Is A Car Ac Or Dc Voltage? Navigating the world of electric vehicle (EV) charging can feel like deciphering a new language, but CARS.EDU.VN is here to help you understand the core concepts! Understanding alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) and their roles in EV charging is essential for every EV owner. Let’s explore how AC and DC voltage affect the charging process, ensuring you’re well-informed about electric vehicle supply equipment, electricity grids, and energy storage for a smooth EV experience.
1. Unveiling the EV Charging Ecosystem
Electric mobility is surging in popularity, and the EV charging ecosystem is expanding right alongside it. The concept seems simple enough: EVs plug into charging stations to replenish their batteries, just like refueling a gas car. However, EV chargers vary considerably in design, capabilities, and current types.
Alt Text: A woman checks her smartphone while her electric car charges at a public station, highlighting the convenience of modern EV charging.
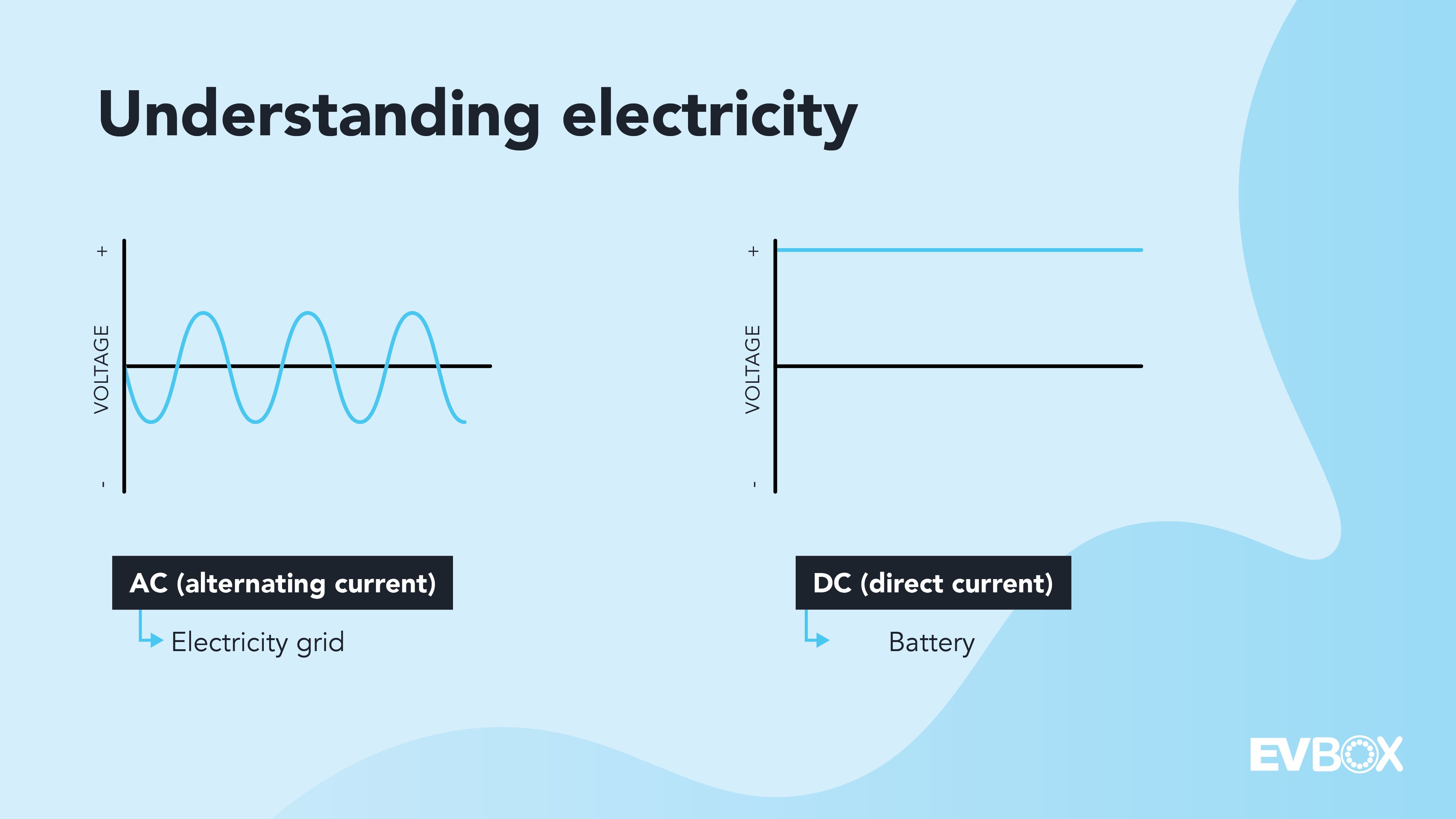
2. AC vs. DC: The Fundamental Differences
Before diving into the technical details, keep these two foundational principles in mind:
- The electricity from the grid—whether it’s a standard wall outlet—is always alternating current (AC).
