For anyone venturing into the realm of car lighting, the term “lumen” quickly emerges as a key metric. If you’ve ever considered upgrading your headlights, understanding lumens is crucial. Lumens are the standard unit for measuring the total amount of visible light emitted from a light source. In simpler terms, lumens tell you how bright your car headlights are – the higher the lumen rating, the brighter the light. Therefore, investing in high-lumen headlights is a straightforward way to significantly enhance visibility during nighttime driving or in challenging weather conditions.
Headlights with superior lumen output not only illuminate the road more effectively but also play a vital role in boosting safety for both the driver and other road users. Improved visibility translates to earlier detection of hazards, pedestrians, and other vehicles, allowing for quicker reaction times and potentially preventing accidents. While the benefits of high-lumen headlights are clear, the question remains: just how many lumens should your car headlights ideally have?
Car headlight lumen output can range considerably, from a modest 500 lumens to over 5000 lumens per bulb. This variance largely depends on the type of headlight bulb utilized. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify headlight brightness, explore the different types of headlights available, and help you determine the optimal lumen output for your vehicle, ensuring both safety and performance.
Understanding Headlight Brightness: Lumens Explained
Decoding Light Output: The Lumen Metric
Lumens are the fundamental unit for quantifying the total visible light emitted by a light source. This measurement stems from the concept of luminous flux and provides a practical method for evaluating the efficiency and effectiveness of various light sources, including car headlights. It’s important to distinguish lumens from watts; while watts measure energy consumption, lumens directly reflect the perceived brightness of light. For assessing lighting performance, lumen is a more relevant and practical metric than watt.
The science behind lumens is closely linked to the human eye’s sensitivity to different wavelengths of light. In photopic vision, which is our daylight vision, our eyes are most sensitive to wavelengths around 555 nanometers, which falls within the green-yellow part of the spectrum. Lumen ratings take this spectral sensitivity into account by weighting the light output across the visible spectrum, ensuring that the measurement accurately reflects how bright the light appears to the human eye. This is why a minimum lumen output is crucial for effective headlights, with many regions and safety standards recommending a minimum of 3000 lumens for car headlights.
Beam Pattern: Directing Light Effectively
Beyond just brightness, the beam pattern of a headlight is equally critical. The beam pattern dictates how light is distributed on the road. A well-designed beam pattern is characterized by its focus and even light distribution, ensuring that the road is adequately illuminated without creating excessive glare for oncoming drivers. Several factors influence the beam pattern, including the type of bulb, the design of the headlight housing, and the precise positioning of the light source relative to the reflector or lens. Optimizing beam patterns is crucial for maximizing the usable light from the available lumens, directing the light exactly where it’s needed on the road. This optimized light distribution significantly enhances a driver’s ability to see clearly and react effectively to varying road conditions.
In the context of automotive lighting, understanding lumens is essential for selecting headlights that offer the best balance of brightness and safety. The goal is to achieve optimal road illumination without causing dangerous glare that can impair the vision of drivers approaching from the opposite direction. Therefore, achieving clear and focused illumination requires a careful balance between lumen output, beam pattern design, and color temperature of the light.
