Formula 1 cars represent the pinnacle of motorsport engineering and technology. How much does a Formula 1 car cost? This detailed exploration by CARS.EDU.VN breaks down the expenses involved in building and running these high-performance machines, considering factors like advanced materials and intricate engineering. Understanding the price tag reveals the financial commitment and technological prowess required to compete in Formula 1.
1. Understanding the Base Cost of an F1 Car
The question, “How much does a Formula 1 car cost?” leads us to explore the multitude of components and complex engineering that contribute to the final price tag. Creating a Formula 1 car is not a simple endeavor; it is a meticulous process that involves extensive research, development, and the use of advanced materials. This section will delve into the general costs and the factors that influence them.
-
Initial Investment: On average, a complete Formula 1 car can cost around $15 million to $20 million. This figure includes the design, manufacturing, and assembly of all the car’s components, per recent estimates.
-
Factors Influencing Cost: Several factors influence the overall cost, including:
- Materials: The use of carbon fiber, titanium, and other high-strength, lightweight materials significantly increases expenses.
- Research and Development: Teams invest heavily in R&D to improve performance, adding to the cost.
- Technology: Advanced technology such as hybrid engines and complex aerodynamic systems also play a vital role.
1.1 Cost Breakdown of Key Components
To fully answer the question, “How much does a Formula 1 car cost?” we need a component-by-component breakdown. The primary components of an F1 car include the chassis, engine, aerodynamics package, electronics, and suspension system. Below is a detailed look at the costs associated with each.
| Component | Estimated Cost | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Chassis | $1.5 million – $2 million | The primary structure of the car, designed for safety and performance. |
| Engine | $8 million – $12 million | A highly sophisticated 1.6-liter V6 turbocharged hybrid engine. |
| Aerodynamics | $2 million – $3 million | Includes front and rear wings, floor, bargeboards, and other aerodynamic elements. |
| Electronics | $1 million – $1.5 million | Consists of various sensors, control units, and telemetry systems. |
| Suspension System | $500,000 – $1 million | Involves intricate designs and advanced materials to optimize handling and stability. |
| Gearbox | $354,000 | Semi-automatic gearboxes with eight forward gears and one reverse, allowing for seamless shifting. |
| Fuel Tank | $31,000 | Constructed from polyurethane and kevlar, designed for maximum safety and fuel efficiency. |
| Steering Wheel | $50,000 | Made from carbon fiber with customizable buttons, switches, and paddles. |
| Hydraulics | $170,000 | Controls power steering, gearshifts, DRS, and other critical functions. |
| Brakes | $78,000 | Includes discs, pads, calipers, and master cylinders designed for high-performance braking. |
| Tyres | $3,000 per set | Custom-designed by Pirelli, optimized for grip and performance. |
| Halo | $17,000 | Provides crucial head protection for the driver. |

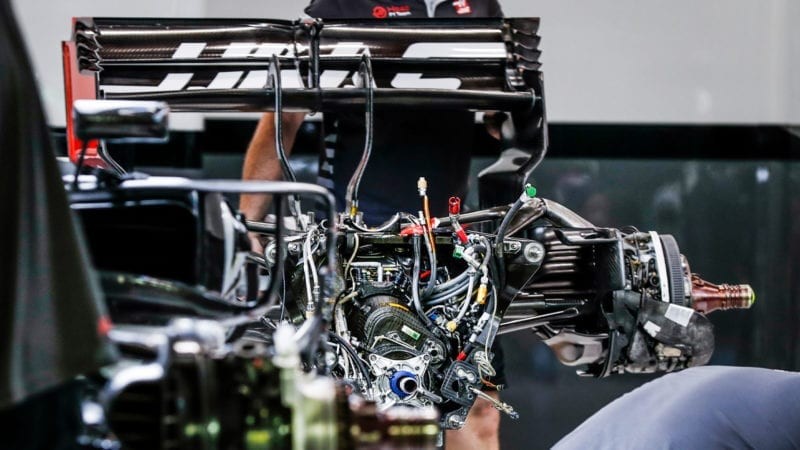
These figures demonstrate the significant investment required in each area to produce a competitive Formula 1 car. Regular maintenance and upgrades further increase the expenses.
1.2 The High Cost of Materials and Technology
The advanced materials and cutting-edge technology used in F1 cars are major cost drivers. For instance, carbon fiber, known for its strength and lightweight properties, is extensively used in the chassis and aerodynamic components.
- Carbon Fiber: The cost of carbon fiber can range from $20 to $50 per pound, and an F1 car uses hundreds of pounds of it.
