Battery cables are essential for the performance and safety of any vehicle’s electrical system. Choosing the correct cable size is vital to ensure efficient power transmission, prevent voltage drops, and avoid overheating. Undersized cables can lead to reduced performance and potential hazards, while correctly sized cables optimize power delivery, extend battery life, and safeguard against electrical issues. Understanding battery cable sizing, particularly when it comes to gauges like 3 gauge, is crucial for anyone working with automotive electrical systems. Let’s delve into the specifics of 3 gauge car battery cables and battery cable sizing in general.
Key Points to Remember
- Battery cables, also known as battery leads, are primarily made of copper and aluminum.
- A typical voltage reading should be between 13 and 15 volts when the engine is running; a reading of 12 volts during operation may indicate a problem.
- Cable thickness is measured using the American Wire Gauge (AWG) standard, ranging from 0000 (thickest) to 40 (thinnest).
- Amperage can be calculated by dividing wattage by voltage.
Understanding Battery Cable Types
A battery cable is essentially a heavy-gauge copper wire with PVC insulation, designed to safely connect a vehicle’s battery to its electrical components. It consists of a positive lead connected to the ignition system and a negative lead grounded to the chassis. Here are common types of battery cables:
- SGX Battery Cable
- SGT Battery Cable
- Marine Battery Cable
- Fuse Link or Fusible Link
- OFC (Oxygen Free Copper)
- CCA (Copper Clad Aluminum)
SGX Battery Cable
SGX cables are known for their flexibility and high-temperature resistance. They feature soft-annealed construction, chemically cross-linked polyolefin insulation, and can operate in temperatures from -40°C to +125°C. While offering excellent heat resistance, SGX cables tend to be thicker and stiffer due to their insulation and high strand count. They are a good choice for high-temperature environments.
SGT Battery Cable
SGT battery cables utilize a THHN-type wiring coating, specifically thermoplastic PVC insulation. THHN stands for Thermoplastic High Heat-resistant Nylon-coated. These insulated SGT cables are rated at 50 volts for temperatures of 85°C or 105°C. SGT cables have a lower strand count with thicker individual strands, making them stiffer and better at holding their shape, which is useful for tight bends and specific routing.
Marine Battery Cable
Marine battery cables are designed to withstand harsh marine environments, including high temperatures and wet or submerged conditions. They are typically self-extinguishing and meet Coast Guard regulations for marine use. Using non-marine rated wires for boat applications is strongly discouraged. Marine cables are rated for 600 volts and can handle +105°C in dry conditions and +75°C in wet conditions.
Fuse Link or Fusible Link
A fuse link, or fusible link, acts as a slow-acting fuse resembling a wire. It features high-temperature insulation that resists burning even when the fuse blows. Fuse links are often used in alternator circuits to protect against alternator diode failures, preventing the alternator wire from melting. They are also used in wire intake grid heater relays in engines.
OFC (Oxygen Free Copper)
Standard oxygen-free copper wire is made of 99.95% copper. OFC (Oxygen-Free Copper) cables, while more expensive than standard cables of the same size, are often preferred in high-power audio systems. Quality OFC wires are typically SAE-approved.
CCA (Copper Clad Aluminum)
CCA cables are made of aluminum plated with copper. Due to aluminum’s lower conductivity (about 60% of copper), CCA wires need to be two gauge sizes larger than copper wires to achieve comparable conductivity.
Understanding Battery Cable Gauges and Sizes
Battery gauge refers to the thickness of the wire. The American Wire Gauge (AWG) system is the standard for measuring wire thickness. Smaller AWG numbers indicate thicker wires, while larger numbers indicate thinner wires. When we talk about “3 gauge car battery cable”, we are referring to its thickness based on this AWG standard.
Here’s a look at various battery gauges:
- 10 Gauge wire
- 8 Gauge wire
- 6 Gauge wire
- 4 Gauge wire
- 3 Gauge wire (Not explicitly listed in the original article’s list, but crucial for this article’s focus)
- 2 Gauge wire
- 1 Gauge wire
- 1/0 Gauge
- 2/0 Gauge
- 3/0 Gauge
- 4/0 Gauge
Now, to directly address the key question: What diameter is 3 gauge car battery cable?
