Are you looking for clear insights on How To Calculate Car Loan Interest and understand the factors influencing your monthly payments? At CARS.EDU.VN, we break down the complexities of auto financing, offering straightforward explanations and practical tools to help you make informed decisions. Learn about interest rate calculation, loan amortization, and strategies to minimize your borrowing costs with our expert guidance on automotive loans.
1. Understanding the Basics of Car Loan Interest
Before diving into the calculations, let’s define car loan interest. It’s essentially the cost you pay for borrowing money to purchase a vehicle. This charge is expressed as an annual percentage rate (APR), which includes the interest rate and any additional fees associated with the loan. Understanding these components is the first step in grasping how to calculate car loan interest effectively.
1.1. What is APR?
The Annual Percentage Rate, or APR, is the total cost of the loan to the borrower, expressed as a percentage. APR includes the interest rate, plus other charges or fees, such as:
- Loan origination fees
- Underwriting fees
- Document preparation fees
Example:
Let’s say you’re comparing two car loans. Loan A has an interest rate of 5% and no fees, while Loan B has an interest rate of 4.5% but includes a $500 origination fee. Although Loan B has a lower interest rate, the APR might be higher due to the added fee. Therefore, always look at the APR to understand the true cost of borrowing.
1.2. Key Factors Affecting Car Loan Interest Rates
Several factors determine the interest rate you’ll receive on your car loan. Here’s a breakdown:
- Credit Score: A higher credit score typically results in lower interest rates. Lenders view borrowers with good credit as less risky.
- Loan Term: Shorter loan terms usually come with lower interest rates but higher monthly payments. Longer loan terms have lower monthly payments but accrue more interest over time.
- Vehicle Type: New cars often qualify for lower interest rates than used cars. This is because new vehicles are considered less risky assets.
- Down Payment: Making a larger down payment can reduce the loan amount, potentially leading to a lower interest rate.
- Lender: Different lenders (banks, credit unions, and online lenders) offer varying interest rates. Shopping around is crucial to finding the best deal.
Table: Impact of Credit Score on Interest Rates (Example)
| Credit Score Range | Average APR (New Car) | Average APR (Used Car) |
|---|---|---|
| 781-850 (Excellent) | 3.50% | 4.50% |
| 661-780 (Good) | 5.00% | 6.00% |
| 601-660 (Fair) | 7.50% | 8.50% |
| 501-600 (Poor) | 10.00% | 11.00% |
| 300-500 (Very Poor) | 12.00% | 13.00% |
Source: Experian, 2023
1.3. Simple vs. Compound Interest
Understanding the type of interest you’re being charged is vital. Car loans typically use simple interest, which is calculated only on the principal balance. Compound interest, on the other hand, calculates interest on both the principal and accumulated interest, which could lead to higher costs over time. Make sure your loan uses simple interest to keep your costs predictable.
2. Methods to Calculate Car Loan Interest
Now, let’s explore different methods to calculate car loan interest, ranging from manual calculations to using online tools.
2.1. Manual Calculation: The Simple Interest Formula
The simplest way to understand how to calculate car loan interest is using the simple interest formula:
Interest = Principal x Rate x Time
- Principal: The initial loan amount.
- Rate: The annual interest rate (as a decimal).
- Time: The loan term (in years).
Example:
Suppose you borrow $20,000 at an annual interest rate of 6% for a term of 5 years.
- Principal = $20,000
- Rate = 0.06
- Time = 5 years
Interest = $20,000 x 0.06 x 5 = $6,000
Therefore, the total interest paid over the loan term would be $6,000.
2.2. Amortization Schedule and Interest Calculation
An amortization schedule breaks down each payment into the portion that goes toward the principal and the portion that covers the interest. This schedule helps you see how to calculate car loan interest on a monthly basis.
Steps to Create an Amortization Schedule:
-
Calculate the Monthly Interest Rate: Divide the annual interest rate by 12.
-
Calculate the Monthly Payment: Use the loan amortization formula:
M = P [ i(1 + i)^n ] / [ (1 + i)^n – 1]
Where:
- M = Monthly payment
- P = Principal loan amount
- i = Monthly interest rate
- n = Number of payments (loan term in months)
-
Determine Interest Payment: For the first month, multiply the principal loan amount by the monthly interest rate.
-
Determine Principal Payment: Subtract the interest payment from the total monthly payment.
-
Calculate Remaining Balance: Subtract the principal payment from the previous balance.
-
Repeat: Continue these steps for each month of the loan term.
