What Is The Suspension System In A Car? It’s the unsung hero ensuring a smooth, safe, and controlled ride. At CARS.EDU.VN, we demystify this critical component, revealing how it absorbs shocks, maintains tire contact, and enhances handling. Explore our expert insights and discover how proper suspension maintenance can save you money and improve your driving experience.
1. Understanding the Core Function of a Car’s Suspension System
The suspension system in a car plays a vital role in ensuring a comfortable ride and maintaining control. Its primary function is to isolate the car’s body from road imperfections, maximizing friction between the tires and the road surface. This ensures stability, enhances handling, and promotes safe driving conditions. Think of the suspension as the car’s shock absorber, smoothing out bumps and dips to deliver a pleasant driving experience.
The suspension system directly influences three key aspects of vehicle dynamics, as noted by experts in Automotive Engineering International:
- Road Isolation: The ability of a vehicle to travel smoothly over rough surfaces, minimizing disturbances to the passengers.
- Road Holding: Ensuring constant tire contact with the road, which is essential for effective steering, braking, and acceleration.
- Cornering Stability: Maintaining vehicle stability while navigating turns, reducing body roll and ensuring precise handling.
Without a properly functioning suspension, every bump, pothole, and undulation would be directly transferred to the vehicle’s frame and, consequently, to the occupants. This not only results in an uncomfortable ride but also compromises the driver’s ability to maintain control, especially in emergency situations.
2. Key Components That Make Up the Suspension System
The suspension system is composed of several interconnected parts, each contributing to its overall performance. Here’s a breakdown of the main components:
-
Coil Springs: These springs absorb and release energy when the wheels encounter bumps, dampening vertical motion.
-
Shock Absorbers (Dampers): Working in tandem with coil springs, shock absorbers control spring oscillation, preventing excessive bouncing and ensuring a smoother ride.
-
Struts: These structural components combine the functions of shock absorbers and springs into a single unit, providing structural support and damping.
Alt text: Detailed view of a car strut assembly showcasing the coil spring, shock absorber, and mounting components.
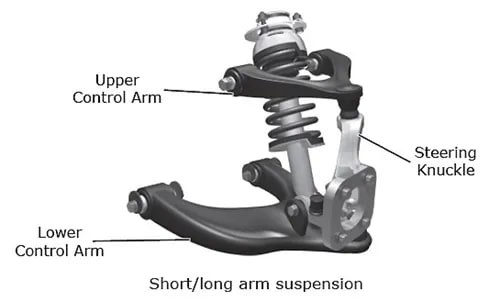
- Control Arms: These connect the vehicle’s frame to the wheel hub, allowing the wheels to move up and down while maintaining proper alignment.
- Ball Joints: Ball joints are pivotal connections that allow the wheels to turn and steer smoothly, facilitating both vertical and horizontal movement.
- Bushings: Made of rubber or polyurethane, bushings cushion the connection points between suspension components, reducing noise, vibration, and wear.
- Stabilizer Bar (Sway Bar): This bar connects the left and right wheels, reducing body roll during cornering and improving stability.
Each of these components plays a critical role in the overall performance of the suspension system. Regular inspection and maintenance of these parts are essential to ensure optimal ride quality and handling.
3. Exploring the Two Main Types of Suspension Systems
There are two primary types of suspension systems, each with its own advantages and applications:
-
Dependent Suspension: In this system, wheels on the same axle are connected by a rigid beam or axle. This design is robust and simple, often found in heavy-duty vehicles. Dependent suspensions excel in off-road conditions, providing excellent axle articulation and load-carrying capacity.
-
Independent Suspension: Each wheel has its own suspension assembly, allowing it to move independently. This results in a smoother ride and improved handling, making it common in modern passenger cars. Independent suspensions offer superior wheel control, reducing the impact of bumps on one wheel on the opposite wheel.
Alt text: A detailed view of an independent car suspension system showcasing the individual components for each wheel and their connections to the vehicle frame.
