform optimally. CARS.EDU.VN is your go-to resource for all things automotive, providing expert advice and services to keep your vehicle in top condition.
10.1. Expert Advice and Services Available
At CARS.EDU.VN, we offer a wide range of expert advice and services to meet your automotive needs.
- Maintenance Tips:
- Learn how to perform routine maintenance tasks such as oil changes, tire rotations, and fluid checks.
- Access detailed guides and videos to help you keep your car running smoothly.
- Repair Services:
- Find trusted mechanics and repair shops in your area.
- Get advice on diagnosing and fixing common car problems.
- Vehicle Reviews:
- Read comprehensive reviews of the latest car models.
- Compare different vehicles to find the perfect one for your needs.
- Troubleshooting Guides:
- Access step-by-step guides to troubleshoot common car issues.
- Learn how to identify and resolve problems quickly and efficiently.
10.2. How CARS.EDU.VN Can Help You Maintain Your Vehicle
CARS.EDU.VN provides the tools and resources you need to maintain your vehicle and prevent costly repairs.
- Preventive Maintenance:
- Follow our recommended maintenance schedules to keep your car in top condition.
- Learn how to identify and address potential problems before they become major issues.
- Cost Savings:
- Save money by performing routine maintenance tasks yourself.
- Avoid expensive repairs by addressing problems early.
- Reliable Information:
- Trust our expert advice to make informed decisions about your car care.
- Access accurate and up-to-date information on all aspects of automotive maintenance and repair.
10.3. Contact Information and Additional Resources
For more information and expert assistance, visit CARS.EDU.VN or contact us today.
- Address: 456 Auto Drive, Anytown, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 555-123-4567
- Website: CARS.EDU.VN
FAQ About Urgent Care and IV Fluids
Here are some frequently asked questions about urgent care and IV fluids:
-
Can urgent care centers administer IV fluids?
Yes, urgent care centers can administer IV fluids to treat dehydration and other conditions. -
What types of IV fluids are available at urgent care centers?
Common types include normal saline, lactated Ringer’s solution, and dextrose solutions. -
How much do IV fluids cost at urgent care centers?
The cost varies but typically ranges from $100 to $700, depending on the type of fluid and additional services. -
Is IV fluid treatment covered by insurance?
Coverage depends on your insurance plan; check with your provider for details. -
What are the risks of IV fluid therapy?
Potential risks include infection, fluid overload, and electrolyte imbalance. -
How long does IV fluid administration take?
The process usually takes 30 minutes to several hours, depending on the severity of dehydration. -
Can IV fluids help with a hangover?
Yes, IV fluids can alleviate hangover symptoms by rehydrating the body and restoring electrolytes. -
Are there alternatives to IV fluids for dehydration?
Mild to moderate dehydration can often be treated with oral hydration, but severe cases may require IV fluids. -
How do I know if I need IV fluids?
Severe symptoms like dizziness, confusion, and rapid heartbeat indicate a need for IV fluids. -
Can CARS.EDU.VN provide automotive care advice?
Yes, CARS.EDU.VN offers expert advice and services for all your automotive needs.
At cars.edu.vn, we’re dedicated to providing you with reliable information and expert services, whether you need automotive advice or guidance on health-related topics like dehydration and IV fluids. Understanding your body and your vehicle’s needs is crucial for maintaining optimal performance.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of medical conditions.