Is your car refusing to start, leaving you stranded? Learning How To Jump Start A Car With Cables is a vital skill for every driver. At CARS.EDU.VN, we provide expert guidance to help you confidently handle this situation and more. Discover invaluable automotive insights, including solutions for a dead battery, troubleshooting starting problems, and understanding the importance of regular auto maintenance for peak performance and longevity.
1. Understanding the Basics of Jump Starting
Jump starting a car is a method of reviving a vehicle with a dead or weak battery by using the power from another car’s functional battery. This process involves connecting the two batteries with jumper cables, allowing the good battery to supply enough power to start the engine of the disabled vehicle. Understanding this fundamental concept is the first step in ensuring a successful and safe jump start.
1.1. Why Cars Need Jump Starts
A car needs a jump start when its battery doesn’t have enough charge to start the engine. Several factors can cause this, including:
- Leaving the headlights or interior lights on.
- A faulty charging system.
- An old or deteriorated battery.
- Infrequent use of the vehicle.
- Extreme weather conditions (both hot and cold).
1.2. Essential Tools and Safety Gear
Before you attempt to jump start a car, make sure you have the right tools and safety gear. This includes:
- Jumper Cables: Heavy-duty cables are recommended for better conductivity and safety.
- Safety Glasses: To protect your eyes from potential sparks or battery acid.
- Gloves: To avoid direct contact with battery terminals and other car parts.
- Owner’s Manual: Consult both car manuals for specific instructions or warnings.
Having these items will not only make the process smoother but also safer.
1.3. Recognizing the Signs of a Dead Battery
Knowing the signs of a dead battery can help you identify the problem quickly. Common indicators include:
- The engine cranks slowly or doesn’t crank at all.
- The dashboard lights are dim or don’t turn on.
- The car makes a clicking sound when you try to start it.
- The headlights are weak or don’t light up.
Recognizing these signs early can prevent further damage and inconvenience. If you find yourself facing any of these issues, CARS.EDU.VN offers a wealth of resources for troubleshooting and maintenance tips.
2. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Jump Start a Car with Cables Safely
Follow these detailed steps to jump start your car safely and effectively. Safety should always be your top priority.
2.1. Positioning the Cars Correctly
- Position the Vehicles: Park the car with the good battery close to the car with the dead battery. Make sure the cars are close enough that the jumper cables can reach both batteries, but they should not be touching each other.
- Engage Parking Brakes: Turn off both vehicles and engage the parking brakes to prevent any movement.
- Turn Off Accessories: Make sure all lights, radios, and other accessories are turned off in both vehicles to minimize the electrical load during the jump start.
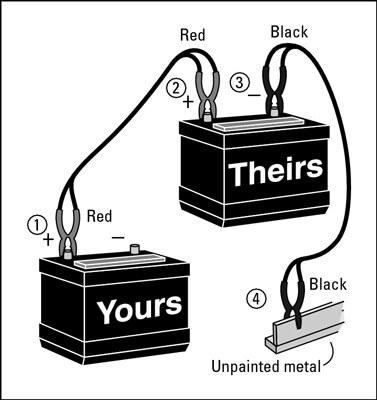
2.2. Connecting the Jumper Cables
- Attach the First Red Clip: Connect one of the red (positive) clips to the positive (+) terminal of the dead battery. The positive terminal is usually marked with a “+” sign or is red in color.
- Attach the Second Red Clip: Connect the other red clip to the positive (+) terminal of the good battery.
- Attach the First Black Clip: Connect one of the black (negative) clips to the negative (-) terminal of the good battery. The negative terminal is usually marked with a “-” sign or is black in color.
- Attach the Second Black Clip: Connect the last black clip to an unpainted metal surface on the car with the dead battery, away from the battery. This helps to ground the circuit and prevent sparks near the battery.
2.3. Starting the Engines
- Start the Good Car: Start the car with the good battery and let it run for a few minutes. This allows the good battery to send a charge to the dead battery.
