Electric car costs are a crucial consideration for prospective buyers. CARS.EDU.VN dives deep into electric vehicle pricing, exploring factors affecting the sticker price and ways to save. Discover electric car costs, government incentives, and ownership expenses. Let’s explore EV affordability and electric vehicle price ranges.
1. Understanding the Initial Cost of Electric Cars
The upfront cost is often the first thing people consider when thinking about switching to an electric car. Electric vehicle prices can vary significantly depending on the model, brand, and features. Here’s a breakdown to help you navigate the electric car market:
1.1. Average Electric Car Price in 2024
As of 2024, the average price of a new electric car in the United States hovers around $50,000. However, this number can be misleading because it doesn’t account for the wide range of EVs available. You can find more affordable models starting in the $30,000 range, while luxury EVs can easily exceed $80,000 or even $100,000.
Consider the Chevrolet Bolt EV, which typically starts around $26,000 before incentives. On the other end of the spectrum, a Tesla Model X can cost upwards of $90,000 depending on the configuration.
1.2. Factors Influencing Electric Car Costs
Several factors contribute to the pricing of electric vehicles:
-
Battery Size and Range: Larger batteries provide longer driving ranges, but they also increase the vehicle’s cost. The battery is one of the most expensive components in an EV, so its size directly impacts the overall price.
-
Brand and Model: Luxury brands like Tesla, BMW, and Mercedes-Benz tend to have higher prices compared to mainstream brands like Nissan, Chevrolet, and Hyundai.
-
Features and Trim Levels: Just like traditional cars, EVs come in various trim levels with different features. Higher trim levels with advanced technology, premium interiors, and enhanced performance will cost more.
-
Manufacturing Costs: The cost of raw materials, labor, and manufacturing processes also influences the final price. As technology advances and production scales up, manufacturing costs are expected to decrease, potentially leading to lower prices for EVs.
1.3. Comparing Electric Car Costs to Gas-Powered Cars
When evaluating the cost of an electric car, it’s essential to compare it to comparable gas-powered vehicles. While the initial price of an EV might be higher, the total cost of ownership can be lower over the vehicle’s lifespan.
Consider these factors:
-
Fuel Costs: Electric cars are significantly cheaper to fuel than gasoline cars. Electricity prices are generally lower than gasoline prices, and EVs are more energy-efficient.
-
Maintenance Costs: EVs typically require less maintenance than gasoline cars. They have fewer moving parts, no oil changes, and regenerative braking systems that extend the life of brake pads.
-
Incentives and Tax Credits: Many governments offer incentives and tax credits to encourage the adoption of EVs. These incentives can significantly reduce the upfront cost of an electric car.
-
Resale Value: The resale value of EVs is improving as the technology matures and demand increases. However, it’s still essential to consider depreciation when comparing the long-term costs of EVs and gasoline cars.
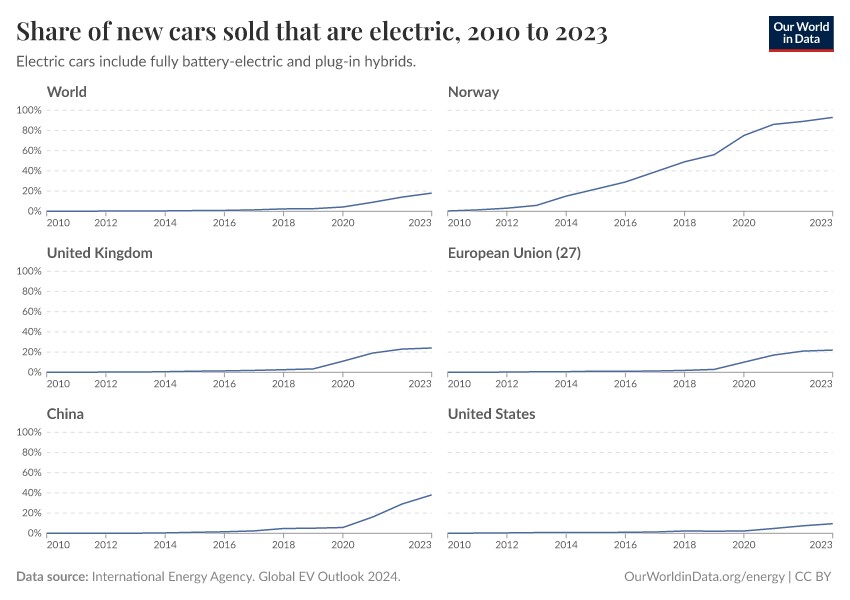
Alt: Global Electric Car Sales Share – Electric vehicle adoption, led by Norway and China, is rapidly increasing worldwide, showcased by the rising percentage of electric car sales.