- Batteries store energy as direct current (DC).
AC and DC are distinct types of electrical current, differing in direction, speed, and application. The legendary rock band AC/DC might have a “High Voltage” album, but they’re unrelated to electrical currents or EV charging!
Alt Text: A man uses an EVBox Livo home charging station as a woman checks her phone, showcasing the ease of home EV charging.
3. AC Charging Explained
AC, or alternating current, is an electrical current that periodically reverses direction. This means the flow of electrical charge alternates. AC power is commonly generated by renewable energy sources using rotating generators, like wind or hydropower turbines. AC’s ability to be efficiently transported over long distances has made it the standard for global electricity grids and household outlets.
Alt Text: A woman charges her electric car at an EVBox Troniq Modular public charging station, illustrating the widespread availability of AC charging.
4. DC Charging Demystified
DC, or direct current, flows in a single direction. It can be produced by renewable energy technologies such as solar panels. DC is used in energy storage, powering electronic devices, and LED lighting. Batteries store DC power. When you charge your laptop, for example, the charger converts AC power from the outlet into DC power for your laptop’s battery.
Essentially, we receive AC power from the grid, which is then converted into DC power for storage in batteries, including the battery that powers your EV.
Alt Text: An infographic contrasts AC and DC charging, highlighting the direction of current flow and conversion locations for electric vehicles.
5. The Key Difference: Conversion Location
When charging an EV, the primary distinction between AC and DC charging lies in where the AC-to-DC conversion takes place. Regardless of whether an EV uses an AC or DC charging station, the battery stores energy as DC.
When using a DC charging station, the conversion from AC (from the grid) to DC occurs within the charging station itself. This allows DC power to flow directly into the car’s battery. Because the conversion happens inside the charging station—a more spacious environment than the EV itself—more powerful converters can be used to rapidly convert AC power. Some DC stations can deliver up to 400 kW of power, fully charging an EV in a matter of minutes. According to a report by McKinsey, widespread adoption of DC fast charging could reduce range anxiety by making charging more convenient and quicker.
Many EV owners worry that DC charging may harm their batteries, but this is not the case.
Alt Text: A visual comparison of AC and DC charging setups, showing the flow of electricity and the location of the AC-to-DC conversion.
6. Understanding EV Charging Curves
Another major difference between AC and DC charging is how their power output changes during a charging session. This is known as the EV charging curve.
6.1. AC Charging Curve: A Steady Stream
With AC charging, the power delivered to an EV remains relatively constant, resulting in a flat charging curve. This is due to the EV’s onboard converter, which has limited power handling capabilities over extended periods.
6.2. DC Charging Curve: Fast Start, Gradual Taper
DC charging bypasses the car’s slower onboard converter, providing much higher power levels. However, this results in a decreasing charging curve. The EV battery initially accepts a high power flow but gradually reduces the intake as it approaches full capacity.
Think of a glass representing the EV’s battery, a water bottle as the DC charging station, and the water as the power. You can quickly fill the glass initially, but you need to slow down as you near the top to prevent overflow.
The same principle applies to DC fast and ultra-fast charging. EVs require less power as the battery reaches around 80 percent full, resulting in the decreasing power output observed in the charging curve.
Alt Text: An infographic illustrating AC and DC charging curves, showing how power delivery changes over time during the charging process.
Numerous factors influence charging speed and power.
7. AC vs DC Charging: Weighing the Pros and Cons
By now, it’s evident that AC and DC charging operate differently and serve different purposes. While DC charging is faster, it requires more bulky and costly equipment and a high-voltage connection to the power grid, making home installation impractical.
Because of the high initial investment, DC charging station operators often pass costs to users through higher pricing than AC chargers. Most EVs can fully charge overnight using even the slowest dedicated AC charging stations. DC charging is perfect for quick top-ups during long journeys. Depending on your car’s charging capacity and the station’s power output, a DC charger can add significant range in under an hour.
Alt Text: A white electric car drives into a sunset on an open road, symbolizing the freedom and convenience enabled by efficient EV charging.
8. Diving Deeper into EV Charging
Understanding the type of current used by a charging station is essential. EV charging involves much more, from finding EV chargers and using them to payment options.
9. CARS.EDU.VN: Your Guide to Mastering EV Charging
At CARS.EDU.VN, we understand that navigating the world of electric vehicles can be overwhelming. That’s why we’re dedicated to providing you with the latest information, expert insights, and practical tips to make your EV ownership experience smooth and enjoyable. Whether you’re a seasoned EV enthusiast or just starting your electric journey, we have something for everyone.
9.1 Comprehensive Guides and Resources
Dive into our extensive library of articles, guides, and resources covering every aspect of EV charging and ownership. Learn about:
- Home Charging Solutions: Discover the best home charging options, from Level 1 and Level 2 chargers to installation tips and cost considerations.
- Public Charging Networks: Get the lowdown on the various public charging networks, including pricing structures, membership benefits, and coverage maps.