- Attempt to Start the Dead Car: After a few minutes, try to start the car with the dead battery. If it doesn’t start immediately, let the good car run for a few more minutes and try again.
- If It Still Doesn’t Start: If the car still doesn’t start after several attempts, there may be a more significant issue with the battery or the car’s electrical system. It’s best to consult a professional mechanic.
2.4. Disconnecting the Jumper Cables
- Turn Off Both Cars: Once the dead car has started, turn off both cars before disconnecting the jumper cables.
- Disconnect in Reverse Order: Disconnect the jumper cables in the reverse order that you connected them. This means:
- Remove the black clip from the unpainted metal surface of the car that was jump-started.
- Remove the black clip from the negative (-) terminal of the good battery.
- Remove the red clip from the positive (+) terminal of the good battery.
- Remove the red clip from the positive (+) terminal of the car that was jump-started.
2.5. Post Jump-Start Procedures
- Keep the Jump-Started Car Running: After successfully jump starting the car, let it run for at least 15-20 minutes to allow the alternator to recharge the battery.
- Drive Around: If possible, drive the car around for an extended period. Driving at highway speeds can help recharge the battery more efficiently.
- Get the Battery Checked: Take the car to a mechanic or auto parts store to have the battery and charging system tested. This will help determine if the battery needs to be replaced or if there is an underlying issue with the charging system.
3. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Jump Starting
Even with a clear understanding of the jump-starting process, it’s easy to make mistakes. Avoiding these common pitfalls can save you time, money, and potential damage to your vehicles.
3.1. Incorrect Cable Connections
One of the most common and dangerous mistakes is connecting the jumper cables in the wrong order or to the wrong terminals. Connecting the positive and negative terminals incorrectly can cause sparks, damage to the batteries, or even an explosion.
Solution: Always double-check the polarity of the terminals before connecting the cables. Follow the correct sequence: red to positive, then black to negative, and finally black to a grounded metal surface.
3.2. Using Damaged Cables
Using jumper cables that are frayed, corroded, or otherwise damaged can be hazardous. Damaged cables may not conduct electricity properly and can cause sparks or even fires.
Solution: Inspect your jumper cables regularly for any signs of damage. Replace them immediately if you notice any issues. Invest in high-quality, heavy-duty cables for better performance and safety.
3.3. Not Ensuring Proper Ventilation
Batteries can release hydrogen gas, which is highly flammable. Jump starting a car in an enclosed space without proper ventilation can create a dangerous situation.
Solution: Always jump start a car in a well-ventilated area. If you are in a garage, open the doors and windows to allow fresh air to circulate.
3.4. Ignoring Safety Precautions
Neglecting basic safety precautions, such as wearing safety glasses and gloves, can lead to injuries from sparks, battery acid, or other hazards.
Solution: Always wear safety glasses and gloves when handling jumper cables and batteries. This will protect your eyes and skin from potential harm.
3.5. Attempting to Jump Start a Frozen Battery
Trying to jump start a frozen battery can be dangerous. Frozen batteries can crack or explode, causing serious injury.
Solution: If you suspect that your battery is frozen, do not attempt to jump start it. Instead, have the car towed to a mechanic or auto parts store for professional assistance.
3.6. Connecting to the Wrong Grounding Point
Connecting the negative cable to a painted surface or near the battery can lead to sparks and potential explosions. The grounding point should be an unpainted metal surface away from the battery.
Solution: Identify a suitable unpainted metal surface, such as a strut or frame component, to use as a grounding point. Ensure that the connection is secure and away from any flammable materials.
4. When Jump Starting Isn’t Enough: Alternative Solutions
Sometimes, jump starting a car may not be enough to solve the problem. In these cases, it’s essential to explore alternative solutions to get your car running again.
4.1. Battery Replacement
If your car battery is old, damaged, or unable to hold a charge, it may need to be replaced. A typical car battery lasts between 3 to 5 years, depending on usage and environmental conditions.
