Having to figure out How To Jump A Car With Cables is something every driver might face. CARS.EDU.VN is here to provide a comprehensive guide, ensuring you can jump-start your vehicle safely and efficiently. From understanding the correct cable connections to troubleshooting common issues, we’ll help you get back on the road with confidence. Remember to check out CARS.EDU.VN for detailed service guides, comparisons, and the latest automotive technology updates to keep your car running smoothly.
1. Understanding the Basics of Jump Starting
Knowing how to jump a car with cables involves more than just connecting wires; it requires understanding the underlying principles to ensure safety and effectiveness. Let’s delve into the essentials:
1.1. What Does Jump Starting Mean?
Jump starting is a procedure used to start a vehicle that has a discharged or dead battery. This process involves using jumper cables to connect the battery of a functioning vehicle to the battery of the disabled one. The good battery provides the necessary electrical current to start the engine of the vehicle with the dead battery. It’s a temporary solution designed to get you to a place where you can either recharge or replace the faulty battery.
1.2. Why Cars Need Jump Starting
There are several reasons why a car might need a jump start:
- Old or Failing Battery: Batteries degrade over time, losing their ability to hold a charge. According to a study by AAA, the average car battery lasts between three to five years.
- Leaving Lights On: Accidentally leaving headlights or interior lights on can drain the battery overnight.
- Extreme Temperatures: Both hot and cold weather can negatively impact battery performance. Cold weather reduces the battery’s chemical reaction rate, making it harder to start the car.
- Short Trips: Consistent short trips may not give the alternator enough time to fully recharge the battery.
- Faulty Alternator: The alternator recharges the battery while the engine is running. If the alternator fails, the battery won’t recharge, leading to a dead battery over time.
1.3. Essential Equipment for Jump Starting
To jump-start a car, you’ll need the following:
- Jumper Cables: These are insulated wires with clamps (or clips) at each end. The clamps are typically color-coded, with red for positive (+) and black for negative (-). Opt for heavy-duty cables, as they provide better conductivity.
- A Second Vehicle: A vehicle with a functioning battery is needed to supply the necessary power.
- Safety Glasses and Gloves (Recommended): Although not always required, wearing safety glasses and gloves can protect your eyes and hands from potential hazards.
1.4. Safety Precautions Before You Begin
Safety should always be the top priority. Follow these precautions before attempting to jump-start a car:
- Read the Manuals: Consult the owner’s manuals for both vehicles. Some cars have specific jump-starting procedures or warnings.
- Turn Off All Electronics: Ensure both vehicles have their ignitions turned off and all electrical devices (lights, radio, etc.) are switched off.
- Inspect the Batteries: Check both batteries for any signs of damage, such as cracks, leaks, or corrosion. Do not attempt to jump-start if either battery is damaged.
- Ensure Proper Ventilation: Jump starting can produce hydrogen gas, which is explosive. Make sure the area is well-ventilated.
- No Smoking or Open Flames: Keep all sources of ignition away from the batteries.
1.5. Understanding Battery Terminals
Correctly identifying the battery terminals is crucial. The positive terminal is marked with a “+” symbol and is often red. The negative terminal is marked with a “-” symbol and is often black. The positive terminal is usually larger than the negative terminal.
2. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Jump a Car with Cables
Now that you understand the basics, let’s get into the detailed steps of how to jump a car with cables:
2.1. Positioning the Vehicles
- Position the Cars: Park the vehicle with the good battery close to the vehicle with the dead battery. The cars should be close enough that the jumper cables can easily reach between the batteries, but they should not be touching each other.
- Engage Parking Brakes: Make sure both vehicles are in Park (P) or Neutral (N) and that the parking brakes are engaged.
2.2. Connecting the Jumper Cables
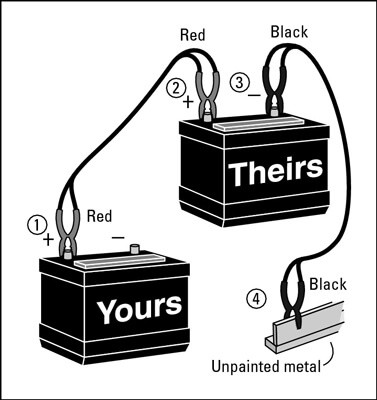
- Attach the First Red Clip: Attach one of the red clips to the positive (+) terminal of the dead battery. Ensure a firm connection.