The choice between dependent and independent suspension systems depends on the vehicle’s intended use. Dependent suspensions are favored for their durability and load-carrying capabilities, while independent suspensions prioritize ride comfort and handling precision.
4. Recognizing the Signs of Suspension System Wear and Tear
Identifying early signs of suspension wear and tear can prevent costly repairs and ensure vehicle safety. Here are common indicators that your suspension system may need attention:
- Pulling to One Side: If your car drifts or pulls to one side while driving straight, it could indicate a problem with the shocks or struts.
- Uneven Tire Wear: Irregular wear patterns on your tires can be a sign of misaligned suspension components or worn shocks.
- Bumpy Ride: An excessively bouncy or rough ride suggests that the shock absorbers are no longer effectively damping the springs’ motion.
- Clunking Noises: Unusual noises, such as clunking or rattling, when driving over bumps or potholes, can indicate worn or damaged suspension parts.
- Excessive Body Roll: If your car leans excessively during turns, the stabilizer bar or other suspension components may be worn.
- Leaking Fluid: Visible fluid leaks around the shock absorbers or struts are a clear sign of damage and reduced performance.
- Nose Diving During Braking: If the front of your car dips excessively when braking, it could indicate worn shocks or struts.
- The Corner Sitting Low: Worn or damaged springs in your suspension can cause a corner of your vehicle to sit lower to the ground.
- Vibrations: Noticeable vibrations coming from the steering wheel area could signal issues with the shock absorbers in the suspension system.
Addressing these issues promptly can prevent further damage and maintain the vehicle’s safety and handling.
5. Step-by-Step Guide: Inspecting Your Car’s Suspension System
Regular inspections of your car’s suspension system can help you catch potential problems early. Follow these steps for a comprehensive check:
- Visual Inspection: Examine the shock absorbers and struts for signs of leaks, damage, or corrosion.
- Bounce Test: Push down firmly on each corner of the vehicle and release. The car should rebound quickly and settle without excessive bouncing.
- Tire Inspection: Check the tire tread for uneven wear patterns, which can indicate suspension misalignment or worn components.
- Component Check: Inspect control arms, ball joints, and bushings for wear, play, or damage.
- Listen for Noises: Pay attention to any unusual noises, such as clunking or rattling, when driving over bumps.
- Professional Evaluation: If you notice any concerning signs, have a trained technician perform a thorough inspection and diagnosis.
Performing these inspections regularly, ideally every 6 months or 12,000 miles, can help identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
6. The Role of Proper Wheel Alignment in Suspension Health
Wheel alignment is a critical aspect of suspension maintenance. Proper alignment ensures that all wheels are correctly angled relative to each other and the road surface. Misalignment can lead to:
- Uneven Tire Wear: Incorrect alignment angles cause tires to wear unevenly, reducing their lifespan.
- Poor Handling: Misalignment can compromise steering precision and vehicle stability, making it difficult to control the car.
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: Misaligned wheels increase rolling resistance, leading to lower fuel economy.
- Suspension Component Stress: Misalignment puts undue stress on suspension components, accelerating wear and tear.
A proper wheel alignment involves adjusting the following angles:
- Camber: The angle of the wheel relative to the vertical axis when viewed from the front.
- Caster: The angle of the steering axis relative to the vertical axis when viewed from the side.
- Toe: The angle of the wheels relative to each other when viewed from above.
Having your wheels aligned regularly, typically every 2 to 3 years or when you replace tires, can prolong the life of your suspension system and ensure optimal handling.
