How Does A Car Ac Work? If you’ve ever wondered about the intricate workings of your car’s air conditioning system, CARS.EDU.VN is here to provide you with a detailed explanation. We’ll explore the components, the process, and even common issues, so you can stay cool and comfortable on the road. Learn about AC system refrigerants and routine auto maintenance for optimal performance.
1. Understanding the Basics of Car AC Systems
The primary function of a car’s air conditioning (AC) system is to keep the cabin cool by removing heat and humidity. The system achieves this by cycling refrigerant between a liquid and gaseous state. This process, controlled by pressure and temperature, allows the AC to absorb heat and provide cool, dry air. CARS.EDU.VN aims to demystify this process for every car owner.
1.1 The Science Behind Cooling
The magic of a car’s AC lies in the principles of thermodynamics. Refrigerant, the key component, absorbs heat as it evaporates from a liquid to a gas. This process occurs in the evaporator, located inside the car’s cabin. As the refrigerant absorbs heat, it cools the surrounding air, which is then blown into the cabin, offering you relief from the heat. The cycle continues as the refrigerant is compressed back into a liquid, releasing the absorbed heat outside the car.
1.2 Historical Evolution of Refrigerants
The refrigerants used in automotive AC systems have evolved significantly over the years. Initially, R-12 (Freon) was the standard, known for its effectiveness and safety. However, due to its ozone-depleting properties, it was phased out in favor of R-134a. Today, the industry is transitioning to R-1234yf, a more environmentally friendly option with a lower global warming potential. According to the EPA, R-1234yf has a global warming potential (GWP) of less than 1, significantly lower than R-134a’s GWP of 1,430.
2. Key Components of a Car AC System
Understanding the individual components of the AC system is crucial for grasping the overall process. Each part plays a vital role in the cooling cycle. Here’s a detailed look at each:
2.1 The Compressor: The Heart of the System
The compressor is the powerhouse of the AC system, responsible for circulating the refrigerant. Driven by the engine via a belt, the compressor increases the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant. It draws in low-pressure gas and compresses it into high-pressure, high-temperature gas, setting the stage for the next phase of the cooling process. The compressor is a critical component, and its failure can render the entire AC system useless.
2.2 The Condenser: Releasing Heat
Located at the front of the car, near the radiator, the condenser dissipates heat from the high-pressure refrigerant. As the refrigerant flows through the condenser, it transforms from a hot gas to a high-pressure liquid. The condenser’s efficiency is vital, and it relies on airflow, often assisted by electric fans, to facilitate heat transfer. A clogged or damaged condenser can significantly reduce the AC’s cooling capacity.
2.3 The Dryer (Receiver/Drier): Removing Moisture
The dryer, also known as the receiver/drier, acts as a filter and moisture absorber. It removes water and contaminants from the refrigerant, ensuring the system’s longevity and efficiency. Moisture in the system can lead to corrosion and the formation of ice, which can block the flow of refrigerant. The dryer contains a desiccant that traps moisture, but it needs to be replaced periodically to maintain its effectiveness.
2.4 The Expansion Valve (or Orifice Tube): Controlling Refrigerant Flow
The expansion valve (or orifice tube in some systems) regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator. It reduces the pressure of the liquid refrigerant, causing it to expand and cool rapidly. This expansion is crucial for the refrigerant to absorb heat effectively in the evaporator. The expansion valve is a precision component, and its proper functioning is essential for optimal cooling.
2.5 The Evaporator: Cooling the Cabin
Positioned inside the car’s dashboard, the evaporator is where the cooling magic happens. Here, the low-pressure refrigerant absorbs heat from the air passing over it, cooling the air that is then blown into the cabin. As the refrigerant absorbs heat, it changes from a liquid to a gas. The evaporator also dehumidifies the air, removing moisture and contributing to the overall comfort inside the vehicle.