- Attach the Second Red Clip: Attach the other red clip to the positive (+) terminal of the good battery.
- Attach the First Black Clip: Attach one of the black clips to the negative (-) terminal of the good battery.
- Attach the Second Black Clip: Attach the last black clip to an unpainted metal surface on the vehicle with the dead battery, away from the battery. A good spot is a metal strut or bolt on the engine block. This is crucial to prevent sparks from igniting any hydrogen gas that may have accumulated around the dead battery.
2.3. Starting the Vehicles
- Start the Working Vehicle: Start the vehicle with the good battery and let it run for a few minutes. This allows the alternator to send some charge to the dead battery.
- Try to Start the Disabled Vehicle: After a few minutes, try to start the vehicle with the dead battery. If it starts, let it run for at least 15-20 minutes to help recharge the battery. If it doesn’t start, proceed to the next steps.
2.4. Troubleshooting If the Car Won’t Start
If the car doesn’t start after the initial attempt, try these troubleshooting steps:
- Check the Connections: Ensure that all the clips are securely attached to the correct terminals.
- Let the Good Vehicle Run Longer: Allow the good vehicle to run for an additional 5-10 minutes to provide more charge to the dead battery.
- Try Again: Attempt to start the disabled vehicle again. If it still doesn’t start, the battery may be beyond saving, or there may be another issue.
2.5. Disconnecting the Jumper Cables
Once the disabled vehicle has started, carefully disconnect the jumper cables in the reverse order that you connected them:
- Remove the Black Clip from the Ground: Remove the black clip from the unpainted metal surface on the vehicle that was jump-started.
- Remove the Black Clip from the Good Battery: Remove the black clip from the negative (-) terminal of the good battery.
- Remove the Red Clip from the Good Battery: Remove the red clip from the positive (+) terminal of the good battery.
- Remove the Red Clip from the Jumped Battery: Remove the red clip from the positive (+) terminal of the vehicle that was jump-started.
2.6. Post-Jump Start Procedures
- Keep the Engine Running: After a successful jump start, don’t turn off the engine immediately. Drive the car for at least 15-20 minutes to allow the alternator to recharge the battery.
- Monitor the Battery: Keep an eye on the battery’s performance. If the car struggles to start the next time, the battery may need to be replaced.
- Get a Battery Test: Have the battery tested by a professional to determine its condition. Most auto parts stores offer free battery testing services.
3. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Jump Starting
Even with a clear understanding of the steps, mistakes can happen. Here are some common pitfalls to avoid:
3.1. Incorrect Cable Connections
Connecting the jumper cables in the wrong order or to the wrong terminals is a common mistake. Always double-check the polarity and the connection order to avoid damaging the electrical systems in either vehicle.
3.2. Allowing the Cables to Touch
Never allow the jumper cable clips to touch each other while connected to a battery. This can cause a short circuit, leading to sparks, heat, and potential damage to the vehicles or personal injury.
3.3. Jumping a Damaged Battery
Attempting to jump-start a battery that is visibly damaged (cracked, leaking, or corroded) is dangerous. Damaged batteries can explode or leak corrosive acid.
3.4. Not Following the Correct Order
Following the correct order for connecting and disconnecting the cables is crucial. Skipping steps or deviating from the recommended sequence can lead to safety hazards.
3.5. Ignoring Safety Precautions
Skipping safety precautions, such as wearing safety glasses and gloves or ensuring proper ventilation, increases the risk of injury. Always prioritize safety when working with car batteries.
4. Understanding the Science Behind Jump Starting
To truly master how to jump a car with cables, it’s helpful to understand the basic science behind the process:
4.1. How Batteries Work
A car battery is a rechargeable lead-acid battery that provides the electrical power needed to start the engine and run the vehicle’s electrical systems. It works through a chemical reaction between lead plates and sulfuric acid electrolyte. When the battery is discharged, this reaction slows down, reducing the battery’s ability to provide current.
