Purchasing a car is a significant investment, and for many, it involves securing an auto loan. Understanding how interest rates work and how they are calculated is crucial for making informed financial decisions. Knowing how to calculate the interest rate on your car loan empowers you to estimate your monthly payments, compare loan offers, and ultimately save money over the life of the loan. This guide will break down the process of calculating car loan interest rates and highlight the factors that influence them.
Understanding the Key Components of Car Loan Interest
Before diving into calculations, it’s essential to understand the key terms involved in car loan interest:
- Principal: This is the original amount of money you borrow from the lender to purchase the car. It’s the purchase price of the vehicle minus any down payment, trade-in value, or rebates.
- Interest Rate: Expressed as a percentage, the interest rate is the cost you pay to borrow money. It represents the lender’s profit for providing the loan and is applied to the principal balance.
- Loan Term: This is the length of time you have to repay the loan, typically expressed in months (e.g., 36 months, 60 months, 72 months).
- Annual Percentage Rate (APR): APR is the broader measure of the cost of borrowing. It includes the interest rate plus other fees associated with the loan, such as origination fees or discount points. While the interest rate is a component of APR, APR provides a more complete picture of the loan’s cost.
The Simple Interest Calculation for Car Loans
While car loans often use more complex amortization schedules, understanding simple interest provides a foundational understanding. Simple interest is calculated only on the principal balance. The formula for simple interest is:
Simple Interest = Principal x Interest Rate x Time
For example, let’s say you borrow $20,000 at a simple annual interest rate of 5% for a loan term of 5 years.
Simple Interest = $20,000 x 0.05 x 5 = $5,000
In this simplified scenario, you would pay $5,000 in interest over the 5-year loan term, in addition to repaying the $20,000 principal.
Amortization and Compound Interest in Car Loans
In reality, car loans typically use an amortization schedule with compound interest. Amortization means that your payments are structured to pay off both the principal and the interest over the loan term. With each payment, a portion goes towards interest and a portion goes towards the principal. In the early stages of the loan, a larger portion of your payment goes towards interest. As you make payments, more of each payment is applied to the principal, and less to interest.
Compound interest means that interest is calculated not only on the initial principal but also on the accumulated interest from previous periods. While the exact calculation for an amortizing loan with compound interest is more complex and often handled by financial calculators or software, understanding the concept is important.
Factors That Influence Your Car Loan Interest Rate
Several factors determine the interest rate you will be offered for a car loan:
- Credit Score: Your credit score is a primary factor. A higher credit score indicates lower risk to lenders, and they will typically offer you a lower interest rate. Conversely, a lower credit score signals higher risk, resulting in a higher interest rate.
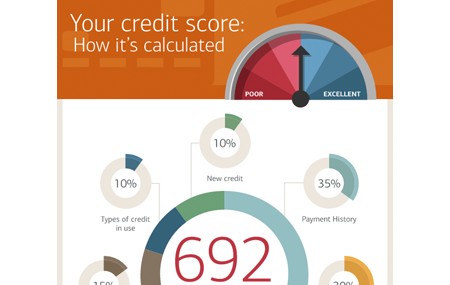 credit score infographic
credit score infographic
Alt text: Infographic illustrating how credit score affects auto loan interest rates, showing a higher credit score leads to a lower interest rate and lower monthly payments.
- Loan Term Length: Shorter loan terms (e.g., 36 months) usually come with lower interest rates compared to longer terms (e.g., 72 months). While longer terms result in lower monthly payments, you will pay significantly more interest over the life of the loan.
- Down Payment: A larger down payment reduces the loan amount, which can sometimes result in a slightly lower interest rate. It also demonstrates to the lender that you are a less risky borrower.
- Type of Vehicle (New vs. Used): Interest rates for new car loans are generally lower than those for used car loans. This is because new cars are typically considered less risky for lenders as they tend to depreciate less rapidly and may have warranties.
- Lender: Different lenders (banks, credit unions, online lenders, dealerships) may offer varying interest rates. It’s crucial to shop around and compare offers from multiple lenders to secure the best rate.
Using Online Car Loan Calculators
While understanding the formulas is helpful, online car loan calculators simplify the process of estimating your monthly payments and total interest. These calculators typically require you to input:
- Loan Amount
- Interest Rate
- Loan Term
They will then calculate your estimated monthly payment and the total interest you will pay over the loan term. Many websites, including banks and financial institutions like Bank of America, provide free car loan calculators. These tools are invaluable for quickly assessing different loan scenarios and understanding the impact of interest rates and loan terms.
Tips to Secure a Lower Car Loan Interest Rate
Getting a lower interest rate can save you thousands of dollars over the life of your car loan. Here are some actionable tips:
- Improve Your Credit Score: Before applying for a car loan, check your credit report and take steps to improve your credit score. Pay bills on time, reduce outstanding debt, and correct any errors on your report.
- Shop Around for Loans: Don’t settle for the first loan offer you receive. Get quotes from multiple lenders, including banks, credit unions, and online lenders. Comparing offers will give you leverage to negotiate a better rate.
- Make a Larger Down Payment: If possible, increase your down payment. This reduces the loan amount and may qualify you for a lower interest rate.
- Consider a Shorter Loan Term: While monthly payments will be higher with a shorter loan term, you’ll pay less interest overall and own your car outright sooner.
Conclusion
Calculating car loan interest rates involves understanding key financial terms and the factors that influence these rates. While the exact calculations for amortizing loans can be complex, online calculators provide user-friendly tools for estimations. By understanding how interest is calculated and taking steps to secure a lower rate, you can make a more informed and financially sound decision when financing your next car. Remember to prioritize improving your credit score and shopping around for the best loan terms to minimize your borrowing costs and enjoy your new vehicle without unnecessary financial burden.