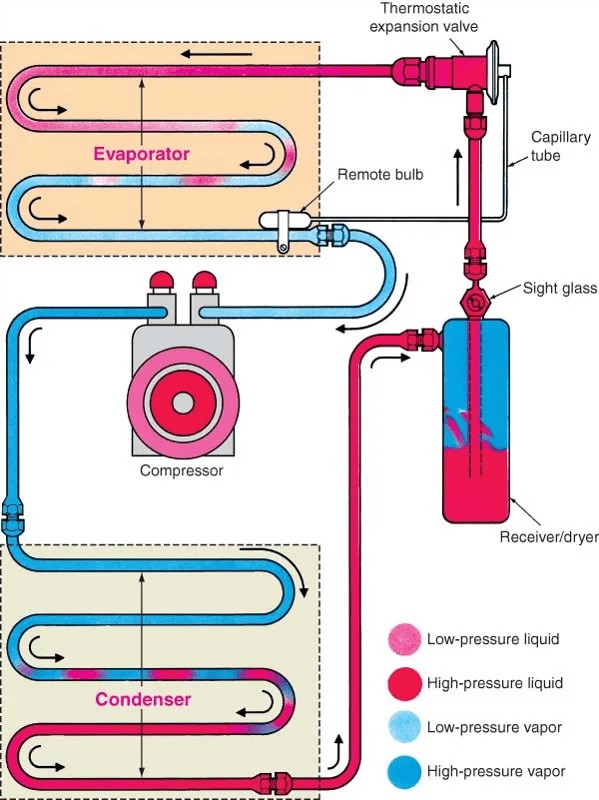 Car AC System Components
Car AC System Components
2.6 Detailed Component Table
To help you visualize and remember the function of each component, here’s a table summarizing their roles:
| Component | Function | Location | State of Refrigerant |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compressor | Compresses low-pressure refrigerant gas into high-pressure, high-temperature gas. | Engine Compartment | Gas |
| Condenser | Dissipates heat from high-pressure refrigerant, converting it to a high-pressure liquid. | Front of the Vehicle, near Radiator | Gas to Liquid |
| Receiver/Drier | Filters and removes moisture from the refrigerant. | High-Pressure Side, between Condenser & Metering Device | Liquid |
| Expansion Valve | Regulates refrigerant flow and reduces its pressure before entering the evaporator. | Between Receiver/Drier & Evaporator | Liquid |
| Evaporator | Absorbs heat from cabin air, cooling it before it’s blown into the car. | Inside the Dashboard | Liquid to Gas |
3. The Refrigerant Cycle: A Step-by-Step Guide
Understanding the refrigerant cycle is vital to grasping how a car AC works. Here’s a breakdown of each stage:
3.1 Compression Phase
The cycle begins with the compressor, which receives low-pressure, low-temperature refrigerant gas. The compressor increases the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant, transforming it into a high-pressure, high-temperature gas. This process requires energy from the engine, which drives the compressor via a belt.
3.2 Condensation Phase
The high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant then flows to the condenser, where it releases heat to the outside air. As the refrigerant cools, it changes from a gas to a high-pressure liquid. The condenser relies on airflow to dissipate heat effectively.
3.3 Drying and Filtering Phase
The high-pressure liquid refrigerant passes through the receiver/drier, where moisture and contaminants are removed. This step is essential to prevent corrosion and ice formation within the system. The dryer ensures that only clean, dry refrigerant proceeds to the next phase.
3.4 Expansion Phase
The high-pressure liquid refrigerant reaches the expansion valve, which reduces its pressure. This sudden drop in pressure causes the refrigerant to expand and cool rapidly, turning it into a low-pressure, low-temperature liquid.
3.5 Evaporation Phase
Finally, the low-pressure, low-temperature refrigerant enters the evaporator. Here, it absorbs heat from the air passing over it, cooling the air that is blown into the car’s cabin. As the refrigerant absorbs heat, it changes from a liquid to a gas, completing the cycle. The refrigerant then returns to the compressor to begin the process anew.