4.2. The Role of the Alternator
The alternator is a generator that recharges the battery while the engine is running. It converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy, which is then used to power the vehicle’s electrical systems and recharge the battery. If the alternator fails, the battery will eventually drain, leading to a dead battery.
4.3. Why Jump Starting Works
Jump starting works by using the battery of a good vehicle to supply the necessary electrical current to start the engine of the disabled vehicle. The jumper cables provide a temporary bridge between the two batteries, allowing the good battery to provide the energy needed to crank the engine. Once the engine is running, the alternator takes over, recharging the battery.
4.4. Voltage and Amperage Explained
- Voltage is the electrical potential difference or pressure that drives the flow of electricity. Most car batteries are 12-volt batteries.
- Amperage is the measure of the amount of electrical current flowing through a circuit. The amperage required to start a car varies depending on the engine size and other factors but is typically in the range of 150-300 amps.
4.5. The Importance of Grounding
Grounding the negative cable to an unpainted metal surface away from the battery is crucial for safety. This prevents sparks from igniting any hydrogen gas that may have accumulated around the battery. Hydrogen gas is highly flammable and can cause an explosion if ignited.
5. Alternative Methods to Jump Starting
While using jumper cables is the most common method, there are alternative ways to jump-start a car:
5.1. Portable Jump Starters
Portable jump starters are self-contained devices that can provide a boost of power to start a car without needing another vehicle. These devices are compact, easy to use, and can be stored in the trunk of your car for emergencies.
Benefits of Portable Jump Starters:
- Convenience: No need for another vehicle.
- Portability: Easy to store and carry.
- Additional Features: Many include USB ports for charging devices and built-in flashlights.
How to Use a Portable Jump Starter:
- Turn Off the Ignition: Make sure the car’s ignition is turned off.
- Connect the Clamps: Attach the red clamp to the positive (+) terminal and the black clamp to the negative (-) terminal.
- Turn on the Jump Starter: Turn on the jump starter and follow the device’s instructions.
- Start the Car: Try to start the car. If it starts, let it run for a few minutes before disconnecting the jump starter.
- Disconnect the Clamps: Disconnect the clamps in the reverse order, starting with the black clamp.
5.2. Battery Chargers
Battery chargers are devices that can recharge a car battery over a longer period. While they can’t provide an immediate jump start, they can restore a dead battery to full capacity.
Benefits of Battery Chargers:
- Full Recharge: Restores the battery to its full charge capacity.
- Maintenance: Can be used to maintain battery health during periods of inactivity.
- Cost-Effective: A good investment for long-term battery care.
How to Use a Battery Charger:
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the battery from the car.
- Connect the Charger: Attach the red clamp to the positive (+) terminal and the black clamp to the negative (-) terminal.
- Set the Charger: Set the charger to the appropriate voltage and amperage settings.
- Charge the Battery: Let the battery charge for the recommended time, usually several hours.
- Disconnect the Charger: Disconnect the charger and reconnect the battery to the car.
5.3. Asking for Assistance
If you don’t have jumper cables or a portable jump starter, you can always ask for assistance from a fellow driver or a roadside assistance service. Many auto insurance companies offer roadside assistance as part of their coverage.
Benefits of Asking for Assistance:
- Professional Help: Roadside assistance services have the expertise and equipment to handle battery issues.
- Convenience: They can come to your location and provide a jump start.
- Safety: Reduces the risk of injury from attempting to jump-start the car yourself.
6. Maintaining Your Car Battery
Preventing a dead battery is always better than needing to jump-start one. Here are some tips for maintaining your car battery:
6.1. Regular Battery Checks
Have your battery checked regularly by a professional. Most auto parts stores offer free battery testing services. These tests can identify potential issues before they lead to a dead battery.
6.2. Keeping Terminals Clean
Corrosion on the battery terminals can reduce the battery’s performance. Clean the terminals regularly with a wire brush and a solution of baking soda and water.
6.3. Minimizing Short Trips
Consistent short trips may not give the alternator enough time to fully recharge the battery. Try to take longer drives periodically to ensure the battery gets a full charge.
6.4. Turning Off Lights and Electronics
Always make sure to turn off all lights and electronics when you park your car. Leaving lights on overnight can drain the battery.