- Charging Etiquette: Brush up on the unspoken rules of EV charging to ensure a harmonious experience for all users.
- Battery Health and Longevity: Learn how to optimize your battery’s performance and extend its lifespan with our expert tips and best practices.
9.2 Expert Reviews and Comparisons
Make informed decisions with our in-depth reviews and comparisons of the latest EV models, charging equipment, and accessories. Our team of automotive experts puts each product through rigorous testing to provide you with unbiased assessments and valuable insights.
- EV Model Reviews: Stay up-to-date with our comprehensive reviews of the latest electric vehicles, covering performance, range, features, and overall value.
- Charging Station Comparisons: Compare different charging stations side-by-side to find the perfect fit for your needs and budget.
- Accessory Recommendations: Discover the must-have accessories that can enhance your EV ownership experience, from portable chargers to cable organizers.
9.3 Community and Support
Join our vibrant community of EV enthusiasts and connect with like-minded individuals who share your passion for electric mobility. Ask questions, share tips, and participate in discussions on our forums and social media channels.
- Forums: Engage in lively discussions on a wide range of EV-related topics, from charging strategies to maintenance tips.
- Social Media: Stay connected with us on social media for the latest news, updates, and exclusive content.
- Expert Q&A: Get your burning questions answered by our team of EV experts in our regular Q&A sessions.
9.4 Practical Tips and Advice
Benefit from our practical tips and advice on how to maximize your EV’s efficiency, reduce your charging costs, and extend your driving range.
- Energy-Saving Techniques: Learn how to optimize your driving habits to conserve energy and increase your EV’s range.
- Smart Charging Strategies: Discover how to take advantage of off-peak electricity rates and smart charging technologies to save money on your energy bills.
- Maintenance Best Practices: Keep your EV running smoothly with our expert advice on routine maintenance and preventative care.
9.5 Stay Informed with the Latest EV News
Stay up-to-date with the latest developments in the electric vehicle industry with our comprehensive news coverage. We bring you breaking stories, in-depth analysis, and expert commentary on everything from new EV models to charging infrastructure advancements.
- Industry Trends: Stay ahead of the curve with our coverage of the latest trends and innovations in the EV industry.
- Policy Updates: Keep track of the latest government incentives, regulations, and policies that affect EV ownership.
- Technology Innovations: Explore the cutting-edge technologies that are shaping the future of electric mobility.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Car AC and DC Voltage
10.1. What is the main difference between AC and DC voltage in a car?
AC voltage alternates direction periodically, while DC voltage flows in one direction. Cars use both: AC for certain components and DC for battery storage and powering many systems.
10.2. Why do electric cars use DC for their batteries?
Batteries store energy in DC form because it provides a stable and consistent flow of electricity, ideal for the chemical reactions within the battery cells.
10.3. Can I use a regular home outlet to charge my EV?
Yes, you can use a standard household outlet (AC) to charge your EV, but it will charge at a slower rate compared to dedicated EV chargers.
10.4. Is DC fast charging bad for my EV battery?
Frequent DC fast charging can potentially increase battery degradation over time compared to Level 2 charging, but modern EVs have thermal management systems to mitigate this.
10.5. How do I choose between AC and DC charging stations?
Choose AC charging for home or overnight charging. Opt for DC fast charging when you need a quick top-up during long trips.
10.6. What voltage is typically used in car AC systems?
Car AC systems typically use 12V DC, which is converted from the engine’s mechanical power via an alternator to AC and then back to DC.
10.7. What is an inverter in an electric car, and what does it do?
An inverter converts DC power from the battery into AC power to drive the electric motor.
10.8. How efficient are AC and DC charging for EVs?
DC charging is generally more efficient because it minimizes energy conversion losses by directly supplying DC power to the battery.
10.9. What is the future of EV charging technology?
The future of EV charging includes higher voltage systems (800V+), wireless charging, and more efficient energy transfer methods to reduce charging times and improve convenience.
10.10. Are there any safety concerns with high-voltage DC charging?
High-voltage DC charging is safe when used correctly. Charging stations and EVs have built-in safety features to prevent electrical hazards.
11. Connect With CARS.EDU.VN Today
Ready to dive deeper into the world of electric vehicles? Visit CARS.EDU.VN today to explore our comprehensive resources, connect with our community, and discover how we can help you make the most of your EV ownership experience.
Address: 456 Auto Drive, Anytown, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 555-123-4567
Website: CARS.EDU.VN
At CARS.EDU.VN, we’re passionate about electric vehicles, and we’re committed to providing you with the knowledge and support you need to confidently embrace the electric future. Whether you’re looking for advice on choosing the right EV, tips on maximizing your driving range, or assistance with finding reliable charging solutions, we’re here to help.
Don’t let the complexities of EV charging hold you back. Visit CARS.EDU.VN today and unlock the full potential of electric mobility! We provide detailed service information, easy-to-understand maintenance guides, and expert car comparisons. Let us help you navigate the road ahead. Visit cars.edu.vn today.