3.6 Visual Representation
Imagine the refrigerant as a messenger carrying heat. It picks up heat inside the car, transports it to the condenser to be released, gets cleaned and prepared, then returns to pick up more heat. This continuous cycle keeps your car cool and comfortable.
4. Common Car AC Problems and Solutions
Even with proper maintenance, AC systems can experience problems. Knowing the common issues and their solutions can save you time and money. CARS.EDU.VN is dedicated to helping you diagnose and address these issues effectively.
4.1 Refrigerant Leaks
One of the most common AC problems is refrigerant leaks. Because AC systems operate under pressure, they need to remain completely sealed from the surrounding environment. These leaks can occur at any point in the system, from the compressor to the evaporator. Signs of a leak include weak cooling, hissing sounds, or visible residue around components. According to a study by the Mobile Air Conditioning Society (MACS), refrigerant leaks account for over 60% of AC system failures.
Solution: Locate and repair the leak. This may involve replacing O-rings, hoses, or even entire components. After the repair, recharge the system with the correct type and amount of refrigerant. A professional AC service is often the best approach.
4.2 Compressor Failure
The compressor is a critical component, and its failure can shut down the entire AC system. Compressors can fail due to age, lack of lubrication, or internal damage. Symptoms of a failing compressor include loud noises, weak cooling, or the compressor not engaging at all.
Solution: Replace the compressor. This is a more involved repair that often requires specialized tools and expertise. It’s also important to flush the system to remove any debris that may have resulted from the compressor failure.
4.3 Clogged Condenser
The condenser is responsible for dissipating heat, and if it becomes clogged with dirt, debris, or bugs, its efficiency can be significantly reduced. This can lead to poor cooling performance, especially in hot weather.
Solution: Clean the condenser. Use a soft brush and a gentle cleaning solution to remove any debris. Be careful not to damage the delicate fins of the condenser. In severe cases, the condenser may need to be replaced.
4.4 Expansion Valve Issues
The expansion valve regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator, and if it becomes clogged or malfunctions, it can disrupt the cooling process. Symptoms of a faulty expansion valve include inconsistent cooling, freezing up of the evaporator, or a complete lack of cooling.
Solution: Replace the expansion valve. This requires evacuating the system and disconnecting the refrigerant lines. It’s a precision component, so proper installation is crucial.
4.5 Electrical Problems
Electrical issues, such as blown fuses, faulty relays, or wiring problems, can also affect the AC system. These issues can prevent the compressor from engaging or disrupt the operation of other components.
Solution: Diagnose and repair the electrical problem. Check fuses, relays, and wiring connections. Use a multimeter to test for voltage and continuity. If necessary, consult a wiring diagram and seek professional help.
4.6 Troubleshooting Table
Here’s a handy table to help you troubleshoot common AC problems:
| Problem | Possible Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Weak or No Cooling | Refrigerant Leak, Compressor Failure, Clogged Condenser | Repair Leak, Replace Compressor, Clean Condenser |
| Loud Noises | Compressor Failure, Worn Belt | Replace Compressor, Replace Belt |
| Inconsistent Cooling | Expansion Valve Issues, Electrical Problems | Replace Expansion Valve, Diagnose and Repair Electrical Issues |
| Evaporator Freezing Up | Expansion Valve Issues, Blocked Drain | Replace Expansion Valve, Clear Drain |
| AC Not Engaging | Electrical Problems, Faulty Compressor Clutch | Diagnose and Repair Electrical Issues, Replace Compressor Clutch |
5. Maintaining Your Car AC System
Regular maintenance is key to keeping your car AC system running efficiently and avoiding costly repairs. CARS.EDU.VN recommends these essential maintenance tips.
5.1 Regular Inspections
Inspect the AC system regularly for any signs of leaks, damage, or wear. Check hoses, belts, and connections for cracks, fraying, or looseness. Catching problems early can prevent them from escalating into major repairs.