2. Government Incentives and Tax Credits for Electric Cars
Government incentives and tax credits play a vital role in making electric cars more affordable. These programs aim to encourage consumers to switch to EVs by reducing the initial purchase price.
2.1. Federal Tax Credit in the United States
The federal government offers a tax credit of up to $7,500 for eligible electric vehicles. However, this tax credit is subject to certain requirements and limitations. The amount of the credit depends on the vehicle’s battery capacity and is phased out as manufacturers sell more than 200,000 eligible vehicles.
To qualify for the federal tax credit, the EV must meet specific criteria, including being manufactured by a qualified manufacturer, having a battery capacity of at least 7 kilowatt-hours (kWh), and meeting certain weight and size requirements.
2.2. State and Local Incentives
In addition to the federal tax credit, many states and local governments offer their own incentives for electric vehicles. These incentives can include:
- Rebates: Direct rebates on the purchase or lease of an EV.
- Tax Credits: State tax credits that can be claimed when filing state income taxes.
- Exemptions: Exemptions from sales tax or vehicle registration fees.
- HOV Lane Access: Access to high-occupancy vehicle (HOV) lanes, even when driving solo.
- Charging Infrastructure Incentives: Incentives for installing home charging stations.
These state and local incentives can vary significantly, so it’s essential to research the programs available in your area. The Database of State Incentives for Renewables & Efficiency (DSIRE) is a valuable resource for finding information on incentives and policies for renewable energy and energy efficiency.
2.3. How to Claim Electric Car Incentives
Claiming electric car incentives typically involves a few steps:
-
Determine Eligibility: Check the eligibility requirements for the federal, state, and local incentives you want to claim.
-
Purchase or Lease an Eligible Vehicle: Make sure the EV you purchase or lease qualifies for the incentives.
-
Complete the Required Paperwork: Fill out the necessary forms and gather the required documentation, such as the vehicle’s purchase agreement and proof of residency.
-
Submit Your Application: Submit your application to the appropriate government agency or organization.
-
Claim the Tax Credit: For the federal tax credit, you’ll need to claim it when filing your federal income taxes.
It’s always a good idea to consult with a tax professional or financial advisor to ensure you’re taking full advantage of the available incentives and understanding the tax implications.
3. Factors Affecting the Price of Used Electric Cars
Buying a used electric car can be an excellent way to save money while still enjoying the benefits of EV ownership. However, the price of used EVs can be influenced by several factors:
3.1. Battery Health and Degradation
The battery is the most critical and expensive component of an electric car, so its health and condition significantly impact the vehicle’s value. Over time, EV batteries degrade, losing some of their original capacity and range.
Battery degradation can be influenced by factors such as age, mileage, charging habits, and climate. Before buying a used EV, it’s essential to have the battery tested to determine its remaining capacity and expected range.
3.2. Mileage and Age
Like traditional cars, the mileage and age of a used EV affect its price. Higher mileage and older vehicles typically have lower values due to increased wear and tear.
However, EVs tend to have fewer mechanical issues than gasoline cars, so mileage might not be as significant of a factor. Still, it’s essential to consider the vehicle’s overall condition and maintenance history.
3.3. Model and Features
The model and features of a used EV also play a role in its price. More popular and desirable models tend to hold their value better than less popular ones.
Features such as advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), premium interiors, and fast-charging capabilities can also increase the value of a used EV.
3.4. Market Demand
The demand for used EVs can fluctuate depending on factors such as gasoline prices, government incentives, and consumer awareness. When demand is high, prices tend to be higher, and vice versa.
It’s essential to research the market and compare prices from different sources to get a fair deal on a used EV.