- Titanium: Used in various engine and suspension components, titanium can cost anywhere from $30 to $100 per pound.
- Hybrid Engine Technology: The complex hybrid engines, which combine a traditional internal combustion engine with electric motors, require substantial investment.
- Aerodynamic Development: Sophisticated wind tunnel testing and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations are necessary to refine the aerodynamic package, adding to the overall cost.
2. Factors Influencing the Cost of F1 Car Development
Development is an ongoing process in Formula 1, and the cost to continually enhance a car is considerable. Teams are always looking for ways to improve performance, and these efforts come with significant financial implications. CARS.EDU.VN is here to provide insights into these expenses.
2.1 Research and Development Expenses
Research and development are vital for maintaining competitiveness in Formula 1. Teams spend millions annually on R&D to explore new technologies and improve existing systems.
- Aerodynamic Research: Teams invest in wind tunnels and CFD simulations to optimize aerodynamics. The cost of running a wind tunnel can be as high as $150,000 per hour.
- Engine Development: Developing a competitive engine requires advanced engineering and rigorous testing. Major manufacturers like Mercedes, Ferrari, and Renault spend hundreds of millions each year on engine development.
- Software and Data Analysis: Teams use advanced software and data analytics tools to analyze performance and identify areas for improvement. These tools can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars each year.
2.2 Team Size and Infrastructure
The size and infrastructure of an F1 team also affect costs. A typical F1 team employs hundreds of engineers, technicians, and support staff.
- Personnel Costs: The salaries of engineers, technicians, and drivers account for a significant portion of the budget. Top drivers can earn tens of millions of dollars per year.
- Infrastructure Costs: Teams require state-of-the-art facilities, including factories, wind tunnels, and testing equipment. These facilities can cost millions to build and maintain.
- Logistics and Travel: Transporting equipment and personnel to races around the world is a logistical challenge. Travel and accommodation expenses can be substantial.
2.3 Impact of Regulations and Rule Changes
Regulatory changes in Formula 1 can have a major impact on costs. New rules often require teams to redesign their cars, leading to additional expenses.
- Chassis Redesign: Significant changes to the chassis regulations can force teams to invest millions in redesigning and retesting their cars.
- Engine Regulations: Changes to the engine regulations can be particularly costly, as they may require teams to develop entirely new power units.
- Standardized Components: The introduction of standardized components aims to reduce costs but can also limit innovation and competitiveness.
CARS.EDU.VN offers in-depth analysis and resources to help you understand how these factors influence the cost of Formula 1 car development. Visit our site to learn more about the intricacies of F1 technology and engineering.
3. Operational Costs of Running an F1 Car During a Season
Beyond the initial cost of the car, operating it during a Formula 1 season entails substantial ongoing expenses. This section, brought to you by CARS.EDU.VN, will detail the various operational costs involved in keeping an F1 car competitive throughout a season.
3.1 Race-Related Expenses
Each race weekend brings its own set of expenses. Transporting equipment, accommodating personnel, and managing the car during the event all add up.
- Transportation: Transporting cars, spare parts, and equipment to each race requires a significant logistical effort. Teams use air freight and sea freight, which can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars per race.
- Personnel Accommodation: Teams must accommodate their personnel in hotels and provide meals. These expenses can range from $50,000 to $100,000 per race.
- Track Fees: Teams must pay fees to participate in each race. These fees vary depending on the event and can be substantial.
3.2 Maintenance and Replacement of Parts
Formula 1 cars require frequent maintenance and replacement of parts due to the high stresses they endure.
- Engine Maintenance: Engines must be regularly serviced to ensure optimal performance. Teams often rotate engines throughout the season to comply with usage limits.
- Component Replacement: Parts such as brakes, suspension components, and aerodynamic elements wear out quickly and must be replaced frequently.
- Accident Damage: Accidents can cause significant damage to the car, requiring costly repairs or replacement of parts.
3.3 Testing and Simulation Costs
Testing and simulation are critical for optimizing car performance and developing new technologies.
- Track Testing: Teams conduct track testing to evaluate new components and fine-tune car setup. These tests can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars per day.
- Wind Tunnel Testing: Wind tunnel testing is used to evaluate aerodynamic performance. Running a wind tunnel can cost as much as $150,000 per hour.
- Simulation: Teams use advanced simulation tools to model car behavior and optimize performance. These tools require significant investment and expertise.