Table: Sample Amortization Schedule (First 3 Months)
| Month | Starting Balance | Monthly Payment | Interest Payment | Principal Payment | Ending Balance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | $20,000 | $386.66 | $100.00 | $286.66 | $19,713.34 |
| 2 | $19,713.34 | $386.66 | $98.57 | $288.09 | $19,425.25 |
| 3 | $19,425.25 | $386.66 | $97.13 | $289.53 | $19,135.72 |
2.3. Utilizing Online Car Loan Calculators
The easiest way to calculate car loan interest is by using online calculators. These tools require you to enter the loan amount, interest rate, and loan term, and they automatically generate an amortization schedule.
Benefits of Using Online Calculators:
- Accuracy: Reduces the risk of manual calculation errors.
- Speed: Provides immediate results.
- Detailed Breakdown: Offers a comprehensive amortization schedule.
- Accessibility: Available on various websites, including CARS.EDU.VN, providing a convenient way to estimate your monthly payments and total interest paid.
3. Step-by-Step Guide: Calculating Interest with CARS.EDU.VN Calculator
CARS.EDU.VN offers a user-friendly car loan calculator that simplifies the process of how to calculate car loan interest. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use it effectively:
- Visit CARS.EDU.VN: Navigate to the car loan calculator section.
- Enter Loan Amount: Input the total amount you plan to borrow.
- Specify Interest Rate: Enter the annual interest rate provided by your lender.
- Set Loan Term: Choose the duration of your loan (e.g., 36, 48, 60 months).
- Optional Fields: Add any down payment or trade-in value to refine your estimate.
- Calculate: Click the “Calculate” button.
The calculator will generate a detailed report, including:
- Monthly Payment: The estimated amount you’ll pay each month.
- Total Interest Paid: The total interest accrued over the loan term.
- Amortization Schedule: A breakdown of each payment, showing the principal and interest portions.
This tool helps you visualize the financial impact of your car loan, making it easier to budget and plan.
4. Understanding Loan Amortization
Loan amortization is a method of repaying a loan through regular payments over a set period. Each payment includes both a portion of the principal and the interest.
4.1. How Amortization Works
In the early months of the loan, a larger portion of your payment goes towards interest. As you continue making payments, more of each payment is applied to the principal. This is because the interest is calculated on the outstanding balance, which decreases over time.
Example:
Using the previous example of a $20,000 loan at 6% interest for 5 years, the amortization schedule will show that in the first few months, most of your payment covers interest. By the end of the loan term, nearly all of your payment goes toward the principal.
4.2. Impact of Loan Term on Amortization
The loan term significantly impacts the amortization schedule. Shorter loan terms mean higher monthly payments, but you’ll pay less interest overall. Longer loan terms result in lower monthly payments, but you’ll pay more interest over the life of the loan.
Table: Impact of Loan Term on Total Interest Paid
| Loan Amount | Interest Rate | Loan Term | Monthly Payment | Total Interest Paid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $20,000 | 6% | 36 months | $608.44 | $1,893.84 |
| $20,000 | 6% | 60 months | $386.66 | $3,199.60 |
| $20,000 | 6% | 72 months | $332.06 | $3,868.32 |
Source: CARS.EDU.VN Car Loan Calculator
This table clearly illustrates that while a longer loan term reduces your monthly payment, it substantially increases the total interest you pay.
5. Tips to Minimize Car Loan Interest
Minimizing the interest you pay on your car loan can save you a significant amount of money. Here are some strategies to consider:
5.1. Improve Your Credit Score
A higher credit score can help you secure a lower interest rate. Take steps to improve your credit score before applying for a car loan:
- Pay Bills on Time: Late payments can negatively impact your credit score.
- Reduce Credit Card Debt: High credit card balances can lower your credit score.
- Check Your Credit Report: Ensure there are no errors on your credit report that could be affecting your score. You can obtain a free credit report annually from each of the major credit bureaus at AnnualCreditReport.com.
5.2. Shop Around for the Best Rates
Don’t settle for the first loan offer you receive. Shop around and compare rates from different lenders, including banks, credit unions, and online lenders. Each lender may offer different terms and interest rates, so it’s essential to explore your options.
How to Compare Loan Offers:
- APR: Focus on the APR, as it includes the interest rate and any additional fees.
- Loan Terms: Compare the loan terms to understand how they affect your monthly payments and total interest paid.
- Fees: Look for any hidden fees, such as prepayment penalties.
5.3. Make a Larger Down Payment
Making a larger down payment reduces the amount you need to borrow, which can lead to a lower interest rate. Additionally, a larger down payment can increase your chances of loan approval.
Benefits of a Larger Down Payment:
- Lower Loan Amount: Reduces the total interest paid.
- Better Approval Odds: Demonstrates financial stability.
- Reduced Monthly Payments: Makes budgeting easier.
5.4. Consider a Shorter Loan Term
Although shorter loan terms come with higher monthly payments, they can save you a significant amount of money on interest. If your budget allows, opt for a shorter loan term to reduce your overall borrowing costs.
