Vehicle Stability Assist, commonly known as VSA, is a pivotal safety feature in modern automobiles that actively enhances vehicle control. Understanding what VSA means in a car is essential for grasping how your vehicle prevents skidding and maintains stability, especially in adverse conditions. At CARS.EDU.VN, we empower drivers with comprehensive knowledge about automotive technologies like VSA, traction control, and electronic stability control, ensuring a safer and more informed driving experience. Explore our site for detailed guides on automotive safety systems, vehicle maintenance, and understanding your car’s features to improve your driving skills.
1. Decoding VSA: Vehicle Stability Assist Explained
VSA stands for Vehicle Stability Assist, an electronic stability control (ESC) system designed to prevent skidding and loss of control. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), ESC systems like VSA have significantly reduced the number of single-vehicle crashes. VSA systems constantly monitor the car’s direction and compare it with the driver’s intended path, intervening when a discrepancy is detected.
- What it Does: VSA automatically applies brakes to individual wheels and adjusts engine power to help steer the vehicle in the intended direction.
- Primary Goal: To maintain stability and prevent loss of control during sudden maneuvers or on slippery surfaces.
- Applicability: Particularly beneficial in situations where oversteer (rear wheels losing grip) or understeer (front wheels losing grip) is detected.
2. The Mechanics of VSA: How it Works
The VSA system is a sophisticated network of sensors and actuators working in tandem to ensure vehicle stability. It uses sensors to monitor various parameters and actuators to make corrections in real-time.
2.1. Core Components of a VSA System
- Wheel Speed Sensors: These sensors monitor the speed of each wheel individually. Discrepancies in wheel speed indicate potential loss of traction.
- Steering Angle Sensor: Measures the angle of the steering wheel, indicating the driver’s intended direction.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: Detects the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis, determining if the car is turning more or less than intended.
- Lateral Acceleration Sensor: Measures the sideways force acting on the vehicle, which helps determine if the car is drifting.
- Engine Control Unit (ECU): The brain of the VSA system, which processes data from the sensors and determines the appropriate corrective actions.
- Hydraulic Control Unit: Applies braking force to individual wheels as directed by the ECU.
- Engine Management System: Adjusts engine power output to reduce wheel spin or improve traction.
2.2. The VSA Process: Step-by-Step
-
Monitoring: Sensors continuously monitor wheel speed, steering angle, yaw rate, and lateral acceleration.
-
Data Analysis: The ECU analyzes the data to determine if the vehicle is behaving as intended.
-
Detection: If the ECU detects a discrepancy between the driver’s intended path and the vehicle’s actual movement (e.g., skidding or drifting), it activates the VSA system.
-
Intervention: The VSA system takes corrective actions:
- Braking: Applies brakes to one or more individual wheels to counteract the skid or drift.
- Engine Power Adjustment: Reduces engine power to decrease wheel spin and improve traction.
-
Correction: The system continuously adjusts braking and engine power until the vehicle is back under control.
2.3. Real-World Example
Imagine driving on a wet road and entering a turn too quickly. The car begins to understeer, meaning the front wheels lose grip and the car doesn’t turn as sharply as you intended. The VSA system detects this understeer:
- Detection: The yaw rate sensor indicates that the car is not turning as much as the steering angle suggests. The lateral acceleration sensor shows the car is drifting wide.
- Intervention: The VSA system applies the brake to the inside rear wheel. This action creates a rotational force that helps steer the car back into the intended path. At the same time, the engine power may be reduced to prevent further wheel spin.
- Correction: The car regains traction, and you maintain control, avoiding a potential accident.
3. Benefits of Having VSA in Your Car
VSA provides numerous benefits, primarily enhancing safety and control in challenging driving conditions. According to a study by the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS), ESC systems like VSA reduce the risk of fatal single-vehicle crashes by as much as 56%.
3.1. Enhanced Safety
- Skid Prevention: VSA helps prevent skids by automatically correcting oversteer and understeer, reducing the risk of accidents on slippery surfaces.
- Improved Control: By maintaining stability, VSA gives drivers greater control over their vehicles during emergency maneuvers.
- Reduced Accident Risk: Studies have shown that ESC systems significantly reduce the likelihood of crashes, particularly in adverse weather conditions.
3.2. Performance and Handling
- Optimized Traction: VSA helps maintain traction by preventing wheel spin, which is crucial for acceleration and climbing steep inclines.
- Cornering Stability: VSA ensures the vehicle remains stable during cornering, preventing loss of control when entering turns at higher speeds.
- Smooth Acceleration: On slippery surfaces, VSA modulates engine power to provide smooth and controlled acceleration.
3.3. Peace of Mind
- Confidence in Adverse Conditions: Knowing your car has VSA can give you peace of mind when driving in rain, snow, or on gravel roads.