While not listed in the original chart, a 3 gauge wire is thicker than a 4 gauge wire and thinner than a 2 gauge wire. According to standard AWG specifications, a 3 gauge wire has a diameter of approximately 0.259 inches (6.54 mm) for the copper conductor itself. When insulation is added, the overall outside diameter will be larger.
Let’s explore the uses of different gauges, including where 3 gauge fits in:
10 Gauge wire: Typically used for low-power applications like starter trigger wires, low-power alternators, and accessory leads.
8-gauge wire: Rated for around 40 amps, often used for low-power alternators and accessory leads.
6 gauge wire: Suitable for up to 55 amps, used for stock alternators, accessory leads, battery cables for ATVs and smaller vehicles, and golf cart wiring.
4 Gauge wire: Commonly used for car battery cables, audio systems, and industrial applications, rated for up to 160 amperes, suitable for alternator wiring.
3 Gauge wire: While the original article skips 3 gauge, it’s a relevant size. A 3 gauge wire is often used for high-power car audio systems, heavy-duty battery connections in vehicles, and for inverter installations. It bridges the gap between 4 gauge and 2 gauge, offering a balance of current carrying capacity and flexibility. It’s thicker than 4 gauge, providing better amperage handling for demanding applications.
2 Gauge wire: Used in high-amperage applications such as heavy machinery, industrial equipment, power converters, and winches. It can handle around 115 amps at 60°C, 150 amps at 90°C, and 130 amps at 167°F.
1 Gauge wire: Suitable for large 6-cylinder or V8 automotive engines, power converters, and higher amperage alternators (around 200 amperes).
1/0 Gauge: Heavy-duty wire used in various high-power electrical applications, including larger 6-cylinder engines, stock V8s, welding equipment, marine batteries, and solar/wind power installations. A 1/0 copper wire can carry about 150A at 75°C depending on insulation type.
2/0 Gauge: Thicker than 2 AWG, used for power distribution, transmission, and grounding. With a diameter of about 0.365 inches (9.27mm), it can handle around 135 amps at 60°C. Suitable for high-compression engines, diesel engines, and large RV power converter batteries.
3/0 Gauge: Used for marine and diesel engines according to the National Electrical Code (NEC). Suitable for dry, damp, and wet locations, and can operate up to 90°C in dry and 75°C in wet conditions.
4/0 Gauge: Rated for around 230 amperes at 75°C, used for high-power applications and large battery banks. Amperage ratings can vary based on conductor material (copper or aluminum) and insulation type.
The Importance of Correct Battery Cable Sizing
Choosing the right battery cable size is critical for safety and performance. Cable sizing standards are in place to prevent electrical hazards. Proper sizing minimizes voltage drops, reduces the risk of overheating, and ensures smooth power flow, optimizing the performance of electrical systems.
Using correctly sized cables can prevent breakdowns and increase the lifespan and productivity of machinery. It also minimizes the risk of electrical failures, protects personnel, and safeguards assets. Appropriately sized cables allow appliances to operate efficiently under normal working conditions without strain.
Wire Gauge Size Chart
To determine the correct wire gauge, check for markings on the wire itself or on the connector. It’s generally better to choose a larger wire size if you are unsure. The AWG system uses numbers to indicate thickness, with smaller numbers meaning thicker wires.
| Wire Gauge Size | Copper Conductor Diameter (inches) | Copper Conductor Diameter (mm) | Overall Outside Diameter with Insulation (inches) | Overall Outside Diameter with Insulation (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 0.143-0.165 | 3.63-4.19 | 0.218-0.270 | 5.54-6.86 |
| 6 | 0.181-0.200 | 4.60-5.08 | 0.305-0.340 | 7.75-8.64 |
| 4 | 0.219-0.252 | 5.56-6.40 | 0.343-0.405 | 8.71-10.29 |
| 3 | ~0.259 | ~6.54 | (Varies with insulation) | (Varies with insulation) |
| 2 | 0.289-0.326 | 7.34-8.28 | 0.418-0.475 | 10.62-12.07 |
| 1 | 0.341-0.361 | 8.66-9.17 | 0.479-0.520 | 12.17-13.21 |
| 1/0 (0) | 0.348-0.405 | 8.84-10.29 | 0.500-0.565 | 12.70-14.35 |
| 2/0 (00) | 0.429-0.460 | 10.90-11.68 | 0.568-0.655 | 14.43-16.64 |
| 3/0 (000) | 0.485-0.510 | 12.32-12.95 | 0.641-0.670 | 16.28-17.02 |
| 4/0 (0000) | 0.555-0.580 | 14.10-14.73 | 0.695-0.741 | 17.65-18.82 |



Note: The diameter for 3 gauge is added based on standard AWG values. Insulation thickness varies by cable type and manufacturer, so overall diameter for 3 gauge will vary.