Exploring Different Types of Car Headlights
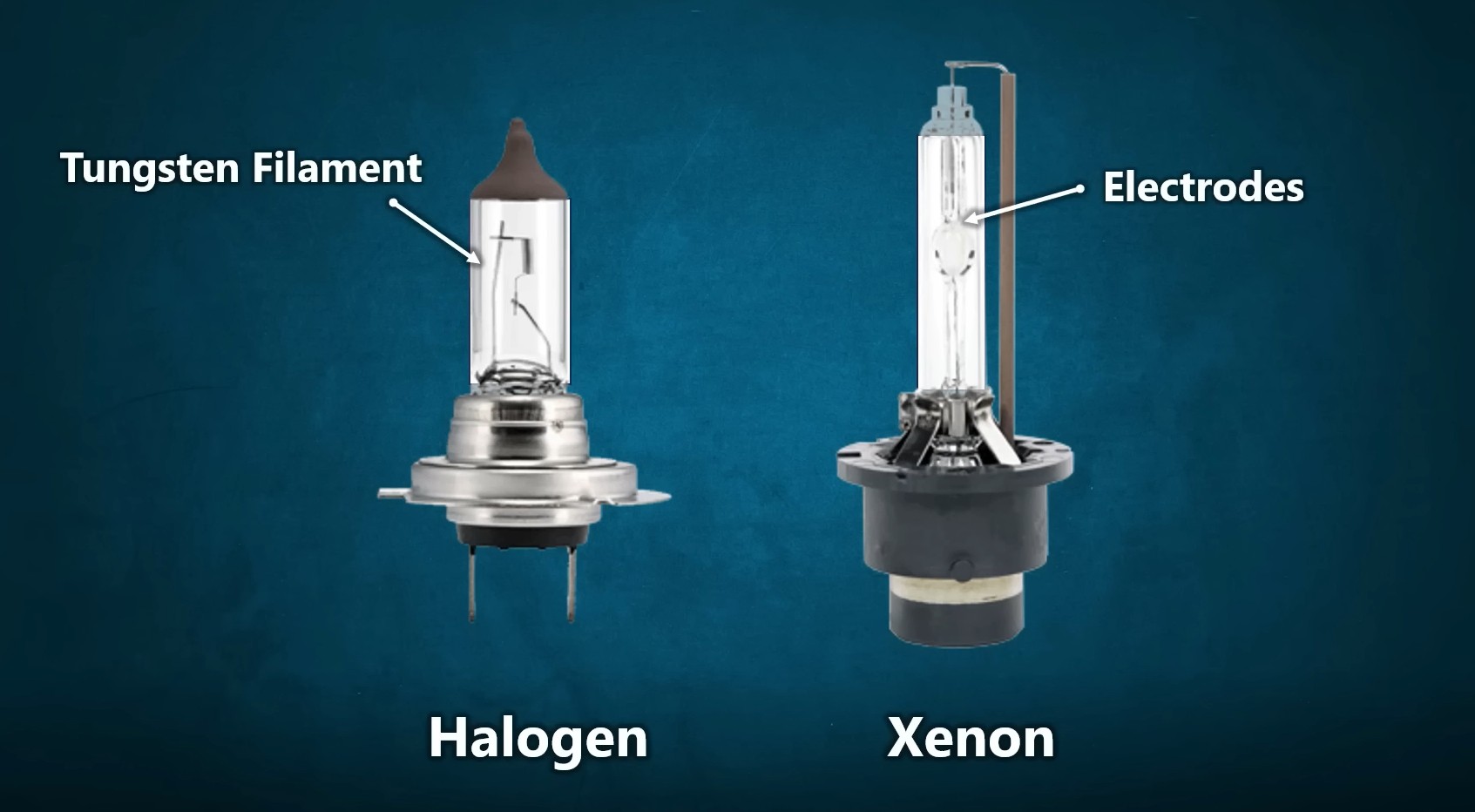
Halogen Headlights: Standard Brightness and Limitations
Halogen headlights, a long-standing technology in automotive lighting, operate by passing electricity through a thin tungsten filament housed within a quartz glass bulb. This bulb is filled with halogen gas, which helps to prolong the filament’s life and enhance light output. When the filament heats up due to the electric current, it emits a warm, yellowish light. On average, halogen bulbs produce around 1,000 lumens per bulb, which is considerably lower compared to more modern headlight technologies like LEDs and HIDs. Despite their lower lumen output, halogen headlights remain prevalent, with a significant percentage of vehicles still equipped with them due to their affordability and established infrastructure.
Key Considerations for Halogen Headlights:
- Higher Power Consumption: Halogen headlights are less energy-efficient, consuming more power compared to LED alternatives. This increased power draw can slightly impact fuel economy over time.
- Shorter Lifespan: Halogen bulbs have a relatively shorter lifespan, typically lasting up to 1,000 hours. This means more frequent replacements compared to HID or LED options.
