The suspension system of a car is a vital component responsible for a smooth, safe, and comfortable driving experience, working in harmony with related vehicle parts. CARS.EDU.VN is dedicated to unraveling the complexities of automotive systems, offering solutions and insights for every car enthusiast and owner. Delve into this detailed guide to discover the importance of your vehicle’s suspension, and explore the world of car maintenance and repair!
1. Understanding the Core Function of a Car’s Suspension System
The car’s suspension system is more than just springs and shocks; it’s a sophisticated network designed to maximize friction between the tires and the road surface. This ensures ride comfort, steering stability, and overall handling performance.
- Friction Maximization: The primary goal is to keep the tires in contact with the road, regardless of surface imperfections.
- Ride Comfort: Absorbs and dampens vibrations, providing a smooth and pleasant ride.
- Steering Stability: Maintains vehicle control and responsiveness, allowing for precise handling.
Consider the challenges a vehicle faces on a typical road. Uneven surfaces, potholes, and bumps can disrupt the car’s stability and driver control. The suspension system is engineered to absorb and mitigate these disruptions, ensuring the body and frame of the car remain stable. This is achieved through the careful design and interaction of various components, each playing a crucial role in the system’s overall effectiveness.
According to a report by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), suspension-related issues contribute to a significant percentage of vehicle accidents annually. Proper maintenance and understanding of the suspension system are therefore essential for road safety.
2. Key Principles of Vehicle Dynamics and Suspension Importance
Vehicle dynamics involve intricate principles like road isolation, road holding, and cornering, all of which are essential to understand for any car owner or enthusiast. These principles are where the suspension system proves its worth.
2.1. Road Isolation
Road isolation refers to the vehicle’s ability to remain undisturbed while traveling over rough and uneven surfaces.
- Function: Minimizes the impact of bumps and irregularities on the vehicle’s body and occupants.
- Mechanism: Achieved through the suspension system’s ability to absorb and dampen vibrations.
2.2. Road Holding
Road holding is the principle that tires must maintain continuous contact with the ground to ensure safe steering, braking, and acceleration.
- Importance: Essential for maintaining control of the vehicle in various driving conditions.
- Suspension Role: The suspension system ensures that the tires remain in contact with the road, even when encountering bumps and uneven surfaces.
2.3. Cornering
Cornering is the vehicle’s ability to navigate curved paths while minimizing body roll, ensuring stability and control during turns.
- Challenge: Body roll can reduce tire contact and compromise handling.
- Suspension Contribution: The suspension system, including components like sway bars and dampers, helps to minimize body roll and maintain tire contact.
These principles are critical to understanding how a vehicle performs in different driving scenarios. The suspension system’s design and condition directly impact these dynamics, affecting safety, comfort, and overall driving experience.
3. Major Components of a Car Suspension System
The suspension system is a complex assembly of numerous parts, each serving a specific function. Understanding these components is essential for proper maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Coil Springs
- Shock Absorbers
- Struts
- Control Arms
- Ball Joints
3.1. Coil Springs: The Foundation of Suspension
Coil springs are fundamental components that absorb the initial impact when a car encounters bumps and other road imperfections.
- Function: Compress and expand to absorb the motion of the wheels, providing a cushion between the road and the vehicle’s body.
- Types:
- Linear Springs: Offer a consistent spring rate throughout their compression range.
- Progressive Springs: Provide a variable spring rate, becoming stiffer as they compress further.
- Placement: Located between the vehicle’s frame and the wheels, supporting the vehicle’s weight and absorbing shocks.
3.2. Shock Absorbers: Damping the Motion
Shock absorbers work in tandem with coil springs to control and dampen the springs’ motion, preventing excessive bouncing and maintaining tire contact with the road.
- Function: Convert kinetic energy into thermal energy, dissipating the motion of the springs.
- Types:
- Hydraulic Shock Absorbers: Use fluid to resist motion, providing a damping force.
- Gas-Charged Shock Absorbers: Contain gas (usually nitrogen) to improve damping performance and reduce fluid aeration.
- Importance: Essential for ride comfort, handling, and braking performance, as they prevent the vehicle from bouncing excessively after encountering a bump.