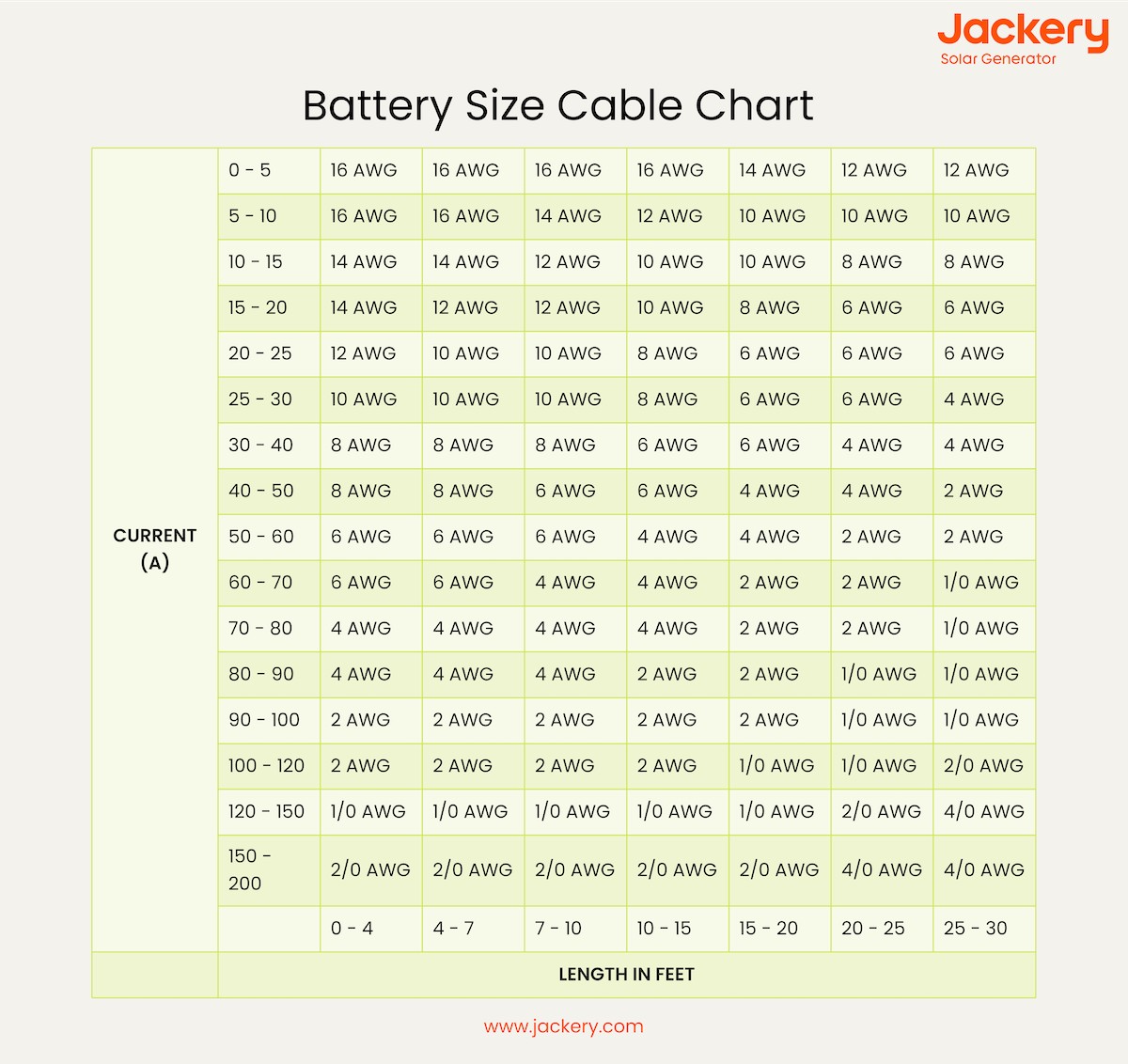
Using a Battery Cable Size Chart
A battery cable size chart helps determine the correct cable size for your application. Here’s how to use one:
Step 1: Determine DC Amp Requirement: Identify the current flow in amperes for your application.