How to Determine If You Need a New Battery:
- The battery fails to hold a charge, even after jump starting.
- The battery case is cracked or swollen.
- The battery terminals are heavily corroded.
- A battery test at an auto parts store indicates that the battery is failing.
Procedure for Battery Replacement:
- Gather Your Tools: You’ll need a wrench (usually 10mm or 13mm), gloves, safety glasses, and a battery terminal cleaner.
- Disconnect the Old Battery: Disconnect the negative terminal first, followed by the positive terminal.
- Remove the Battery: Take out the old battery, being careful not to spill any acid.
- Clean the Terminals: Clean the battery terminals with a battery terminal cleaner.
- Install the New Battery: Place the new battery in the tray and secure it.
- Connect the New Battery: Connect the positive terminal first, followed by the negative terminal.
- Test the Car: Start the car to ensure that the new battery is working correctly.
4.2. Charging the Battery
If the battery is not severely damaged, you may be able to recharge it using a battery charger. This can be a more convenient and cost-effective solution than replacing the battery.
Types of Battery Chargers:
- Trickle Chargers: These chargers provide a slow, steady charge over an extended period.
- Smart Chargers: These chargers automatically adjust the charging rate based on the battery’s condition.
- Jump Starters with Charging Function: Some portable jump starters also have the ability to charge a battery.
How to Charge a Battery:
- Connect the Charger: Connect the charger to the battery terminals, making sure to match the polarity (red to positive, black to negative).
- Set the Charging Rate: Set the charging rate according to the battery charger’s instructions.
- Charge the Battery: Allow the battery to charge for the recommended amount of time.
- Disconnect the Charger: Once the battery is fully charged, disconnect the charger and test the battery.
4.3. Alternator Issues
The alternator is responsible for charging the battery while the car is running. If the alternator is faulty, it may not be charging the battery properly, leading to a dead battery.
Signs of a Faulty Alternator:
- The battery warning light is on.
- The headlights are dim.
- The car stalls frequently.
- The battery is constantly draining.
How to Test the Alternator:
- Use a Multimeter: Use a multimeter to measure the voltage output of the alternator while the car is running. A healthy alternator should produce between 13.5 and 14.5 volts.
- Professional Inspection: Have a mechanic inspect the alternator to determine if it needs to be repaired or replaced.
4.4. Starter Motor Problems
The starter motor is responsible for turning the engine over when you start the car. If the starter motor is faulty, it may not be able to start the engine, even if the battery is fully charged.
Signs of a Faulty Starter Motor:
- The car makes a clicking sound when you try to start it.
- The engine cranks slowly or not at all.
- The starter motor continues to run after the engine has started.
How to Diagnose Starter Motor Problems:
- Listen for Sounds: Listen for any unusual sounds, such as clicking or grinding, when you try to start the car.
- Professional Inspection: Have a mechanic inspect the starter motor to determine if it needs to be repaired or replaced.
4.5. Electrical System Issues
Sometimes, a dead battery can be caused by an underlying issue in the car’s electrical system, such as a short circuit or a parasitic drain.
How to Identify Electrical System Issues:
- Check for blown fuses.
- Look for signs of damaged wiring.
- Use a multimeter to test for voltage drops in the electrical system.
Professional Assistance: It’s best to consult a professional mechanic to diagnose and repair complex electrical system issues.
5. Advanced Tips for Battery Maintenance and Longevity
Maintaining your car battery is crucial for ensuring reliable performance and extending its lifespan. Here are some advanced tips to help you keep your battery in top condition.
5.1. Regular Battery Testing
Regularly testing your car battery can help you identify potential issues before they lead to a dead battery. Most auto parts stores offer free battery testing services.
Benefits of Regular Battery Testing:
- Early detection of battery problems.
- Prevention of unexpected breakdowns.
- Optimization of battery performance.
5.2. Cleaning Battery Terminals
Corrosion on battery terminals can reduce the battery’s ability to deliver power to the car’s electrical system. Cleaning the terminals regularly can help prevent this issue.