- Driver Assistance: VSA acts as an electronic co-pilot, providing an extra layer of safety and control.
- Versatility: VSA is effective in various driving scenarios, from everyday commuting to emergency situations.
4. VSA vs. Other Stability Control Systems
While VSA is Honda’s specific name for its stability control system, other manufacturers use different terms. Understanding the similarities and differences can help clarify what VSA means in a car compared to other vehicles.
4.1. Common Stability Control Systems
| System Name | Manufacturer(s) |
|---|---|
| Vehicle Stability Assist (VSA) | Honda, Acura |
| Electronic Stability Program (ESP) | Mercedes-Benz, Audi, Volkswagen, BMW |
| Dynamic Stability Control (DSC) | BMW, Jaguar, Land Rover |
| StabiliTrak | General Motors (Chevrolet, GMC, Cadillac, Buick) |
| AdvanceTrac | Ford, Lincoln |
| Vehicle Dynamics Integrated Management (VDIM) | Lexus, Toyota |
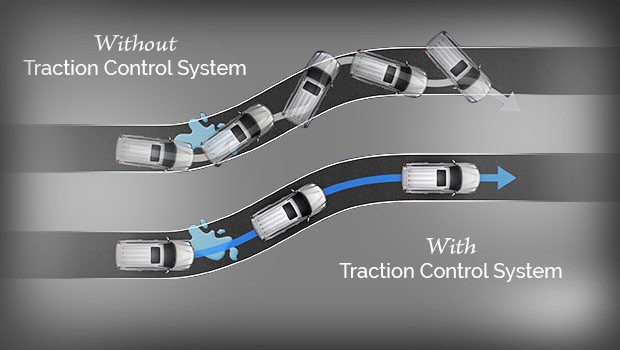

4.2. Functional Equivalence
Despite different names, these systems perform essentially the same function: to enhance vehicle stability by detecting and correcting skids.
- Core Functionality: All ESC systems monitor similar parameters (wheel speed, steering angle, yaw rate) and intervene by applying individual brakes and adjusting engine power.
- Variations in Implementation: While the core function remains the same, manufacturers may implement different algorithms or strategies for detecting and correcting skids.
- Performance Differences: Subtle differences in calibration and responsiveness may exist between systems, but the overall goal is consistent.
4.3. VSA in the Honda Context
In Honda vehicles, VSA is integrated with other safety systems like Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) and Traction Control System (TCS) to provide a comprehensive safety net.
- ABS (Anti-lock Braking System): Prevents the wheels from locking up during hard braking, allowing the driver to maintain steering control.
- TCS (Traction Control System): Limits wheel spin during acceleration, improving traction on slippery surfaces.
- Integration: VSA works in conjunction with ABS and TCS to provide a holistic approach to vehicle stability and control.
5. Understanding VSA Indicator Lights
The VSA system communicates with the driver through indicator lights on the instrument panel. Understanding what these lights mean is crucial for maintaining your vehicle and ensuring the VSA system is functioning correctly.
5.1. VSA Activation Light
- Appearance: A blinking light, often labeled “VSA” or with a car icon and skid marks.
- Meaning: Indicates that the VSA system is actively intervening to correct a skid or loss of control.
- Action: No action is required; the system is working as intended. You may feel slight changes in engine power or braking as the system operates.
5.2. VSA System Indicator Light
-
Appearance: A steady light, often labeled “VSA” or “VSA System.”
-
Meaning: Indicates a problem with the VSA system itself.
-
Action:
- Pull Over: When safe, pull over and turn off the engine.
- Restart: Restart the engine. If the light turns off, the system may have simply needed a reset.
- Service: If the light remains on, schedule a service inspection to diagnose the issue.
-
Driving: It is generally safe to drive with the VSA system indicator light on, but the VSA system will not be active, so exercise extra caution, especially in adverse conditions.
5.3. VSA Off Light
- Appearance: A light indicating that the VSA system has been manually turned off.
- Meaning: The VSA system is disabled and will not intervene to correct skids or loss of control.
- Action: Unless there is a specific reason to disable VSA (such as trying to free a stuck vehicle in deep snow), ensure the system is turned back on for optimal safety.
6. Common Issues and Troubleshooting
While VSA systems are generally reliable, they can experience issues. Knowing common problems and basic troubleshooting steps can help you address minor issues or determine when professional service is needed.
6.1. Causes of VSA System Problems
- Sensor Malfunctions: Wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, or yaw rate sensors can fail, leading to VSA system errors.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged or corroded wiring can disrupt communication between sensors and the ECU.
- Hydraulic Problems: Issues with the hydraulic control unit can prevent the VSA system from applying brakes effectively.
- Software Glitches: Occasionally, software glitches in the ECU can cause the VSA system to malfunction.
- ABS Issues: Since VSA relies on the ABS, problems with the ABS can also affect VSA performance.
6.2. Troubleshooting Steps
- Check Indicator Lights: Note which VSA indicator lights are illuminated (steady, blinking, or off).
- Restart the Car: Turn off the engine, wait a few minutes, and restart the car. This can sometimes reset the system and clear minor errors.
- Check Tire Pressure: Ensure all tires are properly inflated. Uneven tire pressure can affect wheel speed sensors and trigger VSA errors.
- Inspect Sensors: Visually inspect wheel speed sensors for damage or debris. Clean the sensors if necessary.
- Scan for Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to check for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the VSA system.
6.3. When to Seek Professional Help
If the VSA system indicator light remains on after troubleshooting or if you notice any of the following symptoms, seek professional service:
- Unusual Braking: The brakes feel uneven or pulsate erratically.
- Loss of Control: The car feels unstable or difficult to control, even with VSA active.
- ABS Malfunction: The ABS light is also illuminated, indicating a problem with the anti-lock braking system.
- Diagnostic Codes: The OBD-II scanner reveals VSA-related diagnostic trouble codes.
7. Maintaining Your VSA System
Proper maintenance is essential for ensuring the VSA system functions correctly and reliably. Regular inspections and adherence to recommended maintenance schedules can help prevent VSA-related issues.
7.1. Regular Inspections
- Brake System: Inspect the brake pads, rotors, and hydraulic lines regularly. Ensure the brake system is in good condition, as VSA relies on effective braking.
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Check wheel speed sensors for damage or debris during tire rotations or brake service.
- Tire Condition: Maintain proper tire pressure and ensure tires are evenly worn. Uneven tire wear can affect VSA performance.
7.2. Fluid Checks
- Brake Fluid: Check the brake fluid level and condition regularly. Replace brake fluid according to the manufacturer’s recommended schedule.
- Power Steering Fluid: Ensure the power steering system is functioning correctly, as it can affect steering angle sensor readings.
7.3. Scheduled Maintenance
- Follow the Maintenance Schedule: Adhere to the vehicle manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for all systems, including the brake system and ABS.
- Professional Service: Schedule regular check-ups with a qualified mechanic to inspect the VSA system and address any potential issues.
8. The Future of VSA and Stability Technology
Vehicle stability technology continues to evolve, with advancements in sensor technology, algorithms, and integration with other safety systems.
8.1. Advanced Sensor Technology
- Higher Precision: Future VSA systems will likely incorporate more precise sensors that provide more detailed data about vehicle dynamics.
- Predictive Capabilities: Advanced sensors may anticipate potential skids or loss of control before they occur, allowing the system to intervene earlier.
- Integration with ADAS: VSA will become increasingly integrated with Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS), such as lane departure warning and adaptive cruise control, to provide a more comprehensive safety net.
8.2. Enhanced Algorithms
- Adaptive Learning: Future VSA systems may use adaptive learning algorithms that adjust the system’s response based on driving style and road conditions.
- Personalization: Some systems may allow drivers to customize VSA settings to suit their preferences and driving needs.
- Improved Intervention Strategies: Algorithms will become more sophisticated, allowing for smoother and more effective corrective actions.
8.3. Integration with Autonomous Driving Systems
- Redundancy: VSA will serve as a crucial redundancy system in autonomous vehicles, providing an extra layer of safety in case of sensor or software failures.
- Emergency Control: VSA may be used to take over control of the vehicle in emergency situations, such as sudden obstacles or unexpected road conditions.
- Enhanced Safety Net: By working in conjunction with autonomous driving systems, VSA will contribute to a safer and more reliable driving experience.
9. Real-Life Impact: VSA in Action
To fully appreciate what VSA means in a car, it’s helpful to consider real-life scenarios where VSA has made a significant difference.
9.1. Case Study 1: Preventing a Skid on a Snowy Road
A driver is traveling on a snow-covered highway. As they enter a curve, the car begins to lose traction and starts to skid. The VSA system detects the skid:
- Detection: The wheel speed sensors indicate that the rear wheels are spinning faster than the front wheels. The yaw rate sensor shows that the car is rotating more than the steering angle suggests.
- Intervention: The VSA system applies the brake to the outside front wheel. This action creates a rotational force that helps steer the car back into the intended path.
- Outcome: The car regains traction, and the driver maintains control, avoiding a potential collision with a guardrail.
9.2. Case Study 2: Maintaining Control During an Emergency Maneuver
A driver is traveling on a busy city street. A pedestrian suddenly steps out into the road. The driver swerves sharply to avoid the pedestrian:
- Detection: The steering angle sensor indicates a sudden and extreme steering input. The lateral acceleration sensor shows that the car is experiencing significant sideways force.