- Glare Potential: If halogen headlight assemblies are misaligned or improperly adjusted, they can produce glare that can temporarily blind oncoming drivers, posing a safety risk.
- Snow Accumulation: Halogen bulbs generate heat, but in very cold climates, this heat may not be sufficient to melt snow or ice that accumulates on the headlight housing, potentially reducing light output and effectiveness.
HID (Xenon) Headlights: Advantages and Drawbacks
HID, or High-Intensity Discharge, headlights represent a significant step up in brightness and efficiency from halogen technology. HID headlights generate light by creating an electric arc between two tungsten electrodes inside a bulb. This bulb is filled with a combination of xenon gas and metal salts. When the arc is ignited, it vaporizes the metal salts, producing a brilliant white or bluish light. HID bulbs can achieve lumen outputs as high as 5,000 lumens with a standard 35-watt bulb, significantly outperforming halogen headlights in terms of brightness and light intensity.
Key Considerations for HID Headlights:
- Energy Efficiency: HID headlights are more energy-efficient than halogen bulbs, providing more light output for less power consumption.
- Extended Lifespan: HID bulbs typically last longer than halogen bulbs, with lifespans averaging around 2,000 hours, reducing the frequency of replacements.
- Glare Issues: Similar to halogens, misaligned or improperly installed HID headlight assemblies can cause substantial glare for oncoming traffic due to their high light intensity. Proper alignment and projector lenses are crucial to mitigate glare.
- Warm-up Time: HID headlights require a brief warm-up period to reach their full brightness. This means they don’t provide instant full illumination like halogen or LED headlights.
- Heat Generation: HID systems produce a considerable amount of heat, which, while potentially beneficial in melting snow, can also be a concern in enclosed headlight housings and may be more noticeable to other drivers.
- Color Options: HID headlights offer a range of color temperatures, from warmer golden hues to cooler blue tones, allowing for some customization of the light’s appearance.
LED Headlights: Efficiency, High Output, and Customization
LED (Light Emitting Diode) headlight bulbs represent the cutting edge in automotive lighting technology. LEDs utilize semiconductor technology to generate light, offering a highly efficient and durable illumination source. LED headlights can achieve impressive lumen outputs, with some systems delivering up to 12,000 lumens per pair, far exceeding both halogen and HID headlights. Furthermore, LEDs are exceptionally energy-efficient, consuming significantly less power while producing more light. This lower power consumption not only improves fuel efficiency but also reduces the strain on the vehicle’s electrical system. LEDs are also known for their long lifespan and compact size, offering greater design flexibility for headlight housings.
Key Advantages of LED Headlights:
- Superior Brightness: LED headlights produce significantly brighter light, in the range of 3,600 to 4,500 lumens per bulb and up to 12,000 lumens per pair, with lower wattage compared to HID and halogen options.
- Energy Efficiency: LEDs are incredibly energy-efficient, converting a higher percentage of energy into light and wasting very little energy as heat, similar to household LED bulbs.
- Enhanced Efficiency and Brightness: LEDs offer a superior combination of brightness and energy efficiency compared to all other headlight technologies.
- Potential Glare: While generally well-controlled, higher wattage LED bulbs, if improperly designed or installed, can still cause glare. It is crucial to choose reputable LED headlight systems designed to minimize glare and maintain safe beam patterns.
Headlight Technology, Regulations, and Safety
Regulatory Standards: Candela Limits and Glare Prevention
To ensure road safety and minimize glare, headlight power is subject to regulatory limits. These regulations are typically expressed in candela, a unit of luminous intensity. Headlight power regulations generally restrict output to between 20,000 and 75,000 candela. Historically, the United States has lagged behind in adopting modern headlight technologies and updating its regulations to align with global standards. However, new rules are being implemented to bring U.S. headlight standards in line with international best practices, incorporating advancements in headlight technology to enhance both performance and safety. These updated regulations aim to ensure that brighter, more efficient headlights can be used without compromising the safety of oncoming drivers due to excessive glare.