How to Clean Battery Terminals:
- Gather Your Supplies: You’ll need a wrench, gloves, safety glasses, a battery terminal cleaner, and a wire brush.
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative terminal first, followed by the positive terminal.
- Clean the Terminals: Use a battery terminal cleaner and a wire brush to remove any corrosion from the terminals.
- Reassemble the Battery: Reconnect the positive terminal first, followed by the negative terminal.
- Apply Protective Grease: Apply a thin layer of dielectric grease to the terminals to prevent future corrosion.
5.3. Minimizing Electrical Drain
Excessive electrical drain can shorten the lifespan of your car battery. Minimizing electrical drain can help extend the battery’s life.
Tips for Minimizing Electrical Drain:
- Turn off all lights and accessories when the car is not in use.
- Avoid using electronic devices for extended periods while the car is turned off.
- Disconnect the battery if you plan to store the car for an extended period.
5.4. Proper Storage
If you need to store your car for an extended period, proper storage techniques can help prevent battery drain and damage.
Tips for Proper Storage:
- Disconnect the battery to prevent parasitic drain.
- Store the battery in a cool, dry place.
- Use a battery maintainer to keep the battery charged.
5.5. Battery Insulation
In extreme weather conditions, battery insulation can help protect the battery from temperature fluctuations that can shorten its lifespan.
Benefits of Battery Insulation:
- Protection from extreme heat and cold.
- Extended battery life.
- Improved battery performance.
5.6. Upgrading to an AGM Battery
Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) batteries are a type of sealed lead-acid battery that offers several advantages over traditional flooded batteries.
Benefits of AGM Batteries:
- Longer lifespan.
- Better performance in extreme temperatures.
- Maintenance-free operation.
- Greater resistance to vibration.
6. Understanding Battery Types and Their Specific Needs
Knowing the type of battery your car uses is essential for proper maintenance and care. Different battery types have unique characteristics and require specific attention.
6.1. Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries are the most common type of car battery. They are relatively inexpensive and provide reliable power.
Types of Lead-Acid Batteries:
- Flooded Batteries: These batteries have removable caps that allow you to add water to maintain the electrolyte level.
- Sealed Lead-Acid Batteries: These batteries are sealed and do not require adding water.
Maintenance Tips for Lead-Acid Batteries:
- Regularly check the electrolyte level in flooded batteries and add distilled water as needed.
- Keep the battery terminals clean and corrosion-free.
- Avoid deep discharging the battery.
6.2. AGM Batteries
AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) batteries are a type of sealed lead-acid battery that uses a glass mat to absorb the electrolyte. They offer several advantages over traditional flooded batteries, including longer lifespan and better performance in extreme temperatures.
Maintenance Tips for AGM Batteries:
- Keep the battery terminals clean and corrosion-free.
- Avoid overcharging the battery.
- Use a battery charger designed for AGM batteries.
6.3. Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are commonly used in hybrid and electric vehicles. They offer high energy density, long lifespan, and low self-discharge rate.
Maintenance Tips for Lithium-Ion Batteries:
- Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for charging and storage.
- Avoid exposing the battery to extreme temperatures.
- Have the battery inspected by a qualified technician regularly.
6.4. Hybrid Batteries
Hybrid cars use a combination of a gasoline engine and an electric motor, requiring a specialized battery system. These batteries are typically nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) or lithium-ion.
Maintenance Tips for Hybrid Batteries:
- Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance and care.
- Avoid letting the battery discharge completely.
- Have the battery inspected by a qualified technician regularly.
6.5. Electric Vehicle (EV) Batteries
Electric vehicles rely solely on batteries for power, making the battery pack a critical component. These batteries are typically lithium-ion and require specialized care.
Maintenance Tips for EV Batteries:
- Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for charging and storage.
- Avoid frequent fast charging, as it can degrade the battery over time.
- Have the battery inspected by a qualified technician regularly.
