How Does Air Conditioning Work In A Car? Understanding the intricacies of your vehicle’s AC system can enhance your driving comfort and help you identify potential issues early on. At CARS.EDU.VN, we’re committed to providing you with expert insights into automotive systems, ensuring you stay cool and comfortable on the road. This guide will explore the components, operation, and maintenance of your car’s air conditioning, offering practical tips to keep your system running smoothly and addressing common AC problems.
1. The Science Behind Automotive Air Conditioning
The core principle of how air conditioning works in a car involves the manipulation of refrigerant between liquid and gaseous states. This process absorbs heat and humidity from the vehicle’s interior, providing cool, dry air. The system achieves this by controlling the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant as it circulates through various components. This is a fundamental aspect of automotive comfort.
1.1. Refrigerant Phase Changes
The magic of air conditioning lies in the refrigerant’s ability to absorb and release heat as it transitions between liquid and gas. When the refrigerant evaporates (changes from liquid to gas), it absorbs heat from its surroundings, cooling the air that passes over the evaporator. Conversely, when the refrigerant condenses (changes from gas to liquid), it releases heat, which is expelled outside the vehicle.
1.2. Pressure and Temperature Relationship
The air conditioning system meticulously controls the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant to facilitate these phase changes. High pressure typically corresponds to high temperature, while low pressure corresponds to low temperature. This relationship is crucial for efficient heat transfer and cooling.
2. Key Components of a Car AC System
Understanding the components of your car’s AC is the first step to understanding how does air conditioning work in a car. A car’s AC system comprises several essential components, each playing a crucial role in the cooling process. These components work in harmony to ensure efficient and effective air conditioning.
2.1. The Compressor: Heart of the System
The compressor is the power unit of the AC system, acting as a pump that circulates the refrigerant. It separates the low-pressure side from the high-pressure side, compressing low-pressure, low-temperature gas into high-pressure, high-temperature gas. This process is essential for the refrigerant to absorb and release heat effectively.
The compressor is typically mounted on the front of the engine and driven by the serpentine belt. A clutch mechanism engages and disengages the compressor as needed, allowing the AC system to cycle on and off.
2.2. The Condenser: Cooling the Refrigerant
The condenser is responsible for reducing the temperature of the high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant. As the refrigerant flows through the condenser, it releases heat to the outside air, causing it to change from a gaseous state to a liquid state.
The condenser resembles the engine radiator and is typically mounted in front of the vehicle, behind the grill. It uses forced air, either from a fan or vehicle movement, to transfer heat away from the refrigerant.
2.3. The Dryer (Receiver-Dryer): Removing Moisture
The dryer, also known as the receiver-dryer, is a filter that removes moisture from the refrigerant. Moisture in the AC system can lead to corrosion and other issues, so the dryer is essential for maintaining system health.
The dryer contains a desiccant, a drying agent that absorbs water. It also has some system-filtering properties, removing contaminants that could harm the AC system. The dryer is mounted on the high-pressure side of the system, between the condenser and the metering device.
2.4. The Metering Device: Controlling Refrigerant Flow
The metering device controls the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator. It lowers the refrigerant pressure, which causes a rapid drop in temperature. This device can be either an expansion valve or a fixed orifice tube.
- Expansion Valve: An expansion valve is a sophisticated metering device that adjusts the refrigerant flow based on the cooling demand. It provides more precise control over the system’s performance.
- Orifice Tube: A fixed orifice tube is a simpler, less expensive metering device. It provides a constant flow of refrigerant, regardless of the cooling demand.
2.5. The Evaporator: Cooling the Cabin Air
The evaporator is where the refrigerant absorbs heat from the cabin air, providing a cooling effect. As warm air from the vehicle’s interior blows across the evaporator, the refrigerant changes from a liquid state back to a gaseous state, absorbing heat in the process.
The evaporator is the only AC component mounted inside the passenger compartment, typically behind the dashboard. It is designed to maximize surface area for efficient heat transfer.