5.2 Refrigerant Recharging
Over time, refrigerant can leak from the system, reducing its cooling capacity. Have the system recharged by a qualified technician to ensure optimal performance. The frequency of recharging depends on the vehicle and the system, but it’s generally recommended every 2-3 years.
5.3 Cleaning the Condenser
Keep the condenser clean to ensure proper airflow and heat dissipation. Use a soft brush and a gentle cleaning solution to remove any dirt, debris, or bugs. Avoid using high-pressure water, as this can damage the delicate fins of the condenser.
5.4 Replacing the Cabin Air Filter
The cabin air filter filters the air that enters the car’s cabin, including the air that passes through the evaporator. A clogged cabin air filter can reduce airflow and cooling efficiency. Replace the cabin air filter regularly, typically every 12,000 to 15,000 miles, or more often in dusty environments.
5.5 Running the AC Regularly
Even during the winter months, run the AC system periodically to keep the components lubricated and prevent them from drying out. This can help extend the life of the compressor and other parts.
5.6 Maintenance Schedule Table
Here’s a recommended maintenance schedule for your car AC system:
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Monthly | Early detection of leaks, damage, or wear |
| Refrigerant Recharge | Every 2-3 Years | Optimal cooling performance |
| Condenser Cleaning | Annually | Proper airflow and heat dissipation |
| Cabin Air Filter Replacement | Every 12,000-15,000 Miles | Improved airflow and air quality |
| Run AC Regularly | Monthly (Even in Winter) | Keeps components lubricated and prevents drying out |
6. Advanced AC Technologies in Modern Vehicles
Modern vehicles are equipped with advanced AC technologies that enhance comfort, efficiency, and performance. CARS.EDU.VN keeps you updated on these innovations.
6.1 Automatic Climate Control
Automatic climate control systems use sensors and electronic controls to maintain a consistent temperature inside the car. These systems automatically adjust the fan speed, air distribution, and temperature settings to keep the cabin comfortable, regardless of the outside weather.
6.2 Dual-Zone and Multi-Zone Climate Control
Dual-zone and multi-zone climate control systems allow the driver and passengers to set different temperature preferences for different areas of the car. This can be particularly useful for families or individuals who have different temperature preferences.
6.3 Electric Compressors
Electric compressors are becoming increasingly common in hybrid and electric vehicles. Unlike traditional compressors that are driven by the engine, electric compressors are powered by the car’s battery. This allows the AC system to operate even when the engine is off, improving efficiency and reducing emissions.
6.4 Refrigerant Leak Detection Systems
Some modern vehicles are equipped with refrigerant leak detection systems that monitor the refrigerant level and alert the driver if a leak is detected. This can help prevent damage to the AC system and reduce the environmental impact of refrigerant leaks.
6.5 Technology Trends Table
Here’s a look at some of the latest AC technology trends:
| Technology | Benefits | Vehicle Type |
|---|---|---|
| Automatic Climate Control | Maintains consistent temperature automatically | Most Modern Vehicles |
| Dual/Multi-Zone Climate Control | Allows different temperature settings for different areas of the car | Many Modern Vehicles |
| Electric Compressors | Improved efficiency, reduced emissions, AC operation even when engine is off | Hybrid and Electric Vehicles |
| Refrigerant Leak Detection | Prevents damage to AC system, reduces environmental impact | Select Modern Vehicles |
7. The Environmental Impact of Car AC Systems
Car AC systems can have a significant environmental impact due to refrigerant leaks and energy consumption. CARS.EDU.VN is committed to promoting eco-friendly practices.
7.1 Refrigerant and Ozone Depletion
Older refrigerants, such as R-12, were found to deplete the ozone layer. Modern refrigerants, such as R-134a and R-1234yf, are designed to be more environmentally friendly, but they still have a global warming potential. It’s crucial to handle refrigerants properly to prevent leaks and minimize their environmental impact.
7.2 Energy Consumption
Car AC systems consume energy, which can increase fuel consumption and emissions. Running the AC can reduce fuel economy by as much as 20%, according to the U.S. Department of Energy. Using the AC sparingly and maintaining the system properly can help reduce its energy consumption.
7.3 Eco-Friendly Practices
To minimize the environmental impact of car AC systems, follow these eco-friendly practices:
- Have the system serviced by a qualified technician to prevent leaks.
- Use the AC sparingly and only when necessary.
- Park in the shade to reduce the need for AC.
- Maintain the system properly to ensure efficient operation.
- Consider upgrading to a more efficient AC system or vehicle.
7.4 Impact Reduction Table
Here are some ways to reduce the environmental impact of your car AC system:
| Practice | Environmental Benefit |
|---|---|
| Prevent Refrigerant Leaks | Reduces ozone depletion and global warming |
| Use AC Sparingly | Reduces energy consumption and emissions |
| Park in the Shade | Reduces the need for AC |
| Maintain System Properly | Ensures efficient operation and reduces energy consumption |
| Upgrade to Efficient System | Reduces energy consumption and emissions |
8. How to Find Reliable AC Service and Repairs
Finding a trustworthy mechanic for AC service and repairs can be a challenge. CARS.EDU.VN is here to guide you in making the right choice.
8.1 Research and Reviews
Start by researching local auto repair shops. Look for shops that specialize in AC service and have positive reviews from other customers. Online review sites like Google Reviews and Yelp can provide valuable insights into the reputation and quality of service of different shops.
8.2 Certifications and Credentials
Ensure that the technicians working on your AC system are certified and have the necessary credentials. Certifications like ASE (Automotive Service Excellence) demonstrate that the technicians have the knowledge and skills to perform accurate and reliable repairs.
8.3 Transparent Pricing
Choose a shop that provides transparent pricing and detailed estimates before starting any work. A reputable shop will be able to explain the costs involved and answer any questions you have about the repairs. Be wary of shops that offer prices that seem too good to be true, as they may cut corners or use low-quality parts.
8.4 Warranty and Guarantees
Ask about the warranty and guarantees offered by the shop. A good shop will stand behind their work and offer a warranty on parts and labor. This provides peace of mind and ensures that you are protected in case of any issues with the repairs.
8.5 Diagnostic Equipment
Ensure that the shop has the necessary diagnostic equipment to accurately diagnose AC problems. Modern AC systems are complex and require specialized tools to identify issues. A shop with up-to-date diagnostic equipment is more likely to provide accurate and effective repairs.
8.6 Checklist for Choosing a Repair Shop
Here’s a quick checklist to help you choose the right AC repair shop:
| Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
| Reviews | Check online reviews to gauge the shop’s reputation. |
| Certifications | Verify that the technicians have relevant certifications (e.g., ASE). |
| Pricing | Ensure transparent pricing with detailed estimates. |
| Warranty | Ask about warranties on parts and labor. |
| Diagnostic Equipment | Confirm the shop has modern diagnostic tools. |
| Experience | Inquire about their experience with AC systems. |
| Customer Service | Assess their responsiveness and willingness to address concerns. |
| Location and Convenience | Consider accessibility and operating hours. |
| Referrals and Word of Mouth | Seek recommendations from friends, family, or online forums. |
| Cleanliness and Organization | Observe the shop’s physical condition for professionalism. |
9. The Future of Car AC Technology
The future of car AC technology is focused on enhancing efficiency, reducing environmental impact, and improving comfort. CARS.EDU.VN is committed to keeping you informed about these advancements.
9.1 Smart AC Systems
Smart AC systems will use artificial intelligence and machine learning to optimize cooling performance based on real-time conditions and driver preferences. These systems will be able to learn your cooling habits and adjust the temperature and airflow automatically to maximize comfort and efficiency.
9.2 Advanced Refrigerants
Research is ongoing to develop new refrigerants with even lower global warming potentials and improved cooling performance. These refrigerants will help reduce the environmental impact of car AC systems and improve energy efficiency.