7. Troubleshooting Common Car Starting Problems
Even with a healthy battery, your car may experience starting problems. Understanding these issues and how to troubleshoot them can save you time and money.
7.1. No Crank, No Start
If your car doesn’t crank or start, the problem could be due to several factors:
- Dead Battery: The most common cause is a dead battery. Try jump starting the car or testing the battery.
- Faulty Starter Motor: A faulty starter motor may prevent the engine from turning over.
- Ignition Switch Problems: A malfunctioning ignition switch may prevent power from reaching the starter motor.
- Security System Issues: The car’s security system may be preventing the engine from starting.
How to Troubleshoot:
- Check the battery voltage with a multimeter.
- Listen for a clicking sound when you turn the key.
- Check the fuses and relays related to the starter motor.
- Consult a mechanic for further diagnosis.
7.2. Slow Cranking
If the engine cranks slowly, the problem is likely due to:
- Weak Battery: A weak battery may not have enough power to turn the engine over quickly.
- Corroded Battery Terminals: Corrosion on the battery terminals can reduce the flow of electricity.
- Cold Weather: Cold weather can reduce the battery’s ability to deliver power.
How to Troubleshoot:
- Test the battery voltage.
- Clean the battery terminals.
- Consider using a battery warmer in cold weather.
7.3. Engine Cranks But Doesn’t Start
If the engine cranks but doesn’t start, the problem could be due to:
- Fuel System Issues: A problem with the fuel pump, fuel filter, or fuel injectors may prevent fuel from reaching the engine.
- Ignition System Problems: A problem with the spark plugs, ignition coils, or distributor may prevent the engine from firing.
- Sensor Malfunctions: A malfunctioning sensor, such as the crankshaft position sensor or the camshaft position sensor, may prevent the engine from starting.
How to Troubleshoot:
- Check the fuel level in the tank.
- Listen for the fuel pump priming when you turn the key.
- Check the spark plugs for signs of wear or damage.
- Consult a mechanic for further diagnosis.
7.4. Stalling After Starting
If the engine starts but stalls shortly after, the problem could be due to:
- Idle Air Control Valve Issues: A malfunctioning idle air control valve may prevent the engine from maintaining a stable idle.
- Vacuum Leaks: Vacuum leaks can disrupt the air-fuel mixture and cause the engine to stall.
- Mass Airflow Sensor Problems: A malfunctioning mass airflow sensor may provide incorrect data to the engine control unit.
How to Troubleshoot:
- Check the idle air control valve for signs of dirt or damage.
- Inspect the vacuum hoses for leaks.
- Consult a mechanic for further diagnosis.
7.5. Intermittent Starting Problems
Intermittent starting problems can be challenging to diagnose, as they may not occur consistently. Common causes include:
- Loose Electrical Connections: Loose electrical connections can cause intermittent starting problems.
- Faulty Sensors: Faulty sensors may provide incorrect data to the engine control unit.
- Worn Ignition Components: Worn ignition components, such as the ignition switch or the spark plugs, may cause intermittent starting problems.
How to Troubleshoot:
- Check all electrical connections for looseness or corrosion.
- Have the car scanned for diagnostic trouble codes.
- Consult a mechanic for further diagnosis.
8. The Role of CARS.EDU.VN in Automotive Education and Assistance
CARS.EDU.VN is dedicated to providing comprehensive automotive education and assistance to car owners of all levels. We offer a wide range of resources to help you maintain your vehicle, troubleshoot problems, and make informed decisions about car ownership.
8.1. Expert Articles and Guides
CARS.EDU.VN features a vast library of expert articles and guides covering a wide range of automotive topics. From basic maintenance tips to advanced troubleshooting techniques, our resources are designed to empower you with the knowledge you need to keep your car running smoothly.
8.2. Step-by-Step Tutorials
Our step-by-step tutorials provide detailed instructions and visual aids to help you perform common maintenance and repair tasks. Whether you’re changing your oil, replacing your brakes, or jump starting your car, our tutorials make it easy to get the job done right.