5.5. Refinance Your Car Loan
If you already have a car loan, consider refinancing to a lower interest rate. Refinancing involves taking out a new loan to pay off the existing one, ideally at better terms.
When to Consider Refinancing:
- Improved Credit Score: If your credit score has improved since you took out your original loan.
- Lower Interest Rates: If market interest rates have decreased.
- Change in Financial Situation: If you need to adjust your monthly payments or loan term.
6. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Calculating Car Loan Interest
Calculating car loan interest can be tricky, and it’s easy to make mistakes. Here are some common pitfalls to avoid:
6.1. Ignoring the APR
Focusing solely on the interest rate without considering the APR can be misleading. The APR includes all costs associated with the loan, providing a more accurate picture of your borrowing expenses.
6.2. Miscalculating the Loan Term
Ensure you accurately calculate the loan term in months or years. An incorrect loan term can significantly alter your estimated monthly payments and total interest paid.
6.3. Forgetting About Additional Fees
Some lenders charge additional fees, such as origination fees or prepayment penalties. Be sure to factor these fees into your calculations to get an accurate estimate of your total borrowing costs.
6.4. Not Factoring in Sales Tax and Other Charges
When determining the total loan amount, don’t forget to include sales tax, registration fees, and other charges. These costs can increase the amount you need to borrow, affecting your interest payments.
6.5. Relying on Inaccurate Calculators
Not all online calculators are created equal. Use reputable and reliable tools, such as the calculator available on CARS.EDU.VN, to ensure accurate results.
7. Real-World Examples of Interest Calculation
Let’s look at some real-world examples to illustrate how to calculate car loan interest and the impact of different loan terms and interest rates.
7.1. Scenario 1: New Car Purchase
John wants to buy a new car priced at $25,000. He has a credit score of 720 and is considering two loan options:
- Option A: 4.5% interest rate, 60-month term
- Option B: 5.0% interest rate, 48-month term
Using the CARS.EDU.VN calculator, here’s what he finds:
- Option A: Monthly payment of $466.06, total interest paid of $2,963.60
- Option B: Monthly payment of $581.42, total interest paid of $2,807.96
Although Option B has a slightly higher interest rate, the shorter loan term results in lower total interest paid.
7.2. Scenario 2: Used Car Purchase
Maria is buying a used car for $15,000. Her credit score is 650, and she’s comparing these loan options:
- Option A: 7.0% interest rate, 60-month term
- Option B: 7.5% interest rate, 48-month term
Using the CARS.EDU.VN calculator:
- Option A: Monthly payment of $297.03, total interest paid of $2,821.80
- Option B: Monthly payment of $361.48, total interest paid of $2,351.04
Again, the shorter loan term in Option B results in lower total interest paid, despite the higher interest rate.
7.3. Scenario 3: Refinancing an Existing Loan
David has an existing car loan with a balance of $10,000, an interest rate of 8.0%, and 36 months remaining. He wants to refinance to a lower interest rate. He qualifies for a new loan at 6.0% with a 36-month term.
- Original Loan: Monthly payment of $313.36, total interest remaining of $1,281.16
- Refinanced Loan: Monthly payment of $304.22, total interest paid of $951.92
By refinancing, David saves $329.24 in interest over the remaining loan term.
8. How Car Loan Interest Impacts Your Budget
Understanding how to calculate car loan interest is crucial for budgeting. The interest you pay affects your overall financial health and can impact your ability to save and invest.
8.1. Monthly Payment Considerations
Your monthly car payment, including interest, is a recurring expense that needs to fit within your budget. Overestimating or underestimating this expense can lead to financial strain.
Tips for Budgeting:
- Track Your Income and Expenses: Use budgeting apps or spreadsheets to monitor your cash flow.
- Set Realistic Goals: Ensure your car payment is affordable and doesn’t consume too much of your income.
- Plan for Unexpected Expenses: Set aside funds for car repairs, maintenance, and insurance.
8.2. Long-Term Financial Planning
The total interest you pay over the life of the loan can impact your long-term financial goals. High interest payments can reduce your ability to save for retirement, invest, or achieve other financial milestones.
Strategies for Long-Term Savings:
- Minimize Debt: Focus on paying off high-interest debt, including car loans.
- Invest Early: Start saving for retirement as early as possible to take advantage of compounding returns.
- Diversify Investments: Spread your investments across different asset classes to reduce risk.
8.3. The True Cost of Car Ownership
Car ownership involves more than just the purchase price. Consider the total cost of ownership, including:
- Car Loan Payments: Principal and interest.
- Insurance: Monthly or annual premiums.
- Maintenance: Regular servicing, oil changes, and repairs.
- Fuel: Gas expenses.
- Registration and Taxes: Annual fees.
- Depreciation: The decrease in the car’s value over time.
Calculating these costs can help you make informed decisions about car ownership and manage your budget effectively.