4. Formula 1 Budget Cap and Its Impact on Costs
In recent years, Formula 1 has introduced a budget cap to level the playing field and control costs. This section, presented by CARS.EDU.VN, will examine the budget cap and its effects on team spending.
4.1 Overview of the Budget Cap
The budget cap limits the amount of money teams can spend on car development and operations. The aim is to reduce the financial disparity between the top teams and the smaller ones.
- Current Limit: For the 2024 season, the budget cap is set at $135 million. This limit applies to most aspects of car development and operations, but there are some exceptions.
- Exclusions: Certain expenses are excluded from the budget cap, including driver salaries, marketing costs, and non-F1 activities.
- Compliance: Teams must comply with the budget cap regulations and are subject to audits and penalties for violations.
4.2 Strategies for Cost Control
Teams have adopted various strategies to control costs and comply with the budget cap.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: Teams must prioritize their spending and allocate resources efficiently. This involves making tough decisions about which areas to invest in.
- Component Standardization: Standardizing certain components can reduce development costs and simplify logistics.
- Outsourcing: Teams may outsource some activities, such as manufacturing and testing, to reduce internal costs.
4.3 Impact on Team Performance
The budget cap has had a noticeable impact on team performance, particularly for the larger teams.
- Reduced Spending: Top teams have been forced to reduce their spending, which has led to a more level playing field.
- Increased Innovation: The budget cap has encouraged teams to be more innovative and efficient in their development efforts.
- Competitive Balance: The budget cap has contributed to a more competitive balance in Formula 1, with smaller teams having a better chance of success.
CARS.EDU.VN keeps you informed about the latest developments in Formula 1, including the impact of the budget cap on team performance. Visit our site for more insights and analysis.
5. The Price of Individual Components: A Detailed Look
To truly understand “How much does a Formula 1 car cost?” it is beneficial to break down the expenses for each individual component. The intricate details of these components and their associated costs highlight the technological and financial investment required in Formula 1.
5.1 Engine and Power Unit Costs
The engine, or power unit, is one of the most expensive parts of an F1 car. The current 1.6-liter V6 turbocharged hybrid engines are highly sophisticated and costly to develop and maintain.
- Engine Cost: An F1 engine can cost between $8 million and $12 million. This includes the internal combustion engine (ICE), turbocharger (TC), Motor Generator Unit-Kinetic (MGU-K), Motor Generator Unit-Heat (MGU-H), energy store (ES), and control electronics (CE).
- Development Costs: Developing a competitive engine requires significant investment in research and development. Major manufacturers like Mercedes, Ferrari, and Renault spend hundreds of millions each year on engine development.
- Maintenance Costs: Engines must be regularly serviced to ensure optimal performance. Teams often rotate engines throughout the season to comply with usage limits.
5.2 Chassis and Aerodynamic Components
The chassis and aerodynamic components are crucial for car performance and safety. These parts are made from advanced materials and require extensive design and testing.
- Chassis Cost: The chassis, which is the primary structure of the car, can cost between $1.5 million and $2 million. It is designed to provide a safe and stable platform for the driver and other components.
- Aerodynamic Components: The aerodynamic package includes front and rear wings, floor, bargeboards, and other elements. These components can cost between $2 million and $3 million.
- Wind Tunnel Testing: Developing and testing aerodynamic components requires extensive wind tunnel testing, which can cost as much as $150,000 per hour.
5.3 Electronics and Control Systems
Formula 1 cars use advanced electronics and control systems to monitor and manage various aspects of car performance.
- Electronics Cost: The electronics package, which includes sensors, control units, and telemetry systems, can cost between $1 million and $1.5 million.
- Control Systems: The control systems manage engine performance, braking, and other critical functions. These systems require sophisticated software and hardware.
- Data Analysis: Teams use advanced data analytics tools to analyze performance and identify areas for improvement. These tools can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars each year.
6. How F1 Teams Manage Their Budgets: Strategies and Constraints
Understanding “How much does a Formula 1 car cost?” also involves looking at how Formula 1 teams manage their budgets. Given the extensive costs involved in developing, maintaining, and racing F1 cars, teams must implement effective financial strategies to stay competitive.
6.1 Balancing Performance and Cost
F1 teams must constantly balance the desire for improved performance with the need to control costs. This requires careful decision-making and efficient resource allocation.
- Prioritization: Teams must prioritize their spending and focus on areas that will provide the greatest performance gains.
- Value Engineering: Teams use value engineering to find ways to reduce costs without sacrificing performance.
- Risk Management: Teams must manage the risks associated with developing new technologies and components.
6.2 Sponsorship and Revenue Streams
Sponsorship is a major source of revenue for Formula 1 teams. Teams also earn revenue from prize money and other sources.
- Sponsorship Deals: Teams secure sponsorship deals with companies that want to promote their brands through Formula 1. These deals can be worth millions of dollars per year.
- Prize Money: Teams earn prize money based on their performance in races. The amount of prize money varies depending on the team’s position in the championship.
- Other Revenue Streams: Teams may also generate revenue from merchandise sales, licensing agreements, and other activities.
6.3 Long-Term Investment vs. Short-Term Gains
Teams must decide whether to focus on long-term investments or short-term gains. Long-term investments, such as developing new technologies, can provide a competitive advantage in the future. Short-term gains, such as upgrading existing components, can improve performance in the current season.
- Strategic Planning: Teams develop strategic plans that outline their goals and objectives for the future. These plans guide their investment decisions.
- Technology Roadmap: Teams create technology roadmaps that outline their plans for developing new technologies.
- Performance Metrics: Teams use performance metrics to track their progress and evaluate the effectiveness of their investments.
7. The Future of F1 Car Costs: Trends and Predictions
As Formula 1 continues to evolve, understanding “How much does a Formula 1 car cost?” requires consideration of future trends and predictions. Several factors, including technological advancements and regulatory changes, will likely influence the costs of F1 cars in the coming years.
7.1 Sustainable Technologies and Cost Implications
Formula 1 is increasingly focused on sustainability, which could lead to the adoption of new technologies and materials.
- Electric Power Units: The introduction of electric power units could significantly increase engine development costs.
- Sustainable Materials: The use of sustainable materials, such as biofuels and recycled carbon fiber, could reduce costs in the long term.
- Energy Recovery Systems: Advanced energy recovery systems could improve efficiency and reduce fuel consumption.
7.2 Standardized Parts and Their Effect on Budget
The increased use of standardized parts could help to reduce costs and level the playing field.
- Common Components: Standardizing certain components, such as suspension parts and wheel rims, could reduce development costs.
- Supplier Agreements: Teams could enter into supplier agreements to purchase standardized parts at lower prices.
- Simplified Logistics: Standardized parts could simplify logistics and reduce transportation costs.
7.3 Potential Cost-Saving Measures in the Future
Formula 1 could implement additional cost-saving measures to further reduce team spending.
- Reduced Testing: Limiting the amount of testing could reduce costs and encourage teams to focus on simulation and data analysis.
- Shared Resources: Teams could share resources, such as wind tunnels and testing facilities, to reduce individual costs.
- Simplified Regulations: Simplifying regulations could reduce the complexity of car design and development.
CARS.EDU.VN provides the latest updates and insights on how these trends and predictions will affect the costs of Formula 1 cars. Stay informed by visiting our site regularly.
8. The Role of CARS.EDU.VN in Keeping You Informed
At CARS.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of staying informed about the complex world of automotive engineering, including Formula 1. Our platform is dedicated to providing comprehensive, accessible, and reliable information to enthusiasts, professionals, and anyone curious about the intricacies of car technology.
8.1 Comprehensive Guides on Automotive Technology
We offer a wide array of detailed guides that cover various aspects of automotive technology. From the inner workings of hybrid engines to the latest advancements in aerodynamic design, our guides provide in-depth knowledge tailored to different levels of expertise. Whether you’re a seasoned engineer or just starting to explore the automotive world, you’ll find valuable information on our site.
8.2 Expert Analysis of F1 Engineering and Costs
Our team of automotive experts provides insightful analysis of Formula 1 engineering and its associated costs. We delve into the factors that influence the performance and expenses of F1 cars, offering a clear understanding of the financial and technological demands of the sport. Our analysis helps you appreciate the complexities behind each race and the innovations driving the future of automotive technology.
8.3 Resources for Car Maintenance and Repair
Beyond Formula 1, CARS.EDU.VN offers resources for car maintenance and repair, helping you keep your vehicle in top condition. Our guides cover essential maintenance tasks, troubleshooting common issues, and tips for extending the lifespan of your car. We aim to empower car owners with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions about their vehicle’s care.
Navigating the complexities of car maintenance can be challenging. CARS.EDU.VN provides detailed guides and resources to help you keep your vehicle running smoothly.
9. Real-World Examples of F1 Car Costs
To give a clearer picture of “How much does a Formula 1 car cost?” here are some real-world examples that illustrate the expenses associated with specific components and incidents.
9.1 The Halo: A Life-Saving Investment
The Halo, a safety device designed to protect drivers’ heads, costs approximately $17,000. While seemingly a small fraction of the overall car cost, its impact on safety is invaluable. The Halo has been credited with saving lives in several high-profile incidents, underscoring the importance of investing in safety measures.
9.2 The Floor and Bargeboards: Aerodynamic Complexity
The floor and bargeboards of an F1 car are critical for generating downforce. These components can cost around $141,000 due to their complex designs and the need for precise manufacturing. Aerodynamic development is a continuous process, with teams constantly refining these parts to gain a competitive edge.
9.3 The Engine: Heart of the Machine
The engine, or power unit, is the most expensive component of an F1 car, costing between $8 million and $12 million. This reflects the advanced technology and intricate engineering required to produce a high-performance hybrid engine.
10. Optimizing Your Car Ownership Experience with CARS.EDU.VN
As a car owner, you can benefit from the wealth of information and resources available at CARS.EDU.VN. Our platform is designed to help you navigate the challenges of car maintenance, repair, and ownership, ensuring you get the most out of your vehicle.
10.1 Finding Reliable Repair Services
One of the biggest challenges for car owners is finding reliable repair services. CARS.EDU.VN provides a directory of trusted mechanics and service centers, helping you connect with professionals who can provide quality service at fair prices. We also offer tips for evaluating repair shops and avoiding common scams.
10.2 Understanding Maintenance Schedules
Following a regular maintenance schedule is essential for keeping your car in good condition. CARS.EDU.VN provides detailed maintenance schedules for different makes and models, helping you stay on top of essential tasks like oil changes, tire rotations, and brake inspections. Our guides explain the importance of each maintenance item and how to perform them yourself.
10.3 Learning to Troubleshoot Common Issues
Being able to troubleshoot common car issues can save you time and money. CARS.EDU.VN offers guides on diagnosing and fixing simple problems, such as replacing a flat tire, jump-starting a dead battery, or checking fluid levels. Our step-by-step instructions and visual aids make it easy to tackle these tasks.
10.4 Staying Updated on Automotive Technology
The automotive industry is constantly evolving, with new technologies and innovations emerging all the time. CARS.EDU.VN keeps you updated on the latest trends, from electric vehicles and autonomous driving to advanced safety systems and connectivity features. Our articles and news coverage help you stay informed and make smart decisions about your car.
Discover the latest advancements in automotive technology and how they can impact your driving experience with resources from CARS.EDU.VN.
Is your car giving you trouble? Are you unsure about the next steps for maintenance or repairs? Visit CARS.EDU.VN today for expert advice, reliable resources, and comprehensive guides to help you navigate any car-related challenge. Our team is dedicated to providing the information and support you need to keep your vehicle running smoothly. Contact us at 456 Auto Drive, Anytown, CA 90210, United States, or reach out via Whatsapp at +1 555-123-4567. Let CARS.EDU.VN be your trusted partner in car ownership.
FAQ: Formula 1 Car Costs
-
How much does a Formula 1 car cost to build from scratch?
- Building an F1 car from scratch can cost between $15 million and $20 million, including research, development, and manufacturing.
-
What is the most expensive part of a Formula 1 car?
- The engine, or power unit, is the most expensive part, costing between $8 million and $12 million.
-
How much does it cost to run an F1 car for a season?
- Running an F1 car for a season can cost between $50 million and $100 million, including race-related expenses, maintenance, and testing.
-
What is the budget cap in Formula 1?
- The budget cap for the 2024 season is $135 million, aimed at leveling the playing field and controlling costs.
-
How much does a Formula 1 steering wheel cost?
- An F1 steering wheel costs approximately $50,000, due to its complex construction and customizable features.
-
How much does a set of Formula 1 tires cost?
- A set of F1 tires costs around $3,000, designed for optimum performance over a limited number of laps.
-
What is the cost of the Halo safety device on an F1 car?
- The Halo costs about $17,000 and is a crucial safety feature protecting the driver’s head.
-
How much does it cost to replace a front wing on a Formula 1 car?
- Replacing a front wing can cost upwards of $141,500, depending on its complexity and design.
-
What materials contribute to the high cost of an F1 car?
- The use of carbon fiber, titanium, and other high-strength, lightweight materials significantly increases the cost.
-
How can CARS.EDU.VN help me learn more about F1 car costs and technology?
- cars.edu.vn offers comprehensive guides, expert analysis, and resources for car maintenance and repair, keeping you informed about the complexities of F1 technology and costs.