Step 2: Circuit Type: Differentiate between critical and non-critical circuits, especially in RV and marine applications. Critical circuits include solar panel feeds and essential electronics, while non-critical circuits include lighting and appliances.
Step 3: Calculate Cable Length: Generally, double the application length for total cable needed (positive and negative runs). For example, a 20-foot application needs 40 feet of cable.
Step 4: Find the Correct Cable Size: Locate your DC amperage on the chart, intersect it with your cable length, and identify the corresponding cable size.
Step 5: Cable Conversion: Match the chart’s color code (if provided) to the cable size and specifications.
Battery Cable Amperage Capacity Chart
Amperage capacity charts help determine the right cable size based on the current draw of your appliances. Amperage can be calculated by dividing wattage by voltage (Amps = Watts / Volts). Voltage is the electrical potential difference that drives current flow.
This chart shows the relationship between cable size and amperage, helping you find the maximum wire length for a given cable size and amperage. For example, in a 12V system, a 6-gauge wire can handle 50 amps for a maximum run of 11.8 feet.
| Battery Cable Size | 50 Amps | 100 Amps | 150 Amps | 200 Amps | 300 Amps |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 AWG | 11.8ft | 5.9ft | 4.4ft | 2.9ft | 2.2ft |
| 4 AWG | 18.8ft | 9.4ft | 6.3ft | 4.7ft | 3.1ft |
| 2 AWG | 29.8ft | 14.9ft | 9.9ft | 7.4ft | 4.9ft |
| 1 AWG | 37.7ft | 18.9ft | 12.6ft | 9.4ft | 6.3ft |
| 1/0 AWG | 47.5ft | 23.8ft | 15.9ft | 11.9ft | 7.9ft |
| 2/0 AWG | 60ft | 30ft | 20ft | 15ft | 10ft |
| 3/0 AWG | 75.6ft | 37.8ft | 25.2ft | 18.9ft | 12.6ft |
Consequences of Incorrect Battery Cable Size
Undersized Cables:
The primary issue with undersized cables is voltage drop, where the voltage at the end of the wire is significantly lower than at the battery. This can cause appliances to malfunction or stop working. Voltage drop is calculated using Ohm’s law (V=I*R). Higher current and resistance lead to greater voltage drop. Undersized cables increase resistance due to their smaller cross-sectional area.
Overheating and melting are also risks. Current flow generates heat, and higher resistance in undersized cables leads to excessive heat. This can melt insulation and potentially cause fires.
Oversized Cables:
The main disadvantage of oversized cables is cost. Thicker cables are more expensive. For short cable runs, the increased cost might be negligible. However, weight also increases with cable gauge, making thicker cables harder to handle, especially in vehicle applications where flexibility is needed. For portable power solutions like Jackery Solar Generators, cable sizing is optimized for convenience and efficiency.
Jackery Solar Generators: Efficient Power Solutions
Jackery is a leading provider of portable solar power solutions, having sold millions of units including solar generators, portable power stations, and solar panels. A Jackery Solar Generator combines a Jackery Portable Power Station with Jackery SolarSaga Solar Panels. Solar panels convert sunlight into DC electricity, which is then stored in the power station. The built-in inverter converts DC to AC power for household appliances. Jackery Solar Generators are ideal for off-grid living, emergency backup, and outdoor activities.
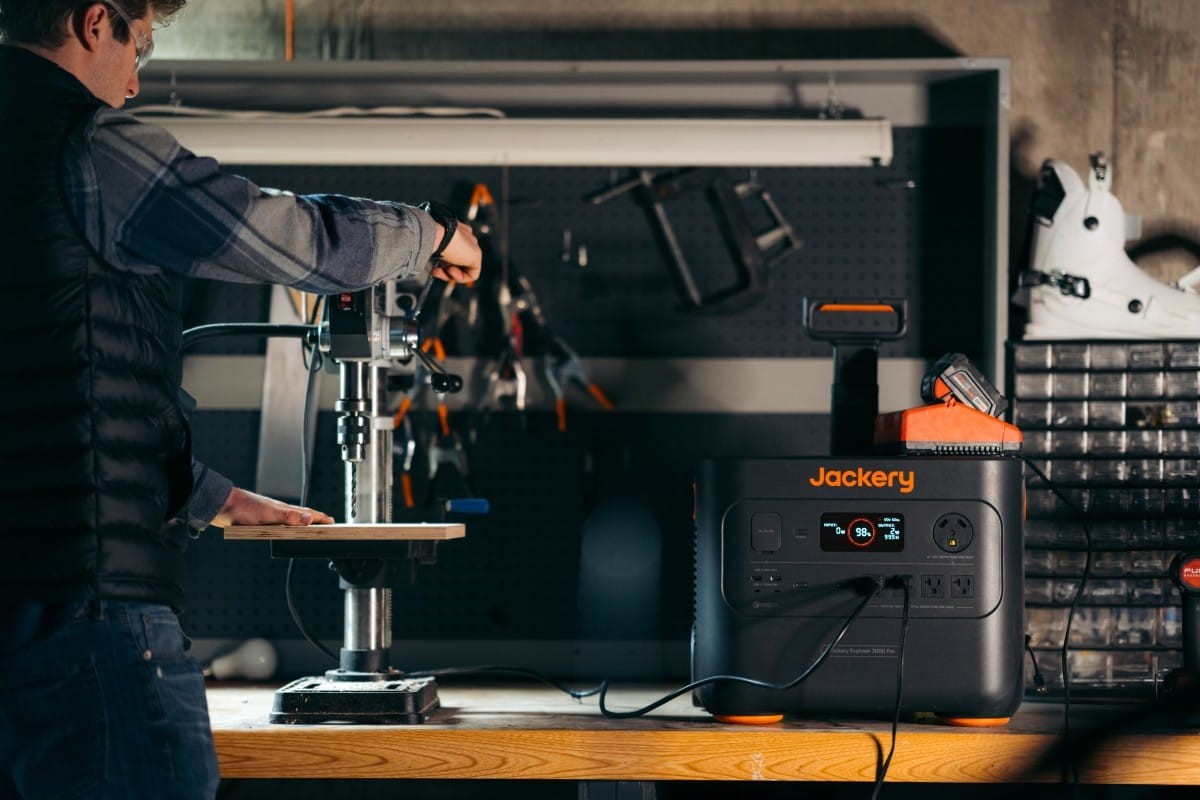
Jackery Solar Generator 3000 Pro
The Jackery Solar Generator 3000 Pro is a high-capacity unit suitable for RV living, camping, and glamping. It includes robust charging cables and a user-friendly handle. It can power 99% of common appliances for both indoor and outdoor use.
Example Appliance Runtimes:
- Refrigerator (520W): ~4.94 hours
- Heater (1800W): ~1.42 hours
- Microwave (960W): ~2.67 hours
Customer Review:
“I have a Jackery Explorer 1500 and 3000 Pro. Both are great generators, and the 3000 Pro is a beast. They are both well-made and work great. I now have 6 panels that I can use simultaneously to charge the 3000 Pro quickly. They have good warranties. Buy with confidence.” – Dustin M.