2.6. AC System Diagram
Below is an AC system diagram that shows the main components used and how they’re connected:
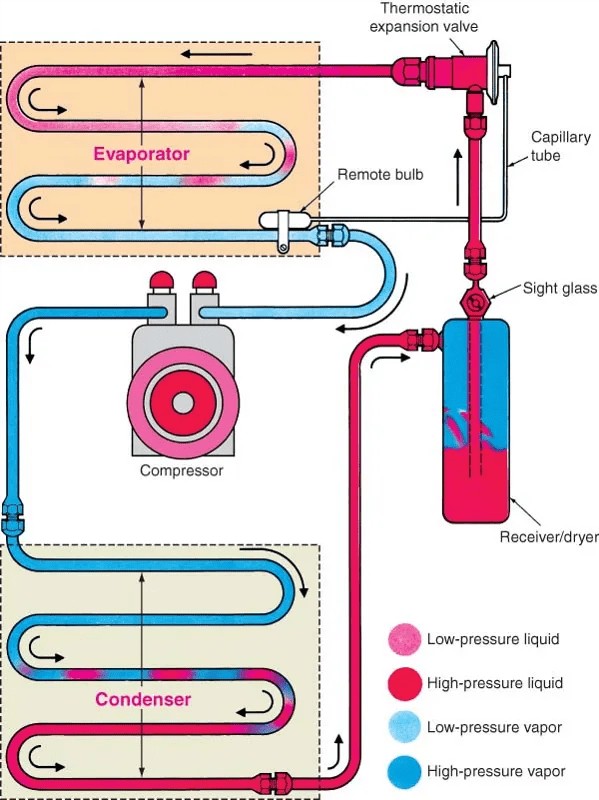 Car AC System Diagram
Car AC System Diagram
3. How a Car AC System Operates: A Step-by-Step Explanation
To truly grasp how does air conditioning work in a car, it’s essential to understand the system’s operation. The AC system operates in a continuous cycle, with the refrigerant circulating through the various components to absorb and release heat.
3.1. Refrigerant Path and Characteristics
- Entry to Compressor: Low-temperature, low-pressure refrigerant enters the compressor as a gas.
- Exit from Compressor: High-temperature, high-pressure refrigerant leaves the compressor as a gas.
- Condensation in Condenser: The refrigerant cools and converts to a liquid in the condenser while still under high pressure.
- Moisture Removal: The receiver/dryer removes water from the refrigerant.
- Pressure Reduction: The expansion valve or orifice tube reduces the refrigerant pressure.
- Evaporation in Evaporator: The refrigerant converts back to a gaseous state in the evaporator.
- Heat Absorption: As air blows across the evaporator, it is cooled and dried. The refrigerant absorbs heat, completing the cycle.
3.2. The Cooling Process in Detail
The cooling process begins with the compressor drawing in low-pressure refrigerant gas. The compressor then compresses this gas, increasing its temperature and pressure. The high-pressure, high-temperature gas flows to the condenser, where it releases heat to the outside air and condenses into a high-pressure liquid.
The high-pressure liquid refrigerant then flows to the dryer, where moisture and contaminants are removed. From the dryer, the refrigerant passes through the metering device, which reduces its pressure and temperature. This low-pressure, low-temperature liquid refrigerant enters the evaporator, where it absorbs heat from the cabin air and evaporates into a low-pressure gas. The cooled and dehumidified air is then blown into the vehicle’s interior, providing a comfortable environment for the occupants.
Finally, the low-pressure refrigerant gas returns to the compressor, and the cycle begins again.
4. Common AC System Problems and How to Address Them
Even the most well-maintained AC systems can experience problems. Knowing the common issues and their solutions can save you time and money.
4.1. Refrigerant Leaks
Refrigerant leaks are one of the most common AC problems. Because automotive air conditioning systems operate under pressure, they need to remain completely sealed from the surrounding environment. Anything that allows refrigerant to escape or contaminants to enter can cause a failure. Leaks can occur at any of the connections or components in the system.
Symptoms:
- Weak or no cooling
- Hissing sound from the AC system
- Visible signs of refrigerant oil near connections
Solutions:
- Locate the leak using a UV dye and a black light or an electronic leak detector.
- Replace the faulty component.
- Evacuate and recharge the system with the correct type and amount of refrigerant.