7. Common Suspension Problems and Their Solutions
Several common issues can plague car suspension systems. Understanding these problems and their solutions can help you address them effectively:
| Problem | Possible Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Worn Shock Absorbers/Struts | Normal wear and tear, age, rough road conditions | Replace shock absorbers/struts |
| Broken or Sagging Springs | Age, corrosion, heavy loads | Replace springs |
| Worn Ball Joints | Lack of lubrication, contamination, age | Replace ball joints |
| Damaged Bushings | Age, exposure to harsh chemicals, wear and tear | Replace bushings |
| Bent Control Arms | Impact damage, accidents | Replace control arms |
| Loose or Damaged Stabilizer Bar Links | Wear and tear, corrosion | Replace stabilizer bar links |
| Misalignment | Impact damage, worn suspension components, improper adjustments | Perform wheel alignment |
| Air Suspension Issues (if applicable) | Leaks in air springs, faulty compressor, damaged sensors | Repair or replace air springs, compressor, sensors |
| Electronic Suspension Issues | Faulty sensors, wiring problems, control module malfunctions | Diagnose and repair electronic components |
| Steering Wheel Vibrations | Loose components, worn-out tires, suspension issues | Check and tighten components, replace tires if necessary, inspect and repair suspension |
| Car Bounces Excessively | Worn shocks or struts, loose springs | Replace shocks or struts, tighten or replace springs |
| Uneven Tire Wear | Misalignment, worn or damaged suspension components | Perform wheel alignment, inspect and replace suspension components |

Addressing these problems promptly can prevent further damage and maintain the vehicle’s safety and handling.
8. The Importance of Choosing Quality Replacement Parts
When replacing suspension components, it’s essential to choose high-quality parts from reputable manufacturers. Using cheap or substandard parts can compromise the performance and safety of your suspension system.
- Durability: High-quality parts are built to withstand the stresses of daily driving, ensuring a longer lifespan.
- Performance: Quality components provide consistent and reliable performance, maintaining optimal ride quality and handling.
- Safety: Reliable suspension parts contribute to vehicle stability and control, enhancing safety in various driving conditions.
- Warranty: Reputable manufacturers typically offer warranties on their products, providing peace of mind and protection against defects.
Consider brands like Bilstein, KYB, Monroe, and Moog, known for their quality and reliability. Consulting with a trusted mechanic can help you choose the best replacement parts for your vehicle.
9. DIY vs. Professional Suspension Repair: Making the Right Choice
Deciding whether to tackle suspension repairs yourself or seek professional help depends on your mechanical skills, experience, and the complexity of the repair.
DIY Suspension Repair:
- Pros:
- Cost savings on labor
- Personal satisfaction
- Opportunity to learn about your car
- Cons:
- Requires specialized tools and equipment
- Can be time-consuming
- Risk of injury or improper repair
- May void warranties
Professional Suspension Repair:
- Pros:
- Expertise and experience
- Access to specialized tools and equipment
- Proper diagnosis and repair
- Warranty on parts and labor
- Cons:
- Higher cost
- Inconvenience of scheduling and dropping off the car
For minor repairs, such as replacing bushings or stabilizer bar links, DIY may be feasible for experienced individuals. However, for more complex repairs like replacing shocks, struts, or springs, professional assistance is recommended.
10. Suspension Upgrades: Enhancing Performance and Ride Quality
For car enthusiasts seeking to improve their vehicle’s handling and ride quality, several suspension upgrades are available:
- Performance Shocks and Struts: Upgrading to high-performance shocks and struts can improve handling, reduce body roll, and enhance ride comfort.
- Lowering Springs: Lowering springs reduce the vehicle’s ride height, improving handling and giving a sportier appearance.
- Coilover Kits: Coilover kits combine adjustable shocks and springs, allowing for precise tuning of ride height and damping characteristics.
- Performance Sway Bars: Upgrading to thicker sway bars reduces body roll during cornering, improving stability and handling.
- Air Suspension Systems: Air suspension systems allow for adjustable ride height and damping, providing a customized driving experience.
These upgrades can significantly enhance your vehicle’s performance and ride quality, but it’s essential to choose components that are compatible with your car and driving style.
11. The Impact of Road Conditions on Suspension Longevity
Road conditions play a significant role in the lifespan of your car’s suspension system. Driving on rough or poorly maintained roads can accelerate wear and tear on suspension components.
- Potholes: Potholes can cause sudden impacts that damage shocks, struts, springs, and other suspension parts.
- Gravel Roads: Driving on gravel roads can lead to increased wear on bushings and ball joints due to dust and debris.