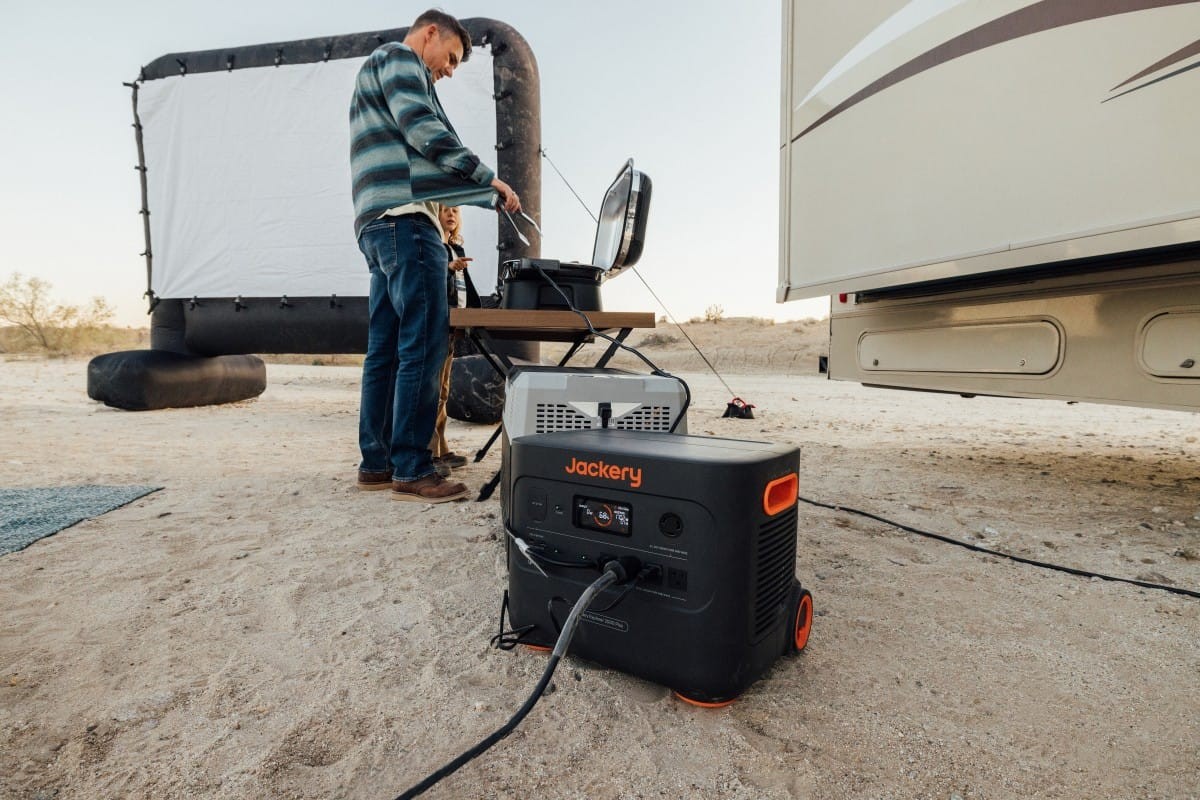
Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus
The Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus supports various cable types for charging devices in different situations. Its expandable capacity provides reliable backup power for outages and emergencies.
Example Appliance Runtimes:
- Portable Air Conditioner (1150W): ~1.5 hours
- Kettle (850W): ~2.04 hours
- Hand drill (400W): ~4.34 hours
Customer Review:
“ Amazing. It was expensive, but I did appreciate the coupon. I went off the grid with it, and we love it. We live in a camper and power up everything for at least two days without charging but using everything, so I’m thrilled that we got it. We have a small jackery that we relied on, but now we have no problem with power.” – Marcin Powichrowski
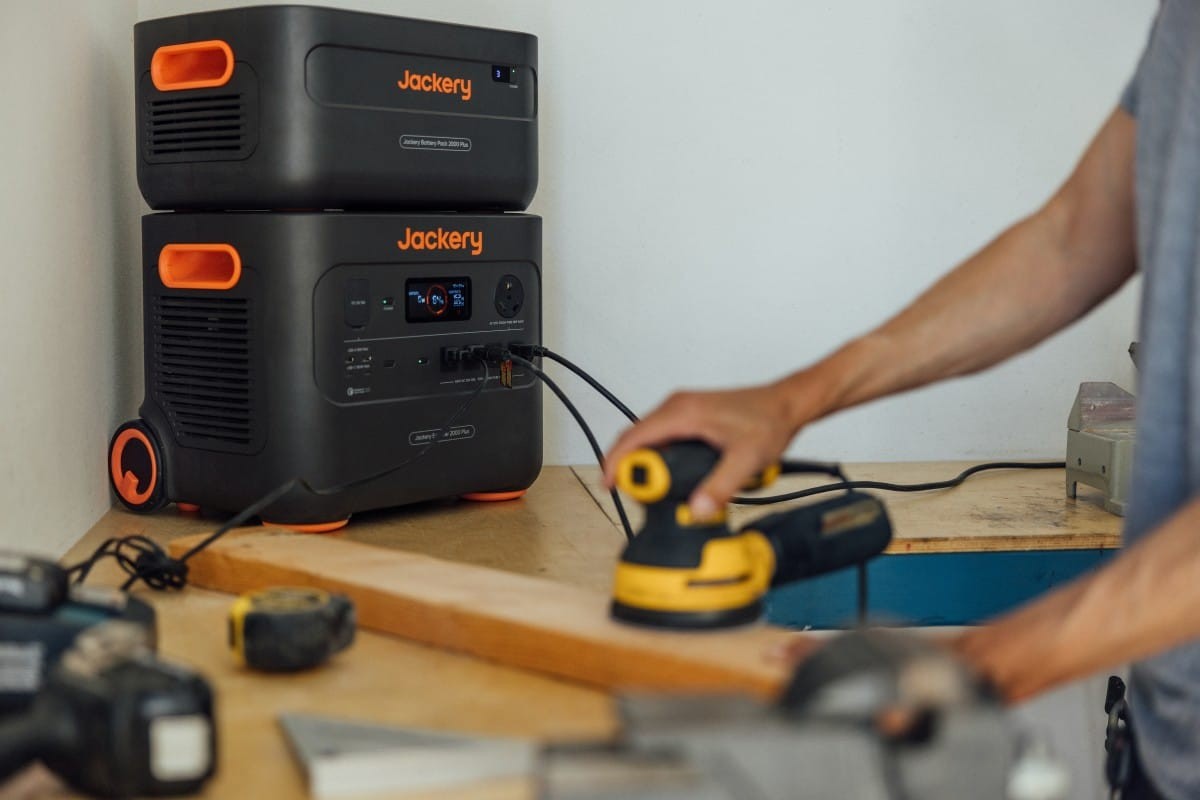
Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus Kit (4kWh)
The Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus Kit (4kWh) is designed for heavy-duty appliances and extended power needs. Jackery Solar Cables ensure easy and efficient charging with solar panels, providing reliable power during blackouts and off-grid living.
Example Appliance Runtimes:
- Coffee Maker (550W): ~6.31 hours
- Outdoor Electric Grill (1700W): ~2.04 hours
- Electric Oven (800W): ~4.34 hours
Customer Review:
“The Jackery Explorer 2000 Plus and Battery Pack with the 400W solar panels package is an excellent combination for home backup and RV usage. The 120VAC and RV receptacles and the others are great on the unit. I like the idea that if I need more power, I can purchase another battery pack.’’ – Larry Gee
Frequently Asked Questions
What size solar generator do I need?
Choosing the right size solar generator depends on your power needs. Consider the number and wattage of appliances you need to run and for how long.
For example, a Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus can power a 520W refrigerator and a 70W laptop for approximately 3 hours:
Working Time = (Generator Capacity in Wh × 0.85) / Total Appliance Wattage