6.5. Using a Battery Tender
If you don’t drive your car frequently, consider using a battery tender. A battery tender is a device that keeps the battery fully charged during periods of inactivity.
7. Advanced Troubleshooting for Battery Issues
Sometimes, a jump start may not solve the underlying issue. Here are some advanced troubleshooting steps to consider:
7.1. Testing the Alternator
If the car starts after a jump start but dies shortly afterward, the alternator may be the problem. The alternator is responsible for recharging the battery while the engine is running. If it’s not working properly, the battery won’t stay charged.
How to Test the Alternator:
- Use a Multimeter: With the engine running, use a multimeter to measure the voltage at the battery terminals. A healthy alternator should produce a voltage between 13.5 and 14.5 volts.
- Load Test: Have a professional perform a load test on the alternator. This test measures the alternator’s ability to produce current under load.
7.2. Checking for Parasitic Drain
Parasitic drain refers to a situation where electrical components in the car continue to draw power from the battery even when the engine is turned off. This can drain the battery over time, especially if the car is not driven frequently.
How to Check for Parasitic Drain:
- Use a Multimeter: Disconnect the negative battery cable and connect a multimeter between the negative terminal and the cable.
- Measure the Current: Measure the current draw with all the car’s electrical systems turned off. A normal parasitic drain should be less than 50 milliamps (0.05 amps).
- Identify the Source: If the current draw is higher than normal, you’ll need to identify the source of the drain by systematically disconnecting fuses and relays until the current drops.
7.3. Inspecting the Starter Motor
The starter motor is responsible for cranking the engine to start the car. If the starter motor is faulty, it may not be able to start the engine, even with a fully charged battery.
Symptoms of a Faulty Starter Motor:
- Clicking Sound: A clicking sound when you turn the key.
- Slow Cranking: The engine cranks slowly or struggles to turn over.
- No Response: The engine does not crank at all.
How to Test the Starter Motor:
- Voltage Test: Use a multimeter to check the voltage at the starter motor terminals while someone turns the key. You should see a voltage reading close to 12 volts.
- Bench Test: Remove the starter motor and have it bench-tested by a professional. This test verifies that the starter motor can spin freely and engage properly.
7.4. Checking the Battery Cables and Connections
Loose or corroded battery cables and connections can prevent the battery from delivering power to the car’s electrical systems. Inspect the cables and connections regularly and clean them if necessary.
How to Check Battery Cables and Connections:
- Visual Inspection: Check the cables for any signs of damage, such as cracks, fraying, or corrosion.
- Tighten Connections: Ensure that the battery terminals are securely tightened.
- Clean Terminals: Clean any corrosion from the terminals with a wire brush and a solution of baking soda and water.
8. Seasonal Battery Care Tips
Car batteries can be affected by extreme temperatures. Here are some seasonal battery care tips to keep your battery in good condition:
8.1. Summer Battery Care
High temperatures can cause the battery’s fluid to evaporate, leading to corrosion and reduced performance.
Summer Battery Care Tips:
- Park in the Shade: Park your car in the shade to reduce the battery’s exposure to heat.
- Regular Checks: Have your battery checked regularly during the summer months.
- Avoid Overcharging: Avoid overcharging the battery, as this can also lead to damage.
8.2. Winter Battery Care
Cold temperatures can reduce the battery’s chemical reaction rate, making it harder to start the car.
Winter Battery Care Tips:
- Keep the Battery Charged: Make sure the battery is fully charged before winter.
- Use a Battery Tender: Use a battery tender to keep the battery charged during periods of inactivity.
- Avoid Short Trips: Avoid consistent short trips, as they may not give the alternator enough time to fully recharge the battery.
9. When to Replace Your Car Battery
Knowing when to replace your car battery is crucial to avoid getting stranded with a dead battery. Here are some signs that it may be time for a new battery:
9.1. Age of the Battery
Most car batteries last between three to five years. If your battery is older than three years, it’s a good idea to have it tested regularly.
9.2. Slow Engine Crank
If the engine cranks slowly when you try to start the car, it could be a sign that the battery is losing its capacity.
9.3. Dimming Lights
Dimming headlights or interior lights, especially when the engine is idling, can indicate a weak battery.