- Speed Bumps: Speed bumps can cause excessive compression of the suspension, leading to premature wear on shocks and springs.
- Salt and Corrosion: In regions with harsh winters, salt and other de-icing chemicals can corrode suspension components, shortening their lifespan.
Taking precautions, such as avoiding potholes and driving cautiously on rough roads, can help prolong the life of your suspension system.
12. How Suspension Affects Braking and Safety Systems
The suspension system is intricately linked to your car’s braking and safety systems. A well-maintained suspension is crucial for effective braking and stability control.
- Braking Performance: A worn suspension can compromise braking performance, leading to longer stopping distances and reduced control.
- ABS (Anti-lock Braking System): The ABS relies on consistent tire contact with the road. A faulty suspension can interfere with ABS function, reducing its effectiveness.
- ESC (Electronic Stability Control): The ESC system uses sensors to detect and correct skids. A worn suspension can make it more difficult for the ESC to maintain control.
Ensuring that your suspension system is in good condition is essential for the proper functioning of these critical safety systems.
13. Advanced Suspension Technologies: A Look into the Future
Advancements in suspension technology are continuously improving ride comfort, handling, and safety. Here are some notable trends:
- Adaptive Suspension: Adaptive suspension systems use sensors and electronic controls to adjust damping characteristics in real-time, optimizing ride quality and handling.
- Magnetic Ride Control: Magnetic ride control uses magneto-rheological fluid in the shock absorbers, allowing for instantaneous adjustment of damping forces.
- Air Suspension with Electronic Control: Air suspension systems with electronic control offer adjustable ride height and damping, providing a customized driving experience.
- Predictive Suspension: Some advanced systems use cameras and sensors to anticipate road conditions, adjusting suspension settings in advance to optimize ride quality.
These technologies represent the future of suspension systems, offering unprecedented levels of comfort, control, and safety.
14. Maintaining Your Suspension: A Checklist for Longevity
Proper maintenance is key to extending the life of your car’s suspension system. Follow this checklist to keep your suspension in top condition:
- Regular Inspections: Inspect suspension components regularly for signs of wear, damage, or leaks.
- Wheel Alignments: Have your wheels aligned every 2 to 3 years or when you replace tires.
- Tire Maintenance: Maintain proper tire pressure and rotate tires regularly to ensure even wear.
- Lubrication: Lubricate ball joints and other grease fittings as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Component Replacement: Replace worn or damaged suspension components promptly.
- Avoid Overloading: Avoid overloading your vehicle, which can put undue stress on the suspension.
- Cautious Driving: Drive cautiously on rough roads and avoid potholes.
- Professional Service: Have your suspension system inspected and serviced by a qualified mechanic.
15. Real-World Examples: Suspension Issues and How They Were Resolved
- Case 1: Worn Shocks on a Family Sedan: A family sedan exhibited excessive bouncing and poor handling. Inspection revealed worn shock absorbers. Replacing the shocks restored ride comfort and handling stability.
- Case 2: Broken Spring on an SUV: An SUV had a noticeable lean to one side. A broken coil spring was identified as the cause. Replacing the spring restored the vehicle’s ride height and stability.
- Case 3: Misalignment on a Sports Car: A sports car exhibited uneven tire wear and poor handling. A wheel alignment corrected the alignment angles, improving handling and prolonging tire life.
- Case 4: Damaged Ball Joints on a Truck: A truck had excessive play in the steering and clunking noises. Worn ball joints were identified as the cause. Replacing the ball joints restored steering precision and eliminated the noises.
16. The Environmental Impact of Suspension Maintenance
Proper suspension maintenance not only benefits your vehicle but also has positive environmental impacts:
- Reduced Tire Wear: A well-maintained suspension system ensures even tire wear, extending tire life and reducing the need for frequent replacements.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: A properly aligned suspension reduces rolling resistance, improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions.
- Fewer Replacement Parts: Regular maintenance and timely repairs can prevent major suspension failures, reducing the demand for replacement parts.
By taking care of your suspension system, you can contribute to a more sustainable automotive ecosystem.
