Home Health Care Near Me offers a supportive solution for individuals seeking personalized assistance and medical attention in the comfort of their own homes, and CARS.EDU.VN is your go-to resource for understanding the ins and outs of home health options. Whether you’re searching for skilled nursing, therapy services, or simply companionship, discovering the right home care assistance and in-home support is crucial for enhancing quality of life; explore CARS.EDU.VN for expert advice on selecting the best in-home care, home care agencies, and personal care services.
1. Understanding the Importance of Home Health Care
Home health care delivers medical care and support services in an individual’s residence. It’s a practical option for those recuperating from an illness, managing a chronic condition, or requiring assistance with daily activities. Home health aides strive to improve health outcomes and overall well-being.
1.1. What is Home Health Care?
Home health care consists of a wide array of healthcare services provided in the comfort of a patient’s home. Unlike nursing homes or assisted living facilities, home health care permits individuals to receive medical attention and support while staying in their familiar and comfortable environment. This care may include skilled nursing, physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, medical social services, and assistance from home health aides. Home health care agencies coordinate these services, tailoring care plans to suit each patient’s specific needs.
1.2. Benefits of Receiving Care at Home
Receiving care at home offers numerous advantages compared to facility-based care. These include:
- Personalized Care: Home health care permits individualized attention and customized care plans tailored to the patient’s unique needs and preferences.
- Comfort and Convenience: Patients can obtain medical care and support services in the familiar surroundings of their own homes, lowering stress and promoting comfort.
- Independence: Home health care helps individuals maintain their independence and autonomy while receiving the assistance they need.
- Family Involvement: Home health care permits family members to be actively involved in the patient’s care, offering emotional support and camaraderie.
- Cost-Effectiveness: In many cases, home health care is more affordable than facility-based care, such as nursing homes or hospitals, especially for those who require long-term support.
1.3. Who Benefits from Home Health Services?
Home health services can significantly benefit a diverse array of individuals, including:
- Seniors: Elderly individuals who may need assistance with activities of daily living or managing chronic health conditions can benefit immensely from home health care.
- Individuals Recovering from Surgery or Illness: Patients recuperating from surgery, injury, or illness can receive the necessary medical care and support at home to facilitate their recovery.
- People with Chronic Conditions: Home health care can help individuals manage chronic conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and respiratory disorders, improving their quality of life and preventing complications.
- Individuals with Disabilities: People with disabilities can receive assistance with personal care, mobility, and other activities to enhance their independence and well-being.
- Those Seeking End-of-Life Care: Hospice care delivered at home offers compassionate support and comfort to individuals nearing the end of their lives, allowing them to spend their final days in a familiar and supportive environment.
2. Types of Home Health Care Services
Home health care encompasses a diverse spectrum of services tailored to meet the varied needs of individuals in their homes. Comprehending the different types of available services is vital for making informed decisions about care.
2.1. Skilled Nursing Care
Skilled nursing care is provided by registered nurses (RNs) or licensed practical nurses (LPNs) and entails medical services that necessitate professional expertise and training. These services may include:
- Medication Management: Administering medications, monitoring for side effects, and ensuring adherence to prescribed regimens.
- Wound Care: Assessing and treating wounds, changing dressings, and preventing infections.
- Disease Management: Providing education and support for individuals managing chronic conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, or COPD.
- Injections and Infusions: Administering injections, IV fluids, and other medications as prescribed by a physician.
- Vital Signs Monitoring: Monitoring vital signs such as blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation to detect changes in condition.
2.2. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy focuses on helping individuals regain strength, mobility, and function following an injury, illness, or surgery. Physical therapists develop individualized exercise programs and therapeutic interventions to address specific needs and goals. Physical therapy services may include:
- Exercise Programs: Developing and instructing exercises to improve strength, flexibility, balance, and coordination.
- Pain Management: Using techniques such as massage, heat, and cold therapy to relieve pain and discomfort.
- Gait Training: Assisting individuals with walking and balance to improve mobility and prevent falls.
- Assistive Device Training: Teaching individuals how to use assistive devices such as walkers, canes, and crutches safely and effectively.
- Home Safety Assessment: Evaluating the home environment for potential hazards and recommending modifications to improve safety and accessibility.
2.3. Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy helps individuals develop or regain the skills needed to perform everyday tasks and activities. Occupational therapists assess individuals’ abilities and develop treatment plans to improve their independence and quality of life. Occupational therapy services may include:
- Activities of Daily Living (ADL) Training: Assisting individuals with tasks such as bathing, dressing, eating, and toileting.