Working time = (2042.8Wh × 0.85) / 580W ≈ 3 hours
Note: The 0.85 factor accounts for power loss during device charging.
How do I calculate my RV’s amp usage?
To calculate the amperage your RV will use, divide the total wattage consumption of all devices by the voltage of your RV system (typically 12V).
How do I determine the battery cable size I need?
Use a battery cable size chart, like the ones provided in this article, and consider your DC amperage requirements, cable length, and circuit type.
What gauge wire should I use for a 12V battery system?
For a 12V system with a 100-150 ampere load, a 4-gauge wire is often appropriate. However, always consult a cable sizing chart based on your specific amperage and length needs.
What does AWG mean in battery cables?
AWG stands for American Wire Gauge, the standard system for measuring wire thickness. Lower AWG numbers indicate thicker wires.
Conclusion
Using a battery cable size chart is crucial for selecting the correct cable size and thickness to match the voltage and current demands of your appliances and electrical systems. Proper cable sizing is essential to prevent voltage drops, overheating, and ensure the reliable and safe operation of your devices. Whether for car batteries, audio systems, or solar generators, choosing the right cable gauge, like understanding the diameter of a 3 gauge car battery cable, is a fundamental aspect of electrical system maintenance and design. Jackery Solar Generators, along with their compatible solar cables, are designed to provide efficient and safe renewable energy solutions, eliminating concerns about undersized or oversized cables for their intended applications.
Disclaimer:
Runtimes for appliances powered by Jackery products are estimates and for reference only. Actual performance may vary based on specific conditions. Always refer to real-world testing for precise results.
Shop products from this article
Jackery Solar Generator 3000 Pro
Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus
Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus kit (4kWh)