8.3. Diagnostic Tools and Resources
CARS.EDU.VN offers a variety of diagnostic tools and resources to help you identify and troubleshoot car problems. From diagnostic trouble code readers to online diagnostic databases, we provide the tools you need to get to the bottom of any issue.
8.4. Community Forums and Support
Our community forums provide a platform for car owners to connect, share information, and get support from experienced mechanics and fellow enthusiasts. Whether you have a question about a specific repair task or need advice on a car-related issue, our community is here to help.
8.5. Vehicle Reviews and Comparisons
CARS.EDU.VN offers comprehensive vehicle reviews and comparisons to help you make informed decisions when buying a new or used car. Our reviews cover a wide range of vehicles, from sedans and SUVs to trucks and sports cars, and provide detailed information on performance, features, and reliability.
8.6. Maintenance Schedules and Tips
Our maintenance schedules and tips provide a comprehensive guide to keeping your car in top condition. From oil changes and tire rotations to brake inspections and fluid flushes, our maintenance schedules help you stay on top of your car’s needs and prevent costly repairs.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Jump Starting Cars
Here are some frequently asked questions about jump starting cars, along with detailed answers to help you better understand the process.
-
Is it safe to jump start a car with a different voltage battery?
No, it is not safe. You should always use a battery with the same voltage to avoid damaging the electrical systems of either vehicle.
-
Can I jump start a car with an electric vehicle?
It’s generally not recommended. Electric vehicles have different electrical systems, and attempting to jump start a car could damage both vehicles.
-
What should I do if my car won’t start after a jump start?
If your car won’t start after a jump start, there may be a more significant issue with the battery, starter, or electrical system. Consult a mechanic for further diagnosis.
-
How long should I let the good car run before attempting to start the dead car?
Let the good car run for at least 3-5 minutes to allow the battery to send a charge to the dead battery before attempting to start the dead car.
-
Can jump starting damage my car’s computer?
Improper jump starting can potentially damage your car’s computer or electrical system. Always follow the correct procedure and use caution.
-
What is the correct order for connecting jumper cables?
The correct order is: red to positive on the dead battery, red to positive on the good battery, black to negative on the good battery, and black to an unpainted metal surface on the dead car.
-
How can I prevent my car battery from dying?
To prevent your car battery from dying, turn off all lights and accessories when the car is not in use, have the battery tested regularly, and keep the battery terminals clean.
-
Should I replace my battery after jump starting it multiple times?
If you have to jump start your car frequently, it’s a sign that the battery is failing and should be replaced.
-
Can I use a portable jump starter instead of jumper cables?
Yes, portable jump starters are a convenient alternative to jumper cables. They are easy to use and can provide enough power to start your car without needing another vehicle.
-
What are the signs that my car battery is about to die?
Signs that your car battery is about to die include slow cranking, dim headlights, and the battery warning light illuminating on the dashboard.
10. Final Thoughts: Ensuring Safe and Successful Jump Starts
Knowing how to safely jump start a car with cables is an invaluable skill for any driver. By following the steps outlined in this guide and avoiding common mistakes, you can confidently handle a dead battery situation and get back on the road quickly. Remember, safety should always be your top priority.
At CARS.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing you with the knowledge and resources you need to maintain your vehicle and handle common car problems. If you have any questions or need further assistance, visit our website at CARS.EDU.VN or contact us at 456 Auto Drive, Anytown, CA 90210, United States, or via Whatsapp at +1 555-123-4567. We’re here to help you keep your car running smoothly and safely.
Are you struggling to find reliable car care and repair information? Do you often feel overwhelmed by the complexity of automotive maintenance? At CARS.EDU.VN, we understand these challenges. That’s why we offer a comprehensive resource for all your automotive needs. Visit CARS.EDU.VN today to discover expert advice, detailed tutorials, and a supportive community dedicated to helping you keep your car in top condition. Don’t let car troubles hold you back – empower yourself with the knowledge and resources you need at cars.edu.vn.