- Adaptive Equipment Recommendations: Recommending and training individuals on the use of adaptive equipment such as reachers, dressing aids, and modified utensils.
- Home Modification Recommendations: Recommending modifications to the home environment to improve safety and accessibility.
- Cognitive Rehabilitation: Providing exercises and strategies to improve memory, attention, and problem-solving skills.
- Ergonomic Assessments: Evaluating work or living environments to identify and address ergonomic risk factors.
2.4. Speech Therapy
Speech therapy helps individuals improve their communication, swallowing, and cognitive skills. Speech therapists assess individuals’ abilities and develop treatment plans to address specific needs and goals. Speech therapy services may include:
- Communication Therapy: Providing exercises and strategies to improve speech, language, and communication skills.
- Swallowing Therapy: Evaluating and treating swallowing disorders (dysphagia) to prevent aspiration and improve nutrition.
- Cognitive Therapy: Providing exercises and strategies to improve memory, attention, and problem-solving skills.
- Voice Therapy: Treating voice disorders such as hoarseness, vocal nodules, and vocal cord paralysis.
- Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC): Evaluating and recommending AAC devices and strategies for individuals with severe communication impairments.
2.5. Home Health Aide Services
Home health aides provide personal care and support services to individuals in their homes. Home health aides work under the supervision of a registered nurse or therapist and assist with activities of daily living. Home health aide services may include:
- Bathing and Dressing: Assisting individuals with bathing, showering, and dressing.
- Toileting Assistance: Providing assistance with toileting and incontinence care.
- Mobility Assistance: Helping individuals with walking, transferring, and positioning.
- Meal Preparation: Planning and preparing nutritious meals according to dietary restrictions.
- Light Housekeeping: Performing light housekeeping tasks such as laundry, dusting, and vacuuming.
- Companionship: Providing companionship and emotional support to individuals who are lonely or isolated.
2.6. Medical Social Services
Medical social workers provide counseling, support, and resources to individuals and families facing medical challenges. Medical social services may include:
- Counseling and Support: Providing emotional support, counseling, and guidance to individuals and families coping with illness, disability, or loss.
- Resource Coordination: Connecting individuals and families with community resources such as support groups, financial assistance programs, and transportation services.
- Advance Care Planning: Assisting individuals with advance care planning, including the completion of advance directives such as living wills and durable power of attorney for health care.
- Discharge Planning: Coordinating discharge planning services to ensure a smooth transition from the hospital or rehabilitation facility to home.
- Crisis Intervention: Providing crisis intervention services to individuals and families experiencing acute emotional or social crises.
3. How to Find Home Health Care Near You
Finding quality home health care near you requires careful research and consideration. Here are some steps to help you in your search:
3.1. Start with Your Physician
Your primary care physician or specialist can be a valuable resource in finding home health care services. They can assess your medical needs and recommend reputable home health agencies or providers in your area. They may also be able to provide referrals to specific healthcare professionals, such as nurses, therapists, or home health aides, who have experience in treating your condition.
3.2. Online Directories and Resources
Several online directories and resources can help you find home health care services in your area. These directories allow you to search for agencies or providers based on location, services offered, and other criteria. Some popular online directories include:
- Medicare.gov: The official website of the U.S. Medicare program provides a searchable database of Medicare-certified home health agencies.
- Home Health Compare: This website, run by Medicare, allows you to compare the quality of care provided by different home health agencies in your area.
- National Association for Home Care & Hospice (NAHC): NAHC is a professional organization for home health and hospice providers. Their website offers a directory of member agencies.
- CARS.EDU.VN: Check CARS.EDU.VN for in-depth articles, reviews, and resources on home health care options.
3.3. Check Online Reviews and Ratings
Before selecting a home health agency or provider, take the time to read online reviews and ratings. Websites such as Yelp, Google Reviews, and Caring.com provide valuable insights into the experiences of other patients and families. Pay attention to both positive and negative reviews, and consider factors such as quality of care, communication, reliability, and responsiveness.
3.4. Ask for Recommendations
Reach out to friends, family members, neighbors, or colleagues who have experience with home health care services. Ask for their recommendations and insights. Personal referrals can be invaluable in finding reputable and trustworthy providers.
3.5. Verify Licenses and Credentials
Before hiring a home health agency or provider, verify their licenses and credentials. Ensure that the agency is licensed and certified by the appropriate state and federal agencies. Check the credentials of individual healthcare professionals, such as nurses, therapists, and social workers, to ensure that they are licensed and in good standing with their respective professional boards.
4. What to Look for in a Home Health Care Agency
When selecting a home health care agency, it’s essential to consider several factors to ensure that you receive quality care and support.
4.1. Accreditation and Licensing
Ensure that the home health care agency is accredited by a reputable organization such as The Joint Commission or the Community Health Accreditation Program (CHAP). Accreditation indicates that the agency meets certain standards of quality and safety. Additionally, verify that the agency is licensed by the appropriate state and federal agencies.
4.2. Range of Services Offered
Choose a home health care agency that offers a comprehensive range of services to meet your specific needs. Consider whether you require skilled nursing care, physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, home health aide services, medical social services, or a combination of these services. Ensure that the agency has the expertise and resources to provide the services you need.
4.3. Caregiver Qualifications and Training
Inquire about the qualifications and training of the agency’s caregivers. Ensure that nurses, therapists, and home health aides are licensed and certified, and that they receive ongoing training to maintain their skills and knowledge. Ask about the agency’s hiring practices, background checks, and employee supervision policies.
4.4. Communication and Coordination
Effective communication and coordination are essential for successful home health care. Choose an agency that emphasizes clear and open communication between caregivers, patients, and family members. Ensure that the agency has systems in place for coordinating care, sharing information, and addressing concerns promptly.
4.5. Cost and Payment Options
Discuss the cost of home health care services and payment options with the agency. Understand what services are covered by Medicare, Medicaid, or private insurance, and what out-of-pocket expenses you may incur. Ask about the agency’s billing practices and payment policies.
4.6. Emergency Procedures
Inquire about the agency’s emergency procedures and protocols. Ensure that caregivers are trained to respond to medical emergencies and that they have access to emergency contact information. Ask about the agency’s after-hours support and on-call services.
5. Paying for Home Health Care
Paying for home health care can be complex, but understanding the different payment options available is essential for accessing the care you need.
5.1. Medicare Coverage
Medicare Part A and Part B may cover certain home health care services for eligible individuals. To qualify for Medicare coverage, you must:
- Be under the care of a physician
- Require skilled nursing care or therapy services
- Be homebound, meaning that you have difficulty leaving your home without assistance
- Receive care from a Medicare-certified home health agency
Medicare covers 100% of the cost of eligible home health services, including skilled nursing care, physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and home health aide services. However, Medicare does not cover homemaker services or 24-hour in-home care.
5.2. Medicaid Coverage
Medicaid is a joint federal and state program that provides health coverage to low-income individuals and families. Medicaid may cover home health care services for eligible individuals who meet certain income and medical criteria. Coverage varies by state, so it’s essential to check with your local Medicaid agency to determine what services are covered.
5.3. Private Insurance
Many private insurance plans cover home health care services to some extent. Check with your insurance provider to determine what services are covered, what out-of-pocket expenses you may incur, and whether you need pre-authorization for home health care services.
5.4. Long-Term Care Insurance
Long-term care insurance is a type of insurance that helps pay for the costs of long-term care services, including home health care, assisted living, and nursing home care. If you have long-term care insurance, review your policy to determine what services are covered and what eligibility requirements you must meet.
5.5. Out-of-Pocket Payments
If you don’t have Medicare, Medicaid, or private insurance coverage for home health care services, you may need to pay out-of-pocket. Home health care costs vary depending on the type and amount of services you need, as well as the location and provider you choose. Discuss payment options and payment plans with the home health agency or provider.
6. Navigating the Home Health Care Process
Navigating the home health care process can be overwhelming, but understanding the steps involved can help you make informed decisions and access the care you need.
6.1. Assessment and Care Planning
The first step in the home health care process is an assessment by a registered nurse or therapist. The assessment involves evaluating your medical condition, functional abilities, and home environment to determine your specific needs and goals. Based on the assessment, the healthcare professional will develop a customized care plan tailored to your individual needs.
6.2. Care Coordination and Scheduling
Once the care plan is developed, the home health agency will coordinate and schedule services. This may involve scheduling visits from nurses, therapists, home health aides, or other healthcare professionals. The agency will work with you and your family to create a schedule that meets your needs and preferences.
6.3. Care Delivery and Monitoring
During home health care visits, caregivers will provide the services outlined in your care plan. This may include skilled nursing care, therapy services, personal care assistance, or other support services. Caregivers will monitor your condition, track your progress, and communicate with your physician and other healthcare providers as needed.
6.4. Communication and Collaboration
Effective communication and collaboration are essential throughout the home health care process. Caregivers will communicate regularly with you, your family, and your physician to ensure that everyone is informed and involved in your care. The home health agency will also coordinate with other healthcare providers, such as hospitals, rehabilitation facilities, and pharmacies, to ensure seamless transitions of care.
6.5. Reassessment and Adjustment
Your care plan will be reassessed and adjusted regularly to ensure that it continues to meet your needs. The healthcare professional will monitor your condition, track your progress, and make changes to your care plan as needed. You and your family will have the opportunity to provide input and feedback on your care plan.
6.6. Discharge Planning
When you no longer require home health care services, the healthcare professional will develop a discharge plan to ensure a smooth transition to self-care or other levels of care. The discharge plan may include instructions for medication management, follow-up appointments, and lifestyle modifications. The home health agency will also coordinate with other healthcare providers to ensure that you have the support and resources you need to continue your care.
7. Common Concerns and Questions About Home Health Care
Home health care can raise many questions and concerns. Addressing these concerns can help you feel more comfortable and confident in your decision to receive care at home.
7.1. Safety and Security
One common concern is the safety and security of receiving care in your home. To address this concern, it’s essential to choose a reputable home health agency that conducts thorough background checks on its employees. Additionally, you can take steps to ensure your safety, such as installing security cameras, keeping valuables out of sight, and notifying the agency of any concerns you may have.
7.2. Privacy and Confidentiality
Privacy and confidentiality are important considerations when receiving home health care. Home health agencies are required to comply with HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) regulations, which protect your privacy and confidentiality. Ensure that the agency has policies and procedures in place to safeguard your personal and medical information.
7.3. Caregiver Compatibility
It’s important to feel comfortable and compatible with your caregivers. If you have concerns about a caregiver’s personality, skills, or communication style, discuss them with the home health agency. The agency may be able to provide a different caregiver who is a better fit for your needs.
7.4. Quality of Care
Ensuring the quality of care is essential when receiving home health care. Choose a home health agency that is accredited and licensed, and that has a reputation for providing high-quality care. Additionally, you can monitor the quality of care by communicating with your caregivers, tracking your progress, and reporting any concerns to the agency.
7.5. Cost of Care
The cost of home health care can be a significant concern. Discuss payment options with the home health agency and explore options such as Medicare, Medicaid, private insurance, and long-term care insurance. Additionally, you can inquire about payment plans and discounts.
8. Optimizing Your Home for Home Health Care
Optimizing your home for home health care can improve safety, accessibility, and comfort. Here are some tips for making your home more conducive to home health care:
8.1. Remove Hazards
Remove tripping hazards such as loose rugs, electrical cords, and clutter. Ensure that walkways are clear and well-lit.
8.2. Improve Lighting
Improve lighting in hallways, stairways, and bathrooms to reduce the risk of falls. Install nightlights in bedrooms and bathrooms.
8.3. Install Grab Bars
Install grab bars in bathrooms near the toilet and shower to provide support and stability.
8.4. Modify Bathrooms
Modify bathrooms to improve accessibility. Consider installing a walk-in shower, raised toilet seat, or handheld showerhead.
8.5. Rearrange Furniture
Rearrange furniture to create wider pathways and more open spaces. Ensure that furniture is stable and easy to get in and out of.
8.6. Add Ramps
Add ramps to entrances and exits to improve accessibility for individuals with mobility impairments.
8.7. Install Handrails
Install handrails on stairways to provide support and stability.
9. The Future of Home Health Care
Home health care is a rapidly evolving field, driven by advances in technology, changes in healthcare policy, and the growing demand for home-based care services.
9.1. Telehealth and Remote Monitoring
Telehealth and remote monitoring technologies are transforming home health care. These technologies allow healthcare providers to monitor patients’ health remotely, provide virtual consultations, and deliver care more efficiently and effectively. Telehealth can improve access to care, reduce hospital readmissions, and enhance patient outcomes.
9.2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are being used to analyze healthcare data, predict patient outcomes, and personalize care plans. AI-powered tools can help healthcare providers identify patients who are at risk of complications, optimize treatment plans, and improve care coordination.
9.3. Wearable Devices and Sensors
Wearable devices and sensors are being used to track patients’ vital signs, activity levels, and sleep patterns. These devices can provide valuable data to healthcare providers, allowing them to monitor patients’ health in real-time and intervene early if necessary.
9.4. Home-Based Primary Care
Home-based primary care is a model of care that brings primary care services to patients’ homes. This model of care is particularly beneficial for individuals who have difficulty accessing traditional healthcare settings due to mobility impairments, chronic illnesses, or other factors. Home-based primary care can improve access to care, reduce hospitalizations, and enhance patient satisfaction.
9.5. Increased Focus on Prevention and Wellness
Home health care is increasingly focusing on prevention and wellness. Home health providers are helping patients manage chronic conditions, prevent falls, and maintain healthy lifestyles. By focusing on prevention and wellness, home health care can help individuals stay healthy and independent for longer.
10. Home Health Care Resources from CARS.EDU.VN
CARS.EDU.VN provides a wealth of resources for individuals and families seeking information about home health care.
10.1. Articles and Guides
CARS.EDU.VN offers a comprehensive collection of articles and guides on various aspects of home health care, including:
- Choosing a Home Health Agency
- Paying for Home Health Care
- Optimizing Your Home for Home Health Care
- Understanding Medicare Coverage for Home Health Care
- Navigating the Home Health Care Process
10.2. Provider Directory
CARS.EDU.VN features a directory of home health care providers in your area. You can search for providers based on location, services offered, and other criteria.
10.3. Expert Advice
CARS.EDU.VN offers expert advice from healthcare professionals, caregivers, and advocates on various topics related to home health care.
10.4. Community Forum
CARS.EDU.VN hosts a community forum where you can connect with other individuals and families who are navigating the home health care process. You can ask questions, share experiences, and find support.
10.5. Tools and Resources
CARS.EDU.VN provides a variety of tools and resources to help you make informed decisions about home health care, including:
- Care Plan Template
- Caregiver Checklist
- Medication Tracker
- Emergency Contact List
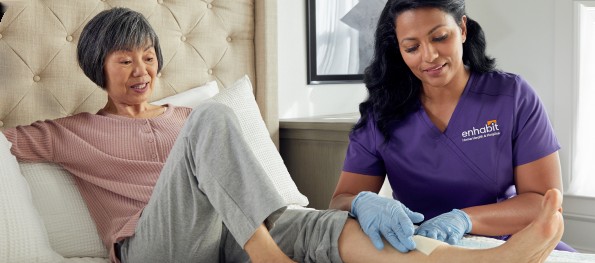 Nurse Assisting Senior Woman
Nurse Assisting Senior Woman
FAQ About Home Health Care
- What is the difference between home health care and home care? Home health care involves skilled medical services provided by licensed healthcare professionals, while home care focuses on non-medical assistance with daily living activities.
- How do I qualify for home health care? Typically, you need a doctor’s order and must require skilled nursing care or therapy services. You also need to be considered homebound.
- Does Medicare cover home health care? Yes, Medicare Part A and Part B can cover home health care if you meet specific conditions, such as being under a doctor’s care and needing skilled services.
- How much does home health care cost? The cost varies depending on the services needed and the location. Medicare, Medicaid, private insurance, and out-of-pocket payments are all possible payment methods.
- What services are typically included in home health care? Services include skilled nursing care, physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, home health aide services, and medical social services.
- How do I find a reputable home health care agency? Look for agencies that are accredited, licensed, and have positive online reviews. Ask for recommendations from your doctor, friends, or family.
- What questions should I ask when choosing a home health care agency? Inquire about caregiver qualifications, communication practices, emergency procedures, and the range of services offered.
- How can I make my home safer for home health care? Remove hazards, improve lighting, install grab bars, and rearrange furniture to create a more accessible environment.
- What are the latest trends in home health care? Telehealth, remote monitoring, AI-powered tools, and home-based primary care are transforming the industry.
- Where can I find more resources about home health care? CARS.EDU.VN offers articles, guides, provider directories, expert advice, and community forums to help you navigate home health care.
Finding the right home health care near you can significantly improve your quality of life or that of your loved ones. By understanding the types of services available, knowing how to find a reputable agency, and preparing your home, you can ensure a safe and supportive environment. For more in-depth information and to explore your options, visit cars.edu.vn today, or contact us at 456 Auto Drive, Anytown, CA 90210, United States, Whatsapp: +1 555-123-4567.