- Intervention: The VSA system applies brakes to individual wheels to stabilize the car and prevent it from rolling over. The system also adjusts engine power to maintain traction.
- Outcome: The driver successfully avoids the pedestrian without losing control of the vehicle, preventing a potential accident.
9.3. Case Study 3: Improving Traction on a Gravel Road
A driver is traveling on a gravel road. The wheels begin to spin as they accelerate, making it difficult to maintain forward momentum:
- Detection: The wheel speed sensors indicate that the wheels are spinning excessively.
- Intervention: The VSA system reduces engine power to limit wheel spin and improve traction.
- Outcome: The car gains traction, and the driver is able to proceed safely on the gravel road.
10. CARS.EDU.VN: Your Source for Automotive Knowledge
At CARS.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing drivers with the knowledge and resources they need to make informed decisions about their vehicles. Understanding systems like VSA is crucial for ensuring safety and maximizing the performance of your car.
10.1. Comprehensive Resources
- Detailed Guides: Explore our website for in-depth articles on various automotive systems, including ABS, TCS, and ADAS.
- Troubleshooting Tips: Find practical troubleshooting tips and maintenance advice to keep your vehicle running smoothly.
- Comparison Tools: Use our comparison tools to evaluate different vehicle models and features, helping you choose the right car for your needs.
10.2. Expert Advice
- Professional Insights: Benefit from expert insights and recommendations from experienced automotive professionals.
- Service Locator: Find reputable service centers and mechanics in your area.
- Customer Support: Contact our customer support team for personalized assistance and answers to your automotive questions.
10.3. Stay Informed
- Latest News: Stay up-to-date with the latest automotive news, trends, and technologies.
- Product Reviews: Read unbiased reviews of new vehicles and automotive products.
- Community Forum: Join our community forum to connect with other car enthusiasts and share your experiences.
If you’re facing challenges finding reliable car repair services, understanding your vehicle’s maintenance needs, or choosing the right car model, CARS.EDU.VN is here to help. Our platform offers detailed information on car care, unbiased reviews, and expert advice to guide you. Visit CARS.EDU.VN today for reliable service recommendations and in-depth automotive insights. For further assistance, reach out to us at 456 Auto Drive, Anytown, CA 90210, United States, or contact us via WhatsApp at +1 555-123-4567.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What exactly does VSA do in a car?
VSA, or Vehicle Stability Assist, enhances vehicle stability by preventing skids and maintaining control during sudden maneuvers or on slippery surfaces. It automatically applies brakes to individual wheels and adjusts engine power to help steer the vehicle in the intended direction.
-
How can I tell if my VSA system is working properly?
If your VSA system is functioning correctly, the VSA activation light will blink when the system is actively intervening to correct a skid. If the VSA system indicator light is illuminated, it indicates a problem with the system itself.
-
Is it safe to drive with the VSA system indicator light on?
It is generally safe to drive with the VSA system indicator light on, but the VSA system will not be active. Exercise extra caution, especially in adverse conditions, and schedule a service inspection to diagnose the issue.
-
Can I turn off the VSA system?
Yes, most vehicles allow you to manually turn off the VSA system. However, unless there is a specific reason to disable VSA, it’s recommended to keep the system turned on for optimal safety.
-
What are some common causes of VSA system problems?
Common causes of VSA system problems include sensor malfunctions, wiring issues, hydraulic problems, software glitches, and ABS issues.
-
How often should I have my VSA system inspected?
The VSA system should be inspected regularly as part of your vehicle’s scheduled maintenance. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for all systems, including the brake system and ABS.
-
Are VSA and ESC the same thing?
VSA (Vehicle Stability Assist) is Honda’s specific name for its Electronic Stability Control (ESC) system. Other manufacturers use different terms, but the core functionality remains the same: to enhance vehicle stability by detecting and correcting skids.
-
What is the relationship between VSA, ABS, and TCS?
VSA (Vehicle Stability Assist), ABS (Anti-lock Braking System), and TCS (Traction Control System) work together to provide a comprehensive safety net. ABS prevents the wheels from locking up during hard braking, TCS limits wheel spin during acceleration, and VSA enhances vehicle stability by preventing skids.
-
How does VSA help in different weather conditions?
VSA is particularly beneficial in adverse weather conditions such as rain, snow, and ice. It helps prevent skids and maintains control by automatically correcting oversteer and understeer, reducing the risk of accidents on slippery surfaces.
-
Where can I find more information about VSA and other automotive systems?
Visit cars.edu.vn for detailed guides, troubleshooting tips, and expert advice on VSA and other automotive systems. We provide comprehensive resources to help drivers make informed decisions about their vehicles.