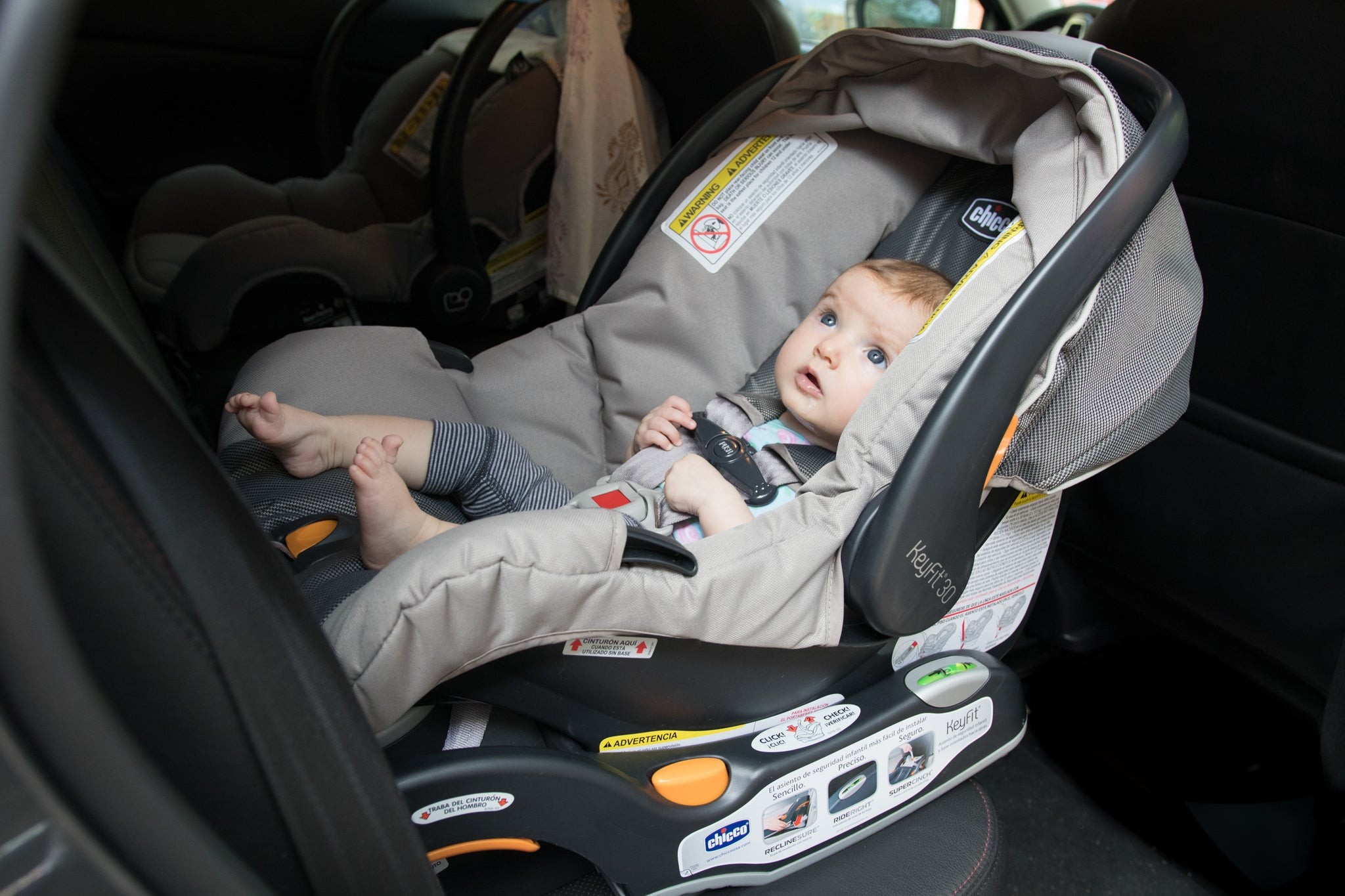
When Do Babies Outgrow Infant Car Seats is a crucial question for parents prioritizing their child’s safety. CARS.EDU.VN offers a comprehensive guide to help you understand the transition from infant car seats to convertible seats, ensuring your little one is always secure. This guide will also cover car seat safety, child passenger safety and selecting the right seat.
1. Understanding Infant Car Seats
Infant car seats are specifically designed for newborns and young babies, offering a safe and snug environment during car rides. These seats are rear-facing and typically come with a base that stays installed in the car, allowing for easy removal and transport of the baby.