4.2. Compressor Issues
The compressor is a critical component, and if it fails, the entire AC system can be affected. Compressors can fail due to age, lack of lubrication, or internal damage.
Symptoms:
- No cooling
- Loud noises from the compressor
- Compressor clutch not engaging
Solutions:
- Replace the compressor.
- Ensure the system is properly lubricated.
- Check and replace the compressor clutch if necessary.
4.3. Condenser Blockage
The condenser needs a steady flow of air to dissipate heat. Road debris and dirt may reduce airflow, causing system malfunction. The condenser is mounted directly behind the vehicle grill, leaving it somewhat exposed and at risk for partial blockage.
Symptoms:
- Reduced cooling efficiency
- Overheating of the AC system
Solutions:
- Clean the condenser fins with a soft brush or compressed air.
- Remove any debris blocking airflow.
- Consider replacing the condenser if it is severely damaged.
4.4. Expansion Valve or Orifice Tube Problems
The expansion valve or orifice tube controls the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator. If these components become clogged or fail, the AC system will not cool properly.
Symptoms:
- Reduced cooling
- Freezing of the evaporator
- High-pressure readings on the AC system
Solutions:
- Replace the expansion valve or orifice tube.
- Ensure the system is clean and free of debris.
4.5. Electrical Issues
Electrical problems can also affect the AC system. These can include faulty wiring, blown fuses, or a malfunctioning AC control module.
Symptoms:
- AC not turning on
- Intermittent cooling
- AC fan not working
Solutions:
- Check and replace any blown fuses.
- Inspect and repair any faulty wiring.
- Test and replace the AC control module if necessary.
5. Benefits of a Well-Functioning AC System
A properly functioning AC system offers numerous benefits beyond just keeping you cool.
5.1. Enhanced Comfort
The primary benefit is, of course, enhanced comfort. A well-maintained AC system keeps the cabin cool and comfortable, even in hot weather.
5.2. Improved Air Quality
The AC system also helps to improve air quality by filtering out dust, pollen, and other allergens. This can be especially beneficial for people with allergies or respiratory problems.
5.3. Increased Safety
By keeping you cool and comfortable, the AC system can help you stay alert and focused while driving, increasing safety.
5.4. Defogging Capabilities
The AC system can also be used to defog the windows quickly, improving visibility in humid or rainy conditions.
5.5. Resale Value
A well-maintained AC system can also increase the resale value of your vehicle.
6. AC System Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance
Regular maintenance is essential for keeping your car’s AC system running smoothly and efficiently. Here are some tips to help you keep your AC system in top condition.
6.1. Regular Use
Operate the AC system regularly, even in cooler months, to keep the components lubricated and prevent leaks.
6.2. Check Refrigerant Levels
Have a technician check the refrigerant levels periodically. Low refrigerant levels can cause the system to work harder and may lead to component failure.
6.3. Inspect Belts and Hoses
Regularly inspect the belts and hoses for cracks, leaks, or damage. Replace them as needed to prevent system failure.
6.4. Clean the Condenser
Keep the condenser clean and free of debris to ensure proper airflow.
6.5. Replace Cabin Air Filter
Replace the cabin air filter regularly to ensure good air quality and efficient airflow through the AC system.
6.6. Professional Servicing
Schedule regular professional servicing to have the AC system inspected, cleaned, and recharged as needed.
7. The Future of Car AC Systems
The world of automotive air conditioning is continuously evolving. New technologies and refrigerants are being developed to improve efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and enhance comfort.
7.1. New Refrigerants
The automotive industry is transitioning to more environmentally friendly refrigerants, such as R-1234yf, which has a lower global warming potential than previous refrigerants like R-134a. Europe requires the use of R-1234yf, and it will likely become the new standard in the United States.
7.2. Electric Compressors
Electric compressors are becoming more common in hybrid and electric vehicles. These compressors are more efficient and can operate independently of the engine, providing cooling even when the vehicle is stopped.
7.3. Improved Filtration Systems
Advanced filtration systems are being developed to improve air quality and remove allergens and pollutants from the cabin air.
7.4. Smart AC Systems
Smart AC systems use sensors and algorithms to automatically adjust the temperature and airflow based on the occupants’ preferences and the vehicle’s environment.
8. Choosing the Right AC Service and Repair
When your AC system needs service or repair, it’s essential to choose a reputable and qualified technician. Here are some factors to consider when selecting an AC service and repair provider.
8.1. Experience and Expertise
Look for a technician with experience and expertise in automotive AC systems. They should be familiar with the latest technologies and refrigerants.
8.2. Certifications
Check if the technician is certified by a recognized organization, such as the Mobile Air Conditioning Society (MACS).
8.3. Reputation
Read online reviews and ask for recommendations to gauge the provider’s reputation.
8.4. Warranty
Choose a provider that offers a warranty on their work. This provides peace of mind and ensures that you are protected if there are any issues with the repair.
8.5. Transparency
The provider should be transparent about their pricing and explain the repair process clearly.
9. CARS.EDU.VN: Your Trusted Source for Automotive Expertise
At CARS.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing you with the most up-to-date and comprehensive information on all aspects of automotive care. Whether you’re looking for maintenance tips, repair advice, or in-depth explanations of vehicle systems, we’ve got you covered.
9.1. Expert Articles and Guides
Our website features a wide range of expert articles and guides on topics such as AC system maintenance, engine repair, brake service, and more.
9.2. Troubleshooting Tips
We provide troubleshooting tips to help you diagnose and resolve common automotive problems.
9.3. Service Locator
Our service locator tool helps you find reputable and qualified service providers in your area.
9.4. Community Forum
Our community forum allows you to connect with other car enthusiasts and ask questions to our team of experts.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Car AC Systems
Here are some frequently asked questions about car AC systems:
-
How often should I recharge my car’s AC system?
- It depends on the vehicle and the system’s condition. Generally, every 2-3 years is recommended, but if you notice a decrease in cooling performance, it’s time to check it.
-
Can I recharge my car’s AC system myself?
- While DIY kits are available, it’s best to have a professional do it to ensure proper handling of refrigerants and avoid damage to the system.
-
Why is my car’s AC blowing warm air?
- Possible causes include low refrigerant, a faulty compressor, a clogged condenser, or an electrical issue.
-
How can I tell if my car’s AC system has a leak?
- Signs include weak cooling, hissing sounds, and visible oil residue near AC components.
-
Is it normal for my car’s AC to make noise?
- Some noise is normal, but loud or unusual noises could indicate a problem with the compressor or other components.
-
What is the difference between R-134a and R-1234yf refrigerants?
- R-1234yf is a newer refrigerant with a lower global warming potential compared to R-134a.
-
How does the car’s AC system affect fuel efficiency?
- Using the AC system can reduce fuel efficiency because the compressor puts a load on the engine.
-
Can I use the AC system to defog my windows?
- Yes, using the AC system in conjunction with the defroster can quickly remove fog from the windows.
-
How can I improve the cooling performance of my car’s AC system?
- Regular maintenance, such as cleaning the condenser and replacing the cabin air filter, can improve cooling performance.
-
What should I do if my car’s AC system stops working?
- Consult a qualified technician to diagnose and repair the problem. Ignoring the issue can lead to more extensive and costly repairs.
11. Keep Your Car Cool with CARS.EDU.VN
Understanding how does air conditioning work in a car is essential for maintaining your vehicle and ensuring a comfortable driving experience. Whether you’re dealing with a minor issue or a major repair, CARS.EDU.VN is here to provide you with the knowledge and resources you need.
Remember, regular maintenance and timely repairs can extend the life of your AC system and keep you cool on the road. Don’t wait until the summer heat hits – take care of your AC system today.
Are you experiencing AC problems or looking for reliable automotive services? Visit CARS.EDU.VN for expert advice, service recommendations, and more. Contact us at 456 Auto Drive, Anytown, CA 90210, United States, or reach out via WhatsApp at +1 555-123-4567. Let CARS.EDU.VN help you stay cool and comfortable behind the wheel.
Now that you know how does air conditioning work in a car and what’s involved in keeping it running smoothly, you’re better equipped to handle any AC-related challenges that come your way. At cars.edu.vn, we’re committed to providing you with the knowledge and resources you need to stay informed and confident about your vehicle.