9. Updates on Car Loan Interest Rates and Market Trends
Staying informed about the latest car loan interest rates and market trends is essential for making smart financial decisions.
9.1. Current Interest Rate Trends
Interest rates can fluctuate based on economic conditions, Federal Reserve policies, and lender competition. Keep an eye on these trends to determine the best time to apply for a car loan or refinance an existing one.
Sources for Tracking Interest Rates:
- Financial News Websites: Reputable sources like the Wall Street Journal and Bloomberg.
- Automotive News Sites: Websites dedicated to the auto industry, such as Automotive News.
- Lender Websites: Banks, credit unions, and online lenders often publish their current interest rates.
9.2. Impact of Economic Factors
Economic factors like inflation, unemployment, and GDP growth can influence interest rates. For example, during periods of high inflation, the Federal Reserve may raise interest rates to cool down the economy, which can lead to higher car loan rates.
9.3. New Car Models and Financing Options
New car models often come with special financing options, such as low-interest loans or lease deals. Keep an eye on these promotions, but be sure to read the fine print and compare them to other loan offers.
Table: Recent Car Model Releases and Financing Options
| Car Model | Release Date | Special Financing Options | Interest Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 Honda Civic | Q1 2024 | 1.9% APR for 36 months | 1.9% |
| 2024 Toyota Camry | Q2 2024 | 2.9% APR for 48 months | 2.9% |
| 2024 Ford F-150 | Q3 2024 | 3.9% APR for 60 months | 3.9% |
| 2024 Chevrolet Equinox | Q4 2024 | 0% APR for 24 months | 0% |
Note: These are hypothetical examples and actual rates may vary.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Car Loan Interest
Here are some common questions about how to calculate car loan interest:
-
How is car loan interest calculated?
Car loan interest is typically calculated using simple interest, based on the principal loan amount, interest rate, and loan term. -
What is APR, and why is it important?
APR (Annual Percentage Rate) is the total cost of the loan, including the interest rate and any fees, expressed as a percentage. It’s important because it provides a comprehensive view of your borrowing costs. -
How does my credit score affect my car loan interest rate?
A higher credit score usually results in a lower interest rate, as lenders view borrowers with good credit as less risky. -
Is it better to choose a shorter or longer loan term?
Shorter loan terms come with higher monthly payments but lower total interest paid. Longer loan terms have lower monthly payments but higher total interest paid. -
What is an amortization schedule?
An amortization schedule is a table that breaks down each payment into the portion that goes toward the principal and the portion that covers the interest. -
How can I lower my car loan interest rate?
Improve your credit score, shop around for the best rates, make a larger down payment, consider a shorter loan term, and refinance your car loan if possible. -
What are some common mistakes to avoid when calculating car loan interest?
Ignoring the APR, miscalculating the loan term, forgetting about additional fees, not factoring in sales tax, and relying on inaccurate calculators. -
Can I refinance my car loan to get a better interest rate?
Yes, refinancing involves taking out a new loan to pay off the existing one, ideally at better terms. -
How do economic factors affect car loan interest rates?
Economic factors like inflation, unemployment, and GDP growth can influence interest rates, with higher inflation often leading to higher car loan rates. -
Where can I find a reliable car loan calculator?
You can find a reliable car loan calculator on CARS.EDU.VN, which provides accurate and detailed calculations to help you estimate your monthly payments and total interest paid.
Conclusion
Understanding how to calculate car loan interest is essential for making informed financial decisions when purchasing a vehicle. By grasping the key factors that affect interest rates, using the right tools, and avoiding common mistakes, you can minimize your borrowing costs and manage your budget effectively. At CARS.EDU.VN, we’re committed to providing you with the resources and information you need to navigate the complexities of auto financing.
For more detailed information and expert advice, visit CARS.EDU.VN today. Whether you’re looking for the best car loan rates, tips on improving your credit score, or guidance on choosing the right vehicle, our team is here to help.
Ready to take the next step? Contact us at 456 Auto Drive, Anytown, CA 90210, United States, or reach out via WhatsApp at +1 555-123-4567. Let cars.edu.vn help you drive away with confidence.
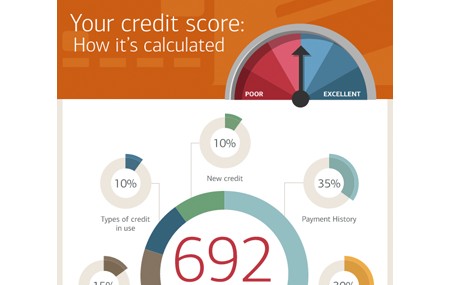 Car Loan Interest Rate Factors
Car Loan Interest Rate Factors
Disclaimer
The content provided in this article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. Consult with a qualified financial advisor before making any decisions related to car loans or financing.