3.3. Struts: Structural Support and Damping
Struts are structural components that combine the functions of shock absorbers and coil springs into a single unit, providing both support and damping for the suspension system.
- Function: Provide structural support for the vehicle’s suspension and wheel assembly, while also controlling the motion of the springs.
- Advantages:
- Compact Design: Combines multiple components into one unit, saving space and weight.
- Improved Handling: Provides precise control over wheel movement, enhancing handling and stability.
- Common Use: Often found in front suspension systems, where they play a crucial role in steering and handling.
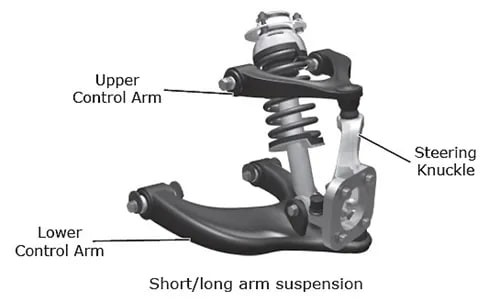
3.4. Control Arms: Connecting the Frame to the Wheels
Control arms are links that connect the vehicle’s frame to the steering knuckle or wheel-hub assembly, allowing the wheels to move up and down while maintaining proper alignment.
- Function: Control the motion of the wheels, ensuring they move in a controlled manner and maintain proper alignment.
- Types:
- Upper Control Arms: Connect the upper part of the wheel assembly to the frame.
- Lower Control Arms: Connect the lower part of the wheel assembly to the frame.
- Importance: Critical for maintaining stability and handling, as they control the wheel’s movement and prevent excessive play.
3.5. Ball Joints: Enabling Steering and Movement
Ball joints are pivotal parts that allow the vehicle to turn left and right, facilitating steering and enabling the control arms to move up and down.
- Function: Provide a pivot point for the steering knuckle, allowing the wheels to turn and the suspension to move freely.
- Importance:
- Smooth Steering: Enable smooth and precise steering, allowing the driver to control the vehicle’s direction with ease.
- Suspension Movement: Allow the control arms to move up and down, accommodating changes in road surface and maintaining tire contact.
- Maintenance: Require regular inspection and lubrication to prevent wear and ensure proper function.
Understanding these components is essential for diagnosing suspension issues and performing maintenance. Each part contributes to the overall performance and safety of the vehicle.
4. Exploring Different Types of Suspension Systems
Various types of suspension systems exist, each designed to meet specific vehicle requirements and driving conditions.
- Dependent Suspension Systems
- Independent Suspension Systems
4.1. Dependent Suspension Systems: Strength and Simplicity
Dependent suspension systems use rigid axles that connect the wheels on each side of the vehicle, providing strength and simplicity.
- Design: Rigid axle connects the wheels, causing them to move together.
- Advantages:
- Durability: Robust and capable of handling heavy loads.
- Off-Road Performance: Ideal for rough terrain, as the wheels share traction and maintain contact with the ground.
- Disadvantages:
- Ride Comfort: Less comfortable on paved roads, as bumps on one wheel affect the other.
- Handling: Limited independent wheel movement reduces handling precision.
- Common Use: Typically found in heavy-duty trucks, SUVs, and older vehicles.
4.2. Independent Suspension Systems: Comfort and Handling
Independent suspension systems allow each wheel to move independently, providing a smoother ride and improved handling.
- Design: Each wheel has its own suspension assembly, allowing independent movement.
- Advantages:
- Ride Comfort: Smoother ride on paved roads, as each wheel can respond independently to bumps and irregularities.
- Handling: Improved handling and stability, as each wheel can maintain optimal contact with the road.
- Disadvantages:
- Complexity: More complex and expensive to manufacture and maintain.
- Durability: Generally less durable than dependent suspension systems.
- Common Use: Widely used in modern passenger vehicles, providing a balance of comfort and performance.
Choosing the right type of suspension system depends on the vehicle’s intended use and the desired balance between comfort, handling, and durability.
5. Identifying Signs of Suspension Wear and Tear
Recognizing the signs of suspension wear and tear is essential for timely repairs and maintaining vehicle safety.
- Pulling to One Side
- Corner Sitting Low
- Increased Bumpiness
- Clunking Noises
- Vibrations
- Irregular Tire Wear
5.1. Pulling to One Side: A Sign of Instability
If your car drifts or pulls to one side of the road, it could indicate issues with the shocks or struts, which are responsible for keeping the vehicle stable.
- Cause: Uneven damping forces due to worn or damaged shocks/struts.
- Impact: Compromised handling and stability, increasing the risk of accidents.
5.2. Corner Sitting Low: Sagging Suspension
When one corner of your vehicle sits lower than the others, it is a sign of worn or damaged springs, which support the vehicle’s weight and maintain ride height.
- Cause: Weakened or broken springs, unable to support the vehicle’s weight evenly.
- Impact: Uneven tire wear, reduced ground clearance, and compromised handling.
5.3. Increased Bumpiness: A Rough Ride
An increase in bumpiness while driving indicates that the suspension system is no longer effectively absorbing shocks and vibrations.
- Cause: Worn or damaged shocks, struts, or other suspension components.
- Impact: Reduced ride comfort, increased wear on other vehicle components, and potential safety hazards.
5.4. Clunking Noises: Worn Components
Loud clunking noises when hitting bumps or uneven surfaces suggest that suspension components are loose, worn, or damaged.
- Cause: Worn ball joints, bushings, or other suspension parts.
- Impact: Reduced handling precision, increased wear on other components, and potential safety hazards.
5.5. Vibrations: Shaky Steering
Noticeable vibrations coming from the steering wheel area could indicate issues with the shock absorbers in the suspension system.
- Cause: Worn or damaged shock absorbers failing to dampen vibrations.
- Impact: Reduced steering precision, driver fatigue, and potential safety hazards.
5.6. Irregular Tire Wear: Uneven Balance
The suspension system helps keep your car balanced. If something is off, you might notice irregular wear on the tread of your tires.
- Cause: Misalignment, worn suspension components, or other issues affecting tire contact with the road.
- Impact: Reduced tire life, compromised handling, and potential safety hazards.
Addressing these signs promptly by seeking professional inspection and repair is essential for maintaining vehicle safety and performance. At CARS.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of a well-maintained suspension system. Our directory of trusted mechanics and service providers can help you find the right experts to diagnose and fix any suspension issues your vehicle may have.
6. Maintaining Your Car’s Suspension: A Proactive Approach
Regular maintenance is crucial for extending the life of your car’s suspension system and ensuring optimal performance.
- Regular Inspections
- Proper Alignment
- Timely Replacements
- Cautious Driving
6.1. Regular Inspections: Spotting Issues Early
Conduct regular inspections of your car’s suspension components to identify signs of wear, damage, or leaks.
- Frequency: At least twice a year, or more frequently if you drive on rough roads or carry heavy loads.
- Focus Areas:
- Shocks and Struts: Look for leaks, damage, or signs of wear.
- Springs: Check for cracks, sagging, or corrosion.
- Control Arms and Ball Joints: Inspect for play, looseness, or damage.
- Bushings: Check for cracks, wear, or deterioration.
6.2. Proper Alignment: Ensuring Balance
Ensure proper wheel alignment to prevent uneven tire wear and maintain optimal handling.
- Frequency: After any significant impact, such as hitting a pothole, or at least once a year.
- Benefits:
- Extended Tire Life: Proper alignment ensures even wear, maximizing tire lifespan.
- Improved Handling: Aligned wheels provide precise steering and stability.
- Enhanced Fuel Efficiency: Reduced rolling resistance improves fuel economy.
6.3. Timely Replacements: Avoiding Further Damage
Replace worn or damaged suspension components promptly to prevent further damage and maintain vehicle safety.
- Shocks and Struts: Replace every 50,000 to 80,000 miles, or as needed based on driving conditions.
- Springs: Replace if cracked, sagging, or corroded.
- Ball Joints and Control Arms: Replace if loose, worn, or damaged.
- Bushings: Replace if cracked, worn, or deteriorated.
6.4. Cautious Driving: Minimizing Stress
Practice cautious driving habits to minimize stress on your car’s suspension system.
- Avoid Potholes and Bumps: Steer clear of road imperfections whenever possible.
- Reduce Speed on Rough Roads: Slow down to minimize impact and vibration.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not exceed the vehicle’s weight capacity, as this can strain the suspension.
By following these maintenance tips, you can extend the life of your car’s suspension system and enjoy a smoother, safer, and more comfortable driving experience.
7. Car Suspension FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
Here are some frequently asked questions about car suspension systems, addressing common concerns and providing valuable insights.
- Is it OK to drive a car with bad suspension?
- What causes a car suspension to go bad?
- How do I maintain my car’s suspension?
- How long does a car suspension last?
- What are the different types of suspension systems available?
- How does the suspension system affect my car’s handling?
- Can I replace suspension parts myself, or should I go to a professional?
- What is the cost of repairing or replacing a car suspension system?
- How does the suspension system affect my car’s braking performance?
- What role do tires play in the overall suspension system?
7.1. Is it OK to drive a car with bad suspension?
Driving with a faulty suspension system is not advisable. It compromises vehicle control and safety, leading to uneven tire wear, reduced braking efficiency, and an increased risk of accidents. It’s crucial to address suspension issues promptly to ensure safe driving conditions.
7.2. What causes a car suspension to go bad?
A car’s suspension system deteriorates due to regular wear and tear, driving on rough roads, lack of maintenance, collisions, and exposure to harsh weather conditions. These factors contribute to the degradation of suspension components, affecting their performance and longevity.
7.3. How do I maintain my car’s suspension?
To maintain your car’s suspension, regularly inspect components for wear and tear, ensure proper alignment, and replace worn parts promptly. Avoid driving on rough terrain whenever possible, and adhere to routine maintenance schedules.
7.4. How long does a car suspension last?
The lifespan of a car suspension system varies depending on driving conditions, maintenance, and component quality. Typically, shocks and struts last between 50,000 to 80,000 miles, while other components may last longer. Regular inspections can help identify when parts need replacement.
7.5. What are the different types of suspension systems available?
The main types of suspension systems include dependent and independent suspensions. Dependent suspensions use a rigid axle connecting wheels, while independent suspensions allow each wheel to move separately, providing a smoother ride and better handling.
7.6. How does the suspension system affect my car’s handling?
The suspension system plays a critical role in your car’s handling by maintaining tire contact with the road, controlling body roll, and absorbing shocks. A well-maintained suspension system enhances stability, steering precision, and overall driving control.
7.7. Can I replace suspension parts myself, or should I go to a professional?
Replacing suspension parts can be complex and requires specialized tools and knowledge. While some experienced DIYers may attempt it, it’s generally recommended to seek professional assistance to ensure the job is done correctly and safely.
7.8. What is the cost of repairing or replacing a car suspension system?
The cost of repairing or replacing a car suspension system varies depending on the specific components involved, the vehicle’s make and model, and labor costs. It can range from a few hundred dollars for minor repairs to several thousand dollars for a complete suspension overhaul.
7.9. How does the suspension system affect my car’s braking performance?
The suspension system affects your car’s braking performance by maintaining tire contact with the road during braking. A well-maintained suspension system ensures that the tires grip the road properly, maximizing braking efficiency and reducing stopping distances.
7.10. What role do tires play in the overall suspension system?
Tires are an integral part of the suspension system, providing the initial contact with the road and absorbing shocks. Proper tire inflation, alignment, and tread depth are essential for optimal suspension performance and overall vehicle handling.
8. The Expert Touch: Why Professional Inspection Matters
While understanding your car’s suspension system is beneficial, professional inspection is invaluable. Trained technicians can identify subtle issues that may go unnoticed, ensuring accurate diagnosis and effective repairs.
- Advanced Diagnostic Tools: Professionals use specialized equipment to assess suspension performance and identify underlying problems.
- Expert Knowledge: Trained technicians have in-depth knowledge of suspension systems and can accurately diagnose and repair issues.
- Safety Assurance: Professional inspection and repair ensure that your car’s suspension system is functioning correctly, maintaining vehicle safety and stability.
- Long-Term Savings: Timely repairs prevent further damage and costly repairs down the road.
At CARS.EDU.VN, we connect you with certified mechanics and service providers who offer comprehensive suspension system inspections and repairs.
9. Innovative Suspension Technologies: A Glimpse into the Future
The automotive industry is continuously evolving, with advancements in suspension technology aimed at improving ride comfort, handling, and overall performance.
- Adaptive Suspension Systems
- Air Suspension Systems
- Magnetic Ride Control Systems
9.1. Adaptive Suspension Systems: Adjusting to Conditions
Adaptive suspension systems automatically adjust damping forces based on road conditions, driving style, and vehicle load, providing optimal comfort and handling in various situations.
- Sensors: Monitor road conditions and driving parameters.
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU): Processes data and adjusts damping forces in real-time.
- Actuators: Control the flow of fluid in the shock absorbers, adjusting their stiffness.
- Benefits:
- Improved Ride Comfort: Adapts to road conditions, providing a smooth and comfortable ride.
- Enhanced Handling: Optimizes damping forces for precise steering and stability.
- Increased Safety: Enhances vehicle control in emergency situations.
9.2. Air Suspension Systems: Ultimate Comfort and Control
Air suspension systems use air springs instead of traditional coil springs, providing adjustable ride height and superior ride comfort.
- Air Springs: Replace traditional coil springs, using compressed air to support the vehicle’s weight.
- Air Compressor: Supplies compressed air to the air springs.
- Height Sensors: Monitor ride height and adjust air pressure to maintain optimal level.
- Benefits:
- Adjustable Ride Height: Allows the driver to raise or lower the vehicle for improved clearance or aerodynamics.
- Superior Ride Comfort: Provides a smooth and comfortable ride, even on rough roads.
- Load Leveling: Maintains consistent ride height, regardless of vehicle load.
9.3. Magnetic Ride Control Systems: Precision and Responsiveness
Magnetic Ride Control systems use magneto-rheological (MR) dampers filled with fluid containing iron particles, which can be controlled by an electromagnetic field to adjust damping forces in real-time.
- MR Dampers: Filled with fluid containing iron particles.
- Electromagnetic Coils: Control the alignment of iron particles, adjusting damping forces.
- Sensors: Monitor road conditions and driving parameters.
- ECU: Processes data and adjusts damping forces in milliseconds.
- Benefits:
- Ultra-Fast Response: Adjusts damping forces in milliseconds, providing unparalleled control.
- Precise Handling: Optimizes damping forces for precise steering and stability.
- Smooth Ride: Adapts to road conditions, providing a comfortable and controlled ride.
These innovative suspension technologies represent the future of automotive engineering, offering enhanced performance, comfort, and safety for drivers and passengers alike.
10. Explore Further with CARS.EDU.VN: Your Automotive Resource
At CARS.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing comprehensive automotive information and resources, empowering you to make informed decisions about your vehicle’s maintenance, repair, and care.
10.1. Comprehensive Guides and Articles
Explore our extensive library of guides and articles covering various automotive topics, from basic maintenance tips to advanced repair techniques.
10.2. Trusted Mechanic Directory
Find certified mechanics and service providers in your area through our trusted directory, ensuring reliable and professional service for your vehicle.
10.3. Community Forums
Connect with fellow car enthusiasts and experts in our community forums, sharing knowledge, asking questions, and discussing all things automotive.
10.4. Latest Automotive News and Reviews
Stay up-to-date with the latest automotive news, reviews, and industry trends, ensuring you are always informed about the latest developments in the automotive world.
Visit CARS.EDU.VN today to discover a wealth of automotive knowledge and resources, empowering you to take control of your vehicle’s maintenance and care. For expert advice and assistance, contact us at 456 Auto Drive, Anytown, CA 90210, United States, Whatsapp: +1 555-123-4567, or visit our website at CARS.EDU.VN. Let us help you keep your car running smoothly and safely for years to come!
(CTA)
Are you experiencing suspension problems or simply want to ensure your vehicle is in top condition? Visit cars.edu.vn today for expert advice, trusted mechanic referrals, and a wealth of automotive resources. Let us help you keep your car running smoothly and safely. Explore now!
Alt text: Car undergoing suspension maintenance, highlighting the importance of regular check-ups for optimal vehicle performance.