Balancing Brightness and Safety: High Beams and Light Output
While bright headlights are undeniably beneficial for improving driver visibility, it’s crucial to strike a balance to avoid creating glare and discomfort for other drivers. Overly bright headlights can not only cause temporary vision impairment for oncoming drivers but can also paradoxically reduce the driver’s own visibility in certain conditions due to reflection and excessive foreground illumination. For optimal safety and visibility, it is generally recommended to opt for headlights with a brightness range of 2,500 to 3,000 lumens per bulb for standard driving conditions. This lumen range offers a significant improvement in visibility compared to older halogen systems without being excessively bright and causing undue glare.
Choosing the Right Headlight Brightness
Finding the Sweet Spot: Balancing Light Output and Beam Pattern
Achieving optimal headlight performance is not just about maximizing brightness; it’s about finding the right balance between lumen output and beam pattern design. While brighter headlights can enhance visibility and improve road safety, excessive brightness can lead to glare, negating these benefits and creating hazards for other drivers. As a general guideline, if you prefer brighter headlights, ensure that the total light output remains below 3,500 lumens per bulb to minimize the risk of glare.
| Headlight Type | Average Lumen Output per Bulb | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Halogen | 1,000 – 1,500 lumens | Traditional, widely adopted, shorter lifespan |
| HID (Xenon) | 3,000 – 5,000 lumens | Bright, energy-efficient, warm-up time |
| LED | 3,600 – 4,500 lumens (up to 12,000 lumens per pair) | Highly efficient, long lifespan, customizable color |
| Laser | Up to 6,000 lumens | Extremely bright, high efficiency, premium cost |

Excessive brightness, especially when combined with a poorly designed beam pattern, can lead to discomfort and impaired vision for oncoming traffic. Therefore, achieving optimal headlight performance requires ensuring that headlights are properly aimed and adjusted, and that the beam pattern is carefully engineered to focus light effectively on the road surface and distribute it evenly across the driver’s field of view.
Recommended Brightness for Various Driving Conditions
Different driving environments and conditions demand varying levels of headlight brightness. Here are some general recommendations for lumen output based on driving conditions:
Low-Beam Headlights (Standard Driving): For typical driving conditions, including city streets and well-lit suburban roads, a lumen range of 1,500 to 2,000 lumens per bulb is generally sufficient. This level of brightness provides adequate illumination for safe driving without causing excessive glare in urban environments.
High-Beam Headlights (Poorly Lit Roads): When driving on dark rural roads or highways with limited ambient lighting, high-beam headlights with a lumen range of 2,500 to 3,500 lumens per bulb are recommended. This increased brightness provides a longer sight distance, allowing drivers to see further down the road and react to potential hazards in advance.
Fog Lights (Foggy or Misty Conditions): Fog lights are specifically designed for low-visibility conditions like fog or mist. They typically produce between 1,000 and 1,500 lumens per bulb. Their key feature is a wide, low beam pattern that cuts through the fog and minimizes glare by directing light downwards and outwards, illuminating the road surface beneath the fog layer.
Off-Road Lights (Off-Roading): For off-road driving, where maximum visibility is crucial, auxiliary off-road lights can produce significantly higher lumen outputs, ranging from 3,000 to 5,000 lumens per bulb or more. These powerful lights are designed to provide extensive illumination of the surrounding terrain, aiding navigation and obstacle avoidance in challenging off-road environments.
Delving Deeper into LED Headlights
Advantages of LED Headlights: Longevity and Customization
LED headlights offer a compelling combination of benefits, including extended lifespan, superior energy efficiency, and greater flexibility in terms of color temperature and brightness customization. LEDs are known for their long operational life, often lasting tens of thousands of hours, significantly outperforming halogen and HID bulbs. They also produce a crisp, white light that closely resembles daylight, enhancing visibility and reducing eye strain during nighttime driving. Furthermore, LED technology allows for precise control over light output and beam pattern, enabling manufacturers to create highly optimized headlight designs.
Cooling Systems for LED Headlights: Maintaining Performance
While LEDs themselves generate very little heat in the form of infrared radiation, the electronic components that drive them can produce heat. Although LED headlights are far more efficient than traditional bulbs, managing heat is still crucial to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Overheating can negatively impact both the light output and lifespan of LEDs. Therefore, effective cooling systems are often integrated into LED headlight designs. These systems can range from passive heat sinks that dissipate heat into the surrounding air to active cooling solutions like small fans that force air circulation around the LED components. Proper thermal management ensures that LED headlights operate at their optimal temperature, maintaining consistent brightness and maximizing their lifespan.
Installation and Compatibility Considerations
Ensuring the Right Fit for Your Vehicle
Selecting the correct headlight bulb size and type is essential for ensuring compatibility with your vehicle. Before purchasing replacement headlights, it’s crucial to identify the specific bulb size and type required for your car. This information can typically be found in your vehicle’s owner’s manual or by using online bulb finder tools that are available on many automotive parts retailer websites. Beyond bulb size, also consider the electrical requirements of the new headlights. Ensure that your vehicle’s electrical system can accommodate the power draw and voltage requirements of the replacement bulbs, especially when upgrading to LED or HID systems. Additionally, physically check the headlight housing to ensure it can accommodate the size and shape of the new LED or HID units. If you are uncertain about compatibility or installation, consulting with professional automotive installers is highly recommended to ensure a proper fit and optimal performance.
Ease of Installation: DIY vs. Professional
The ease of installation for replacement headlights can vary significantly depending on the type of headlight and the vehicle’s design. Some LED headlight bulbs are designed for straightforward plug-and-play installation, making them accessible for DIY enthusiasts. These typically require no modifications to the vehicle’s wiring or headlight housings and can be installed with basic tools and mechanical skills. However, other headlight upgrades, particularly those involving HID or more complex LED systems, may require professional installation. Factors such as complex wiring, ballast installation (for HID), or modifications to the headlight housing can make these installations more challenging and potentially risky for inexperienced individuals. Before attempting a DIY installation, honestly assess your skills and comfort level. If you are unsure or uncomfortable with any aspect of the installation process, seeking professional installation is always the safest and most reliable option to guarantee proper functionality and avoid potential electrical issues or damage to your vehicle.
Conclusion: Illuminating the Path Ahead
The Importance of Lumens and Beam Patterns
Understanding lumens and beam patterns is paramount when selecting the right headlight bulbs for your vehicle. Lumens provide a clear indication of brightness, while beam patterns determine how effectively that light is distributed on the road. Choosing headlights with an appropriate lumen output for your typical driving conditions, combined with a well-engineered beam pattern, is crucial for maximizing visibility and ensuring safe nighttime driving.
LED headlights stand out as a superior choice, offering improved energy efficiency, greater brightness, and a wider range of customization options. By carefully considering lumen output, beam pattern characteristics, and color temperature, you can fine-tune your vehicle’s headlights to achieve the perfect balance of usable light, minimize glare, and optimize visibility. Furthermore, being mindful of technical factors such as power consumption and heat management will contribute to the longevity and reliable performance of your chosen headlights.
Final Thoughts: Making an Informed Headlight Choice
Ultimately, selecting the right headlights is a matter of balancing your individual needs and preferences with safety and regulatory considerations. When making your choice, carefully evaluate factors such as brightness (lumens), color temperature, and beam pattern. Ensure compatibility with your vehicle’s electrical system and headlight housings, and always adhere to local regulations regarding maximum and minimum lumen output. Remember that your car’s headlights are your eyes on the road during nighttime driving. Investing in quality headlights and making informed choices about brightness and technology is a crucial aspect of vehicle safety and responsible driving.
Upgrade Your Fleet’s Headlights Today!
For more in-depth guidance on selecting the ideal headlights for your vehicle, visit us anytime! Explore our extensive resources, browse our diverse range of models, and benefit from expert recommendations to make a well-informed decision. Come chat with us, and share your thoughts and ideas!