17. Future Trends in Suspension Design and Technology
The automotive industry is constantly evolving, and suspension design is no exception. Here are some emerging trends to watch:
- Active Suspension Systems: Active suspension systems use advanced sensors and electronic controls to continuously adjust damping and ride height, providing optimal performance in all driving conditions.
- Lightweight Materials: The use of lightweight materials, such as aluminum and carbon fiber, is becoming more common in suspension components, reducing weight and improving handling.
- Connectivity and Data Analytics: Future suspension systems will be connected to the internet, allowing for remote diagnostics and predictive maintenance. Data analytics will be used to optimize suspension performance and identify potential problems before they occur.
These innovations promise to deliver even greater levels of comfort, control, and safety in future vehicles.
18. Finding Reliable Suspension Services Near You
Finding a reputable mechanic for suspension services is crucial for ensuring quality repairs and maintenance. Here are some tips for finding reliable suspension services near you:
- Ask for Recommendations: Ask friends, family, and colleagues for recommendations.
- Read Online Reviews: Check online review sites like Google, Yelp, and Facebook to see what other customers have to say.
- Check for Certifications: Look for mechanics who are certified by organizations like ASE (Automotive Service Excellence).
- Get Multiple Quotes: Obtain quotes from several mechanics to compare prices and services.
- Ask About Warranty: Inquire about the warranty offered on parts and labor.
19. Expert Advice: Tips from Mechanics on Suspension Care
We consulted with experienced mechanics to gather their top tips for suspension care:
- Inspect Regularly: “Inspect your suspension components regularly for signs of wear or damage. Catching problems early can prevent costly repairs.”
- Maintain Tire Pressure: “Maintain proper tire pressure to ensure even tire wear and optimal suspension performance.”
- Avoid Overloading: “Avoid overloading your vehicle, as this can put undue stress on the suspension.”
- Drive Cautiously: “Drive cautiously on rough roads and avoid potholes to minimize impacts on the suspension.”
- Get Wheel Alignments: “Get your wheels aligned regularly, especially after hitting a major pothole or curb.”
- Use Quality Parts: “When replacing suspension components, use high-quality parts from reputable manufacturers.”
20. Suspension System FAQs – Your Questions Answered
- Is it OK to drive a car with a bad suspension? No, driving with a bad suspension is unsafe as it compromises vehicle control and braking.
- What causes a car suspension to go bad? Regular wear and tear, rough roads, lack of maintenance, and collisions.
- How do I maintain my car’s suspension? Inspect regularly, ensure proper alignment, and replace worn parts promptly.
- How long does a car suspension last? Typically, 5 to 10 years or 60,000 to 100,000 miles, depending on driving conditions.
- What are the signs of a bad suspension? Pulling to one side, uneven tire wear, a bumpy ride, and clunking noises.
- How much does it cost to replace a suspension? Costs vary widely, but expect to pay between $1,000 and $5,000 depending on the vehicle and extent of repair.
- Can I replace my car suspension myself? Minor repairs may be DIY, but complex repairs should be done by a professional.
- What is the difference between shocks and struts? Shocks dampen spring oscillations, while struts combine shocks and structural support.
- How often should I get a wheel alignment? Every 2 to 3 years or when you replace tires.
- What are the benefits of upgrading my suspension? Improved handling, ride comfort, and vehicle stability.
At CARS.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of a well-maintained suspension system for your vehicle’s safety, performance, and comfort. Whether you’re experiencing suspension issues or seeking to upgrade your system, we offer comprehensive information and resources to guide you. Our goal is to provide expert insights and practical advice to help you make informed decisions about your car’s suspension.
Ready to learn more and find the best suspension solutions for your car?
Visit CARS.EDU.VN for in-depth articles, expert reviews, and local service recommendations.
Address: 456 Auto Drive, Anytown, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 555-123-4567
Website: cars.edu.vn
This article provides general information and should not be considered professional automotive advice. Always consult with a qualified mechanic for specific suspension issues and repairs.