9.4. Swollen or Leaking Battery Case
A swollen or leaking battery case is a sign of internal damage. Do not attempt to jump-start a battery with a swollen or leaking case.
9.5. Trouble Starting in Cold Weather
If the car struggles to start in cold weather, it could be a sign that the battery is losing its ability to provide enough current.
10. Understanding Battery Types
There are several types of car batteries available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
10.1. Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries are the most common type of car battery. They are relatively inexpensive and provide reliable performance.
Types of Lead-Acid Batteries:
- Flooded Lead-Acid Batteries: These batteries contain liquid electrolyte that can spill if the battery is tilted.
- Sealed Lead-Acid Batteries: These batteries are sealed to prevent spills and are more resistant to vibration.
10.2. AGM Batteries
AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) batteries are a type of sealed lead-acid battery that uses a glass mat to hold the electrolyte in place. They are more expensive than flooded lead-acid batteries but offer better performance and longer life.
Benefits of AGM Batteries:
- Spill-Proof: Sealed design prevents spills.
- Vibration Resistance: More resistant to vibration than flooded batteries.
- Longer Life: Longer lifespan than flooded batteries.
10.3. Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are a newer type of car battery that offers several advantages over lead-acid batteries. They are lighter, more energy-dense, and have a longer lifespan.
Benefits of Lithium-Ion Batteries:
- Lightweight: Lighter than lead-acid batteries.
- Energy-Dense: Higher energy density provides more power.
- Longer Life: Longer lifespan than lead-acid batteries.
11. Jump Starting Different Types of Vehicles
The basic procedure for how to jump a car with cables is generally the same for most vehicles, but there are some specific considerations for different types of vehicles:
11.1. Jump Starting Hybrid Vehicles
Hybrid vehicles have both an internal combustion engine and an electric motor. The jump-starting procedure is similar to that of a regular car, but it’s important to consult the owner’s manual for specific instructions.
Key Considerations for Hybrid Vehicles:
- Location of the Battery: The battery may be located in the trunk or under the rear seat.
- Specific Jump-Starting Points: Some hybrid vehicles have specific jump-starting points under the hood.
- Voltage Compatibility: Ensure that the jump-starting vehicle has the same voltage as the hybrid vehicle’s battery.
11.2. Jump Starting Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) use a high-voltage battery to power the electric motor. Jump starting an EV is generally not recommended, as it can damage the vehicle’s electrical system. If an EV needs a jump start, it’s best to contact a professional EV technician.
Key Considerations for Electric Vehicles:
- High-Voltage System: EVs use a high-voltage battery that can be dangerous to work with.
- Potential Damage: Jump starting an EV can damage the vehicle’s electrical system.
- Professional Assistance: Contact a professional EV technician for assistance.
11.3. Jump Starting Motorcycles
Jump starting a motorcycle is similar to jump starting a car, but the battery is typically smaller and more difficult to access.
Key Considerations for Motorcycles:
- Battery Location: The battery may be located under the seat or behind a side panel.
- Smaller Battery: Use a smaller set of jumper cables designed for motorcycles.
- Secure Connections: Ensure that the jumper cables are securely connected to the battery terminals.
12. Environmental Considerations
Car batteries contain hazardous materials, such as lead and sulfuric acid. It’s important to dispose of old batteries properly to protect the environment.
12.1. Proper Battery Disposal
Never throw a car battery in the trash. Take it to a recycling center or auto parts store that accepts used batteries. These facilities will recycle the battery and safely dispose of the hazardous materials.
12.2. Recycling Programs
Many auto parts stores and recycling centers offer recycling programs for car batteries. These programs ensure that the batteries are recycled properly and that the hazardous materials are kept out of the environment.
12.3. Reducing Battery Waste
By maintaining your car battery properly and replacing it only when necessary, you can reduce battery waste and help protect the environment.
13. The Future of Car Batteries
Car battery technology is constantly evolving. Here are some of the trends and developments that are shaping the future of car batteries:
13.1. Solid-State Batteries
Solid-state batteries are a new type of battery that uses a solid electrolyte instead of a liquid electrolyte. They offer several advantages over traditional lithium-ion batteries, including higher energy density, faster charging times, and improved safety.
13.2. Wireless Charging
Wireless charging technology allows electric vehicles to be charged without using a cable. This technology is becoming increasingly popular and could make it easier and more convenient to charge EVs.
13.3. Battery Swapping
Battery swapping is a technology that allows electric vehicle owners to quickly swap a depleted battery for a fully charged one. This can be faster than charging the battery and could help to reduce range anxiety.
14. Jump Starting: A Summary
Knowing how to jump a car with cables is a valuable skill for any driver. By following the steps outlined in this guide and taking the necessary safety precautions, you can safely and effectively jump-start a car with a dead battery. Remember to maintain your car battery properly and replace it when necessary to avoid getting stranded with a dead battery.
15. CARS.EDU.VN: Your Automotive Resource
At CARS.EDU.VN, we’re dedicated to providing you with the most up-to-date and comprehensive information about cars. Whether you need advice on car maintenance, repair tips, or the latest automotive news, we’re here to help.
 Jumper Cables
Jumper Cables
15.1. Explore Our Wide Range of Topics
We cover a wide range of topics, including:
- Car Maintenance: Tips and guides for keeping your car in top condition.
- Repair Guides: Step-by-step instructions for common car repairs.
- Car Reviews: In-depth reviews of the latest car models.
- Automotive News: Stay up-to-date with the latest news and trends in the automotive industry.
- Troubleshooting: Solutions for a wide range of car problems.
15.2. Expert Advice and Insights
Our team of experienced automotive experts provides you with the advice and insights you need to make informed decisions about your car. Whether you’re a seasoned car enthusiast or a first-time car owner, we have something for everyone.
15.3. Join Our Community
Join our community of car enthusiasts and share your experiences, ask questions, and get advice from other car owners.
FAQ: Jump Starting Your Car
1. Can I jump-start a car with a different voltage battery?
No, you should only jump-start a car with a battery that has the same voltage. Most cars use 12-volt batteries. Using a different voltage can damage the electrical systems in both vehicles.
2. Is it safe to jump-start a car with an electronic ignition system?
Yes, it is generally safe to jump-start a car with an electronic ignition system, but you should consult the owner’s manual for specific instructions. Follow the recommended procedure carefully to avoid damaging the system.
3. What if the car still won’t start after jump starting?
If the car still won’t start after jump-starting, there may be other issues, such as a faulty starter motor, a clogged fuel filter, or a problem with the ignition system. It’s best to have the car inspected by a professional mechanic.
4. Can I jump-start a car by myself?
Yes, you can jump-start a car by yourself using a portable jump starter. These devices are easy to use and can provide a boost of power to start the car without needing another vehicle.
5. How long should I let the car run after a jump start?
You should let the car run for at least 15-20 minutes after a jump start to allow the alternator to recharge the battery.
6. Can a jump start damage my car’s computer?
If the jump start is done incorrectly, it can potentially damage your car’s computer. Always follow the correct procedure and take the necessary safety precautions to avoid electrical damage.
7. Is it better to replace a dead battery or try to recharge it?
If the battery is old or damaged, it’s generally better to replace it. If the battery is relatively new and in good condition, you can try to recharge it using a battery charger.
8. How often should I have my car battery tested?
You should have your car battery tested at least twice a year, especially before the winter and summer months. Most auto parts stores offer free battery testing services.
9. What is the best way to store jumper cables?
The best way to store jumper cables is in a cool, dry place. Keep them in a carrying case or bag to prevent them from getting tangled or damaged.
10. What should I do if I accidentally touch the jumper cable clips together?
If you accidentally touch the jumper cable clips together while connected to a battery, it can cause a short circuit. Disconnect the cables immediately and inspect them for any damage.
Having trouble jump-starting your car or dealing with persistent battery issues? Don’t hesitate to reach out to CARS.EDU.VN for expert advice and solutions! Our comprehensive resources and experienced team are here to help you diagnose and resolve any automotive problem. Visit our website or contact us today for personalized assistance.
Address: 456 Auto Drive, Anytown, CA 90210, United States
Whatsapp: +1 555-123-4567
Website: CARS.EDU.VN
Let cars.edu.vn be your trusted partner in keeping your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently. We look forward to helping you with all your automotive needs!