3.5. Vehicle History
A clean vehicle history is crucial when buying any used car, including EVs. Check the vehicle’s history report for accidents, damage, and title issues.
A well-maintained EV with a clean history will generally command a higher price than one with a questionable past.
Alt: Electric Car Sales Breakdown – Battery-electric vehicles are gaining dominance over plug-in hybrids in the electric car market.
4. Long-Term Costs of Electric Car Ownership
While the initial cost of an electric car might be higher than a gasoline car, the long-term costs of ownership can be lower. Several factors contribute to the cost savings associated with EVs:
4.1. Fuel and Energy Costs
Electric cars are significantly cheaper to fuel than gasoline cars. Electricity prices are generally lower than gasoline prices, and EVs are more energy-efficient.
The cost of charging an EV depends on factors such as electricity rates, battery size, and driving habits. However, even with higher electricity rates, EVs typically cost less per mile to fuel than gasoline cars.
4.2. Maintenance and Repair Costs
EVs require less maintenance than gasoline cars. They have fewer moving parts, no oil changes, and regenerative braking systems that extend the life of brake pads.
The reduced maintenance requirements can lead to significant cost savings over the vehicle’s lifespan. However, EV-specific repairs, such as battery replacements, can be expensive.
4.3. Insurance Costs
Insurance costs for EVs can vary depending on factors such as the vehicle’s value, the driver’s history, and the insurance company. Some insurance companies offer discounts for EVs due to their lower risk of accidents.
It’s essential to shop around and compare quotes from different insurance companies to get the best rate for your EV.
4.4. Depreciation
Depreciation is the loss of value over time. EVs tend to depreciate faster than gasoline cars, especially in the early years of ownership.
However, the resale value of EVs is improving as the technology matures and demand increases. Factors such as battery health, mileage, and condition can also impact an EV’s depreciation rate.
4.5. Charging Infrastructure Costs
If you plan to charge your EV at home, you might need to invest in a Level 2 charging station. The cost of a Level 2 charger can range from $500 to $1,000, plus installation costs.
However, many states and local governments offer incentives for installing home charging stations. Public charging is also an option, but it can be more expensive than home charging.
5. Affordable Electric Car Models
While some electric cars can be quite expensive, several affordable models are available that offer excellent value for money. These are a few examples:
5.1. Chevrolet Bolt EV
The Chevrolet Bolt EV is one of the most affordable electric cars on the market. It offers a range of over 250 miles and comes standard with features such as a touchscreen infotainment system and advanced safety technologies.
5.2. Nissan LEAF
The Nissan LEAF is another affordable EV that has been on the market for over a decade. It offers a range of over 200 miles and comes standard with features such as a rearview camera and automatic emergency braking.
5.3. Hyundai Kona Electric
The Hyundai Kona Electric is a subcompact SUV that offers a range of over 250 miles. It comes standard with features such as a touchscreen infotainment system and advanced safety technologies.
5.4. Kia Niro EV
The Kia Niro EV is another subcompact SUV that offers a range of over 250 miles. It comes standard with features such as a touchscreen infotainment system and advanced safety technologies.
5.5. Fiat 500e
The Fiat 500e is a small, stylish EV that’s perfect for city driving. It offers a range of over 100 miles and comes standard with features such as a touchscreen infotainment system and automatic climate control.
When considering affordable EV models, it’s essential to compare their features, range, and overall value to determine which one best fits your needs and budget.
6. Luxury Electric Car Options and Their Price Points
If you’re looking for a high-end electric car, several luxury options are available with premium features, advanced technology, and impressive performance. Here are a few examples:
6.1. Tesla Model S
The Tesla Model S is a flagship sedan that offers a long range, blistering acceleration, and advanced technology features such as Autopilot. Prices for the Model S start at around $90,000.
6.2. Tesla Model X
The Tesla Model X is an SUV that offers a long range, impressive performance, and unique features such as falcon-wing doors. Prices for the Model X start at around $100,000.
6.3. Porsche Taycan
The Porsche Taycan is a high-performance electric sedan that offers sporty handling, luxurious interiors, and fast-charging capabilities. Prices for the Taycan start at around $80,000.