9.3 Solar-Powered AC
Solar-powered AC systems are being explored as a way to reduce the energy consumption of car AC. These systems use solar panels to generate electricity that powers the AC compressor, reducing the load on the vehicle’s engine or battery.
9.4 Personalized Climate Control
Future AC systems will offer even more personalized climate control options, allowing individual occupants to customize their temperature and airflow settings. These systems may use sensors to detect body temperature and adjust the cooling accordingly.
9.5 Trend Forecast
Here’s a forecast of the future trends in car AC technology:
| Trend | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Smart AC | AI-powered systems that optimize cooling based on real-time conditions and driver preferences. | Enhanced comfort and energy efficiency. |
| Advanced Refrigerants | New refrigerants with lower global warming potentials and improved cooling performance. | Reduced environmental impact. |
| Solar-Powered AC | Solar panels that generate electricity to power the AC compressor. | Reduced energy consumption. |
| Personalized Climate Control | Systems that allow individual occupants to customize their temperature and airflow settings. | Increased comfort and convenience. |
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Car AC Systems
To further assist you, here are some frequently asked questions about car AC systems:
10.1 How often should I recharge my car’s AC system?
It’s generally recommended to recharge your car’s AC system every 2-3 years. However, if you notice a decrease in cooling performance, it may be necessary to recharge it sooner.
10.2 Can I recharge my car’s AC system myself?
While DIY AC recharge kits are available, it’s generally recommended to have the system recharged by a qualified technician. They have the proper equipment and expertise to ensure that the system is recharged correctly and safely.
10.3 What causes refrigerant leaks in car AC systems?
Refrigerant leaks can be caused by a variety of factors, including age, corrosion, damage, and loose connections. Regular inspections and maintenance can help prevent leaks.
10.4 How can I tell if my car’s AC compressor is failing?
Signs of a failing AC compressor include weak cooling, loud noises, and the compressor not engaging at all. If you notice any of these symptoms, have the system inspected by a qualified technician.
10.5 What is the difference between R-134a and R-1234yf refrigerants?
R-134a is a hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) refrigerant that was commonly used in car AC systems until recently. R-1234yf is a newer refrigerant with a much lower global warming potential. It is being phased in as a replacement for R-134a.
10.6 Can I convert my car’s AC system from R-134a to R-1234yf?
Converting an AC system from R-134a to R-1234yf is possible, but it’s not always recommended. The conversion may require modifications to the system, and it’s important to ensure that the new refrigerant is compatible with all of the components.
10.7 How does a car AC affect gas mileage?
Running the AC can reduce fuel economy by as much as 20%. Using the AC sparingly and maintaining the system properly can help reduce its impact on gas mileage.
10.8 What is the cabin air filter, and why is it important?
The cabin air filter filters the air that enters the car’s cabin, including the air that passes through the evaporator. A clogged cabin air filter can reduce airflow and cooling efficiency. Replace the cabin air filter regularly, typically every 12,000 to 15,000 miles.
10.9 How can I keep my car cool without using the AC?
Parking in the shade, using window shades, and opening windows while driving can help keep your car cool without using the AC.
10.10 Is it normal for water to drip from my car when the AC is running?
Yes, it’s normal for water to drip from your car when the AC is running. This is condensation that forms on the evaporator and drips out of the drain tube.
Conclusion
Understanding how your car’s AC system works can empower you to maintain it effectively and address any issues promptly. From the compressor to the evaporator, each component plays a crucial role in keeping you cool and comfortable on the road. Regular maintenance, timely repairs, and eco-friendly practices can ensure the longevity and efficiency of your AC system.
Do you have more questions about your car’s AC or need reliable service and repairs? Visit CARS.EDU.VN today for expert advice, maintenance tips, and trusted service providers. Our team is dedicated to helping you keep your car running smoothly and comfortably.
Contact us:
Address: 456 Auto Drive, Anytown, CA 90210, United States
Whatsapp: +1 555-123-4567
Website: CARS.EDU.VN
Let cars.edu.vn be your go-to resource for all things automotive.