1.1. Key Features of Infant Car Seats
- Rear-Facing Design: This is the safest position for infants as it distributes crash forces across the entire back, protecting the head, neck, and spine.
- Five-Point Harness: Provides a secure fit, keeping the baby in place during sudden stops or impacts.
- Removable Base: Allows for easy transfer of the seat between vehicles without disturbing the baby.
- Newborn Inserts: Offer extra support for smaller babies, ensuring a snug and secure fit.
- Carry Handle: Makes it convenient to carry the baby in the seat outside of the car.
1.2. Importance of Proper Installation
Correct installation is paramount for the safety of your child. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions and use the Lower Anchors and Tethers for Children (LATCH) system or the vehicle’s seat belt to secure the base.
1.3. Expert Advice on Infant Car Seat Usage
Lani Harrison, a certified Child Passenger Safety Technician (CPST) from Car Seats for the Littles, emphasizes the importance of proper recline angles for newborns. According to Harrison, “When a parent reports their baby is crying constantly in the car, it’s often because the infant car seat is set at too steep an angle.”
2. Recognizing When Your Baby Has Outgrown Their Infant Car Seat
Knowing when to transition your baby to the next stage car seat is essential for their safety. Here are the primary indicators that your baby has outgrown their infant car seat:
2.1. Height and Weight Limits
- Maximum Height: Most infant car seats have a maximum height limit of 30 to 32 inches.
- Maximum Weight: The weight limit typically ranges from 30 to 35 pounds.
Always refer to the car seat’s manual for the specific height and weight limits. Exceeding these limits compromises the seat’s ability to protect your child in a crash.
2.2. Head Position
Another critical indicator is the position of your baby’s head in relation to the top of the car seat. If the top of their head is less than one inch from the top of the seat while buckled in, it’s time to move to a convertible seat.
2.3. General Timeline
While every child grows at their own pace, most babies outgrow their infant car seats between 9 months and 2 years old. Bigger babies may reach the height and weight limits sooner.
2.4. Practical Considerations
Beyond the numbers, consider practical aspects. If the infant car seat becomes too heavy to carry comfortably, it might be time to switch to a convertible seat that stays installed in the car.
3. Understanding Convertible Car Seats
Convertible car seats are designed to accommodate growing children, offering the flexibility to be used in both rear-facing and forward-facing positions. This makes them a versatile option for parents looking to extend the rear-facing period for their children.
3.1. Benefits of Convertible Car Seats
- Extended Rear-Facing Use: Convertible seats allow children to remain in the rear-facing position for a longer period, which is significantly safer.
- Versatility: These seats can be converted to forward-facing mode as the child grows, providing a long-term seating solution.
- Higher Weight and Height Limits: Convertible seats generally have higher weight and height limits compared to infant seats.
3.2. Rear-Facing Recommendations
Both the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) and the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) recommend that children remain rear-facing as long as possible, up to the highest weight or height allowed by the car seat manufacturer.
3.3. Safety Advantages of Rear-Facing
In a head-on collision, the rear-facing position provides superior protection for a young child’s head, neck, and spine. The impact is absorbed by the car seat’s shell, reducing the risk of injury.
3.4. Swedish Model for Child Passenger Safety
Sweden, a country with remarkably low child fatality rates in car crashes, typically keeps children rear-facing until they are 4 years old. This practice underscores the safety benefits of extended rear-facing.
4. Transitioning to a Convertible Car Seat
Making the move to a convertible car seat requires careful consideration of your child’s development and the car seat’s specifications.
4.1. Meeting the Requirements
Ensure your child meets the minimum weight and height requirements for the convertible seat in the rear-facing position. Consult the car seat’s manual for specific guidelines.
4.2. Proper Installation
As with infant car seats, proper installation is critical. Use the LATCH system or the vehicle’s seat belt to securely install the convertible seat, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
4.3. Adjusting the Harness
The harness straps should be positioned at or slightly below your child’s shoulders when rear-facing. Ensure the harness is snug but not too tight, allowing only one finger to fit between the strap and your child’s collarbone.
4.4. Recline Angle
Adjust the recline angle to ensure your child’s head doesn’t slump forward, which can obstruct their airway. Most convertible seats have multiple recline positions to accommodate different ages and sizes.
5. Forward-Facing Considerations
Once your child outgrows the rear-facing limits of their convertible seat, it’s time to transition to the forward-facing position.