6.4. Audi e-tron
The Audi e-tron is an SUV that offers a comfortable ride, luxurious interiors, and advanced technology features. Prices for the e-tron start at around $70,000.
6.5. BMW iX
The BMW iX is an SUV that offers a spacious interior, advanced technology features, and a range of over 300 miles. Prices for the iX start at around $80,000.
Luxury EVs typically come with higher price tags, but they also offer a premium driving experience, advanced features, and cutting-edge technology.
Alt: Battery Electric Vehicle Market Share – The increasing dominance of battery-electric vehicles signifies a shift towards zero-emission transportation solutions.
7. Future Trends in Electric Car Pricing
The electric car market is constantly evolving, and several trends are expected to impact EV pricing in the future:
7.1. Battery Technology Advancements
Advancements in battery technology are expected to lead to lower battery costs, higher energy density, and faster charging times. These improvements will likely result in lower prices for EVs and increased driving ranges.
Solid-state batteries, for example, are a promising technology that could significantly improve EV performance and reduce costs.
7.2. Increased Production Volume
As more manufacturers enter the EV market and production volumes increase, economies of scale will likely drive down manufacturing costs. This could lead to lower prices for EVs across the board.
7.3. Government Regulations and Incentives
Government regulations and incentives will continue to play a significant role in shaping the EV market. Stricter emission standards and continued incentives for EV adoption could further accelerate the transition to electric vehicles and drive down prices.
7.4. Competition Among Manufacturers
Increased competition among EV manufacturers will likely lead to more competitive pricing and a wider range of models and features. This will give consumers more choices and potentially lower prices.
7.5. Standardization of Charging Infrastructure
The standardization of charging infrastructure will make it easier and more convenient to charge EVs, which could increase demand and drive down prices. Widespread availability of fast-charging stations will also help alleviate range anxiety and encourage EV adoption.
8. Factors to Consider When Budgeting for an Electric Car
When budgeting for an electric car, it’s essential to consider all the costs associated with ownership, not just the initial purchase price. Here are some factors to keep in mind:
8.1. Purchase Price or Lease Payments
Determine your budget for the purchase price or lease payments. Factor in any down payments, trade-in value, and financing costs.
8.2. Incentives and Tax Credits
Research the available incentives and tax credits in your area and factor them into your budget. Remember that some incentives might be phased out or have eligibility requirements.
8.3. Charging Costs
Estimate your charging costs based on your driving habits and electricity rates. Consider whether you’ll be charging at home, at public charging stations, or a combination of both.
8.4. Maintenance and Repair Costs
Factor in the potential maintenance and repair costs. While EVs typically require less maintenance than gasoline cars, EV-specific repairs, such as battery replacements, can be expensive.
8.5. Insurance Costs
Get quotes from different insurance companies to estimate your insurance costs. Remember that insurance rates can vary depending on the vehicle’s value, your driving history, and other factors.
8.6. Home Charging Station Costs
If you plan to charge your EV at home, factor in the cost of a Level 2 charging station and installation. Research available incentives for home charging stations.
8.7. Registration Fees and Taxes
Consider any registration fees and taxes associated with owning an EV. Some states offer exemptions or discounts for EVs.
By carefully considering all these factors, you can create a realistic budget for your electric car and avoid any surprises down the road.
9. Tips for Saving Money on an Electric Car Purchase
If you’re looking to save money on an electric car purchase, here are some tips to consider:
9.1. Shop Around and Compare Prices
Don’t settle for the first price you see. Shop around and compare prices from different dealerships and online sources.
9.2. Consider a Used EV
Buying a used EV can be a great way to save money. Just be sure to have the battery tested and check the vehicle’s history.
9.3. Take Advantage of Incentives and Tax Credits
Research the available incentives and tax credits in your area and take full advantage of them.
9.4. Negotiate the Price
Don’t be afraid to negotiate the price with the dealership. You might be able to get a better deal than you think.
9.5. Consider Leasing
Leasing can be a good option if you’re not sure you want to commit to owning an EV long-term. Lease payments are typically lower than loan payments.
9.6. Choose a More Affordable Model
Consider a more affordable EV model if you’re on a tight budget. Several excellent options offer excellent value for money.
9.7. Be Flexible with Options and Features
Be flexible with the options and features you want. You might be able to save money by choosing a lower trim level or skipping some of the extras.
By following these tips, you can increase your chances of getting a great deal on an electric car and saving money in the process.
10. Debunking Common Myths About Electric Car Costs
Several myths and misconceptions surround electric car costs. Let’s debunk some of the most common ones:
10.1. Myth: Electric Cars Are Too Expensive
While some electric cars can be expensive, several affordable models are available that offer excellent value for money. Additionally, the long-term costs of ownership can be lower than gasoline cars due to lower fuel and maintenance costs.
10.2. Myth: Battery Replacements Are Too Expensive
While battery replacements can be expensive, they’re not as common as some people think. EV batteries are designed to last for many years, and most manufacturers offer warranties that cover battery replacements.
10.3. Myth: Electric Cars Are Only for the Wealthy
Electric cars are becoming more accessible to a wider range of consumers. Affordable models are available, and government incentives can help lower the upfront cost.
10.4. Myth: Charging Is Too Expensive
Charging an electric car is typically cheaper than fueling a gasoline car. Electricity prices are generally lower than gasoline prices, and EVs are more energy-efficient.
10.5. Myth: Electric Cars Depreciate Too Quickly
While EVs used to depreciate faster than gasoline cars, the resale value of EVs is improving as the technology matures and demand increases.
By understanding the facts about electric car costs, you can make an informed decision about whether an EV is right for you.
Alt: Global Electric Car Sales Volume – The global electric car market is experiencing rapid growth, with sales figures indicating an increasing preference for sustainable transportation.
Electric cars offer numerous benefits, including reduced emissions, lower fuel costs, and a smoother driving experience. While the initial cost can be a barrier for some, government incentives and long-term savings can make EVs a cost-effective option.
Interested in learning more about electric cars and finding the perfect model for your needs? Visit CARS.EDU.VN today for in-depth reviews, comparisons, and expert advice. We can help you navigate the world of EVs and make an informed decision.
Are you struggling to find reliable information about electric car costs? Do you need help comparing different models and understanding the incentives available in your area? CARS.EDU.VN is here to help. Our team of experts provides comprehensive information and personalized guidance to make your EV buying journey easier. Visit CARS.EDU.VN today to explore our resources and connect with our team.
Contact us:
Address: 456 Auto Drive, Anytown, CA 90210, United States
Whatsapp: +1 555-123-4567
Website: CARS.EDU.VN
FAQ: Electric Car Costs
Q1: How much does an electric car typically cost?
The average new electric car costs around $50,000 in 2024. However, prices can range from $30,000 for more affordable models to over $80,000 for luxury EVs.
Q2: Are there any government incentives for buying an electric car?
Yes, the federal government offers a tax credit of up to $7,500 for eligible EVs. Many states and local governments also offer incentives, such as rebates and tax credits.
Q3: Is it cheaper to own an electric car in the long run?
In many cases, yes. While the initial cost might be higher, EVs typically have lower fuel and maintenance costs than gasoline cars.
Q4: How much does it cost to charge an electric car?
The cost of charging an EV depends on factors such as electricity rates, battery size, and driving habits. However, it’s generally cheaper than fueling a gasoline car.
Q5: How long do electric car batteries last?
EV batteries are designed to last for many years. Most manufacturers offer warranties that cover battery replacements for at least 8 years or 100,000 miles.
Q6: What are the most affordable electric car models?
Some of the most affordable EV models include the Chevrolet Bolt EV, Nissan LEAF, Hyundai Kona Electric, and Kia Niro EV.
Q7: Do used electric cars depreciate quickly?
While EVs used to depreciate faster than gasoline cars, the resale value of EVs is improving as the technology matures and demand increases.
Q8: How can I save money on an electric car purchase?
Shop around, consider a used EV, take advantage of incentives, negotiate the price, and be flexible with options and features.
Q9: Are electric cars only for the wealthy?
No, electric cars are becoming more accessible to a wider range of consumers. Affordable models are available, and government incentives can help lower the upfront cost.
Q10: Where can I find more information about electric car costs?
Visit cars.edu.vn for in-depth reviews, comparisons, and expert advice on electric cars. We can help you navigate the world of EVs and make an informed decision.