5.1. Minimum Requirements
While some parents may be tempted to turn their child forward-facing early, it’s crucial to wait until they meet the minimum requirements, typically around 2 years old and at least 20 pounds. However, experts recommend waiting longer.
5.2. Harness Straps
When forward-facing, the harness straps should be positioned at or slightly above your child’s shoulders. Adjust the straps as your child grows to ensure a secure fit.
5.3. Top Tether
Always use the top tether when installing a forward-facing car seat. The top tether anchors the car seat to the vehicle, reducing forward movement in a crash and minimizing the risk of head and neck injuries.
5.4. Expert Recommendations
The AAP recommends keeping children in a five-point harness until they outgrow the seat’s height and weight limits. Don’t rush the transition to a booster seat.
6. Booster Seat Basics
Booster seats are the next step after convertible car seats, designed to properly position the vehicle’s seat belt on the child’s body.
6.1. Types of Booster Seats
- High-Back Boosters: These provide additional side-impact protection for the head, neck, and upper back.
- Backless Boosters: These simply raise the child to the correct height for the seat belt.
6.2. When to Transition to a Booster Seat
A child should meet the following guidelines before moving to a booster seat:
- Weigh at least 40 pounds (minimum) and be 38 to 40 inches tall.
- Be at least 4 years old (minimum).
- Be able to understand and accept the need to sit still in the car.
- Be able to avoid slumping or slouching over in the car.
6.3. Proper Seat Belt Fit
The seat belt should fit properly, positioned across the collarbone and low on the hips, touching the tops of the thighs.
6.4. High-Back vs. Backless Boosters
For everyday use, high-back boosters are generally recommended due to the additional protection they provide.
6.5. Transitioning from High-Back to Backless
A child should stay in a high-back booster until they reach the seat’s high-back height or weight limits, or until the tops of their ears reach the top of the head restraint, and then move to a backless booster.
7. Final Stage: Using the Vehicle’s Seat Belt Alone
The NHTSA estimates that most children are ready to use the vehicle’s seat belt alone between the ages of 8 and 12.
7.1. Readiness Checklist
A child is ready to ride without a booster when:
- They are tall enough to remain in place if the car stops suddenly.
- They are able to keep their back against the vehicle seat, knees bent over the edge, and feet flat on the floor.
- They fit in a seat belt properly.
- They can maintain correct posture for the entire car ride.
7.2. Back Seat Safety
Regardless of the type of safety restraint, experts recommend that children continue sitting in the back seat of the car until they are at least 13 years old.
8. State Laws and Regulations
Child passenger safety laws vary by state. It’s essential to be aware of the specific requirements in your state to ensure compliance and, most importantly, your child’s safety.
8.1. Rear-Facing Laws
Many states require children under a year old to ride rear-facing, and increasingly, state laws require kids to stay rear-facing up to the age of 2.
8.2. Harness Laws
Many states require that a kid remain in a car seat with a five-point harness until they’re at least 40 pounds or 4 years old.
8.3. Booster Seat Laws
State laws vary regarding the age, weight, and height requirements for booster seats. Refer to resources like the Governors Highway Safety Association (GHSA) for detailed information on state-specific laws.
9. Additional Resources and Information
Stay informed and up-to-date on the latest car seat safety guidelines and best practices by consulting reputable resources.
9.1. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA)
The NHTSA provides comprehensive information on car seat safety, including recommendations, recall notices, and safety ratings.
9.2. American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP)
The AAP offers guidance on child passenger safety, including recommendations for rear-facing and forward-facing car seats.
9.3. Car Seats for the Littles
This website provides valuable resources and support for parents, including car seat reviews, installation tips, and expert advice.
9.4. Safe Kids Worldwide
Safe Kids Worldwide offers educational programs and resources to help parents keep their children safe in cars and other environments.
10. Addressing Common Concerns and Misconceptions
Clearing up common misconceptions about car seat safety can help parents make informed decisions.
10.1. Car Sickness
Some parents turn their child forward-facing early, thinking it will reduce car sickness. However, there’s no scientific evidence to support this claim.
10.2. Comfort
While some children may seem more comfortable forward-facing, the rear-facing position is significantly safer for young children.
10.3. Interaction
Parents may find it easier to interact with their child when they are forward-facing. However, there are ways to engage with a rear-facing child, such as using a mirror or stopping frequently for breaks.
11. The Role of CARS.EDU.VN in Child Passenger Safety
At CARS.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing accurate, up-to-date information to help parents make the best decisions for their children’s safety.
11.1. Comprehensive Car Seat Guides
We offer detailed guides on choosing, installing, and using car seats, covering infant seats, convertible seats, and booster seats.
11.2. Expert Reviews and Recommendations
Our team of experts reviews and recommends the best car seats on the market, considering safety ratings, ease of use, and comfort.
11.3. Safety Tips and Best Practices
We provide practical tips and best practices for ensuring your child’s safety in the car, from proper harness positioning to avoiding common installation errors.
11.4. Community Support
Join our community of parents and experts to share your experiences, ask questions, and learn from others.
12. Maximizing Car Seat Safety: A Detailed Guide
To maximize car seat safety, it is important to adhere to established guidelines and recommendations.
12.1. Choosing the Right Car Seat
Selecting the appropriate car seat for your child’s age, weight, and height is the first crucial step. Refer to the car seat’s manual for specific guidelines.
12.2. Proper Installation Techniques
Proper installation is paramount. Use either the LATCH system or the vehicle’s seat belt, following the manufacturer’s instructions meticulously. Ensure the seat is tightly secured and does not move more than one inch in any direction.
12.3. Harness Adjustment and Positioning
The harness straps should be correctly positioned: at or slightly below the shoulders for rear-facing and at or slightly above the shoulders for forward-facing. The harness should be snug, allowing only one finger to fit between the strap and your child’s collarbone.
12.4. Recline Angle Optimization
Adjust the recline angle to ensure your child’s head does not slump forward, which can obstruct their airway. Most car seats offer multiple recline positions.
12.5. Regular Car Seat Inspection
Regularly inspect the car seat for any signs of wear or damage. Replace the car seat immediately if it has been involved in a crash.
12.6. Avoiding Aftermarket Products
Avoid using aftermarket products that are not approved by the car seat manufacturer, as they may compromise the seat’s safety performance.
12.7. Staying Informed on Recalls
Stay informed about car seat recalls by registering your car seat with the manufacturer and monitoring recall notices from the NHTSA.
13. Addressing Special Needs and Medical Conditions
Children with special needs or medical conditions may require specialized car seats or positioning devices.
13.1. Consulting with Healthcare Professionals
Consult with your child’s pediatrician or a certified child passenger safety technician (CPST) to determine the best car seat and positioning options for your child’s specific needs.
13.2. Car Beds
Tiny preemies or babies with special needs or medical conditions may not be able to sit in a reclined position yet, and they might require different solutions than a typical car seat, such as a car bed.
13.3. Adaptive Car Seats
Adaptive car seats are designed to accommodate children with physical disabilities or medical conditions that make it difficult to use standard car seats.
13.4. Proper Positioning
Ensure proper positioning to maintain your child’s airway and prevent any discomfort or complications during car rides.
14. Exploring Advanced Car Seat Technologies
Advancements in car seat technology continue to improve child passenger safety.
14.1. SensorSafe Technology
Some car seats feature SensorSafe technology, which alerts parents if the child is left unattended in the car or if the harness is unbuckled during the ride.
14.2. Load Leg
A load leg is a support that extends from the base of the car seat to the vehicle floor, providing additional stability and reducing the risk of injury in a crash.
14.3. Side-Impact Protection
Many car seats offer advanced side-impact protection, including energy-absorbing foam and adjustable headrests, to minimize the risk of head and neck injuries in side-impact collisions.
14.4. Anti-Rebound Bar
An anti-rebound bar is a feature that helps to limit the movement of the car seat in a crash, reducing the risk of injury.
15. Car Seat Safety and Vehicle Compatibility
Ensuring that your car seat is compatible with your vehicle is essential for proper installation and safety.
15.1. Checking Vehicle Manual
Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for information on car seat installation and compatibility.
15.2. Lower Anchors and Tethers for Children (LATCH)
Use the LATCH system if available in your vehicle, following the car seat and vehicle manufacturer’s instructions.
15.3. Seat Belt Installation
If your vehicle does not have LATCH anchors, use the vehicle’s seat belt to install the car seat, ensuring a tight and secure fit.
15.4. Top Tether Usage
Always use the top tether when installing a forward-facing car seat to reduce forward movement in a crash.
15.5. Car Seat Inspection Stations
Visit a certified car seat inspection station to have your car seat installation checked by a trained professional.
16. Maintaining a Safe Driving Environment
Creating a safe driving environment is crucial for protecting your child in the car.
16.1. Avoiding Distractions
Avoid distractions such as cell phones, eating, and adjusting the radio while driving.
16.2. Following Speed Limits
Adhere to speed limits and adjust your driving to weather and road conditions.
16.3. Avoiding Aggressive Driving
Avoid aggressive driving behaviors such as tailgating, speeding, and weaving in and out of traffic.
16.4. Regular Vehicle Maintenance
Regularly maintain your vehicle to ensure it is in safe operating condition, including checking tires, brakes, and lights.
17. Financial Assistance Programs for Car Seats
Several programs offer financial assistance to help families afford car seats.
17.1. State and Local Programs
Check with your state and local health departments for information on car seat assistance programs.
17.2. Non-Profit Organizations
Non-profit organizations such as Safe Kids Worldwide and the National Safety Council may offer car seat assistance programs.
17.3. Hospital Programs
Some hospitals offer car seat programs for low-income families.
17.4. Community Resources
Check with local community centers and social service agencies for information on car seat assistance programs.
18. Promoting Car Seat Safety Awareness
Promoting car seat safety awareness can help protect more children.
18.1. Sharing Information
Share information on car seat safety with friends, family, and community members.
18.2. Participating in Community Events
Participate in community events that promote car seat safety awareness.
18.3. Volunteering
Volunteer at car seat inspection stations or other car seat safety programs.
18.4. Advocacy
Advocate for stronger car seat safety laws and policies.
19. Practical Tips for Long Car Rides
Ensure your child’s comfort and safety during long car rides.
19.1. Planning Regular Breaks
Plan regular stops to allow your child to stretch, move around, and use the restroom.
19.2. Packing Snacks and Drinks
Pack healthy snacks and drinks to keep your child nourished and hydrated.
19.3. Providing Entertainment
Provide entertainment such as books, music, and movies to keep your child occupied.
19.4. Ensuring Comfort
Ensure your child is comfortable by providing pillows, blankets, and appropriate clothing.
19.5. Monitoring Child’s Well-being
Monitor your child’s well-being throughout the car ride, checking for signs of discomfort or illness.
20. Debunking Common Car Seat Myths
Address and debunk common car seat myths to ensure parents have accurate information.
20.1. Myth: All Car Seats Are Equally Safe
Fact: Car seats vary in safety performance, ease of use, and features. Choose a car seat that meets your child’s needs and fits your vehicle properly.
20.2. Myth: Used Car Seats Are Always Safe
Fact: Used car seats may have been involved in a crash or have expired. Only use a used car seat if you know its history and it meets current safety standards.
20.3. Myth: More Expensive Car Seats Are Always Safer
Fact: Price does not always correlate with safety. Choose a car seat based on safety ratings, features, and ease of use, rather than price.
20.4. Myth: Children Can Ride Forward-Facing at 1 Year Old
Fact: The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that children remain rear-facing as long as possible, up to the highest weight or height allowed by the car seat manufacturer.
20.5. Myth: It’s Okay to Loosen Harness Straps in Hot Weather
Fact: Harness straps should always be snug, regardless of the weather. Loose straps can compromise the car seat’s safety performance in a crash.
21. Understanding Car Seat Expiration Dates
Car seats have expiration dates for safety reasons.
21.1. Plastic Degradation
The plastic components of a car seat can degrade over time, especially when exposed to temperature extremes and sunlight, making them less effective in a crash.
21.2. Changes in Regulations
Car seat safety regulations and standards may change over time. An expired car seat may not meet current safety standards.
21.3. Wear and Tear
Car seats can experience wear and tear over time, which can compromise their structural integrity.
21.4. How to Find the Expiration Date
The expiration date is typically printed on a label on the car seat. If you cannot find the expiration date, contact the car seat manufacturer.
21.5. Proper Disposal
Dispose of expired car seats properly to prevent them from being used by others. Cut the harness straps and remove the car seat cover before disposing of the seat.
22. Resources Available at CARS.EDU.VN
CARS.EDU.VN offers a wealth of resources to help you navigate the complexities of car seat safety.
22.1. Car Seat Buying Guides
Our comprehensive buying guides provide detailed information on choosing the right car seat for your child’s age, weight, and height.
22.2. Car Seat Installation Tutorials
Our step-by-step tutorials guide you through the process of installing car seats correctly, ensuring a tight and secure fit.
22.3. Car Seat Reviews
Our expert reviews provide unbiased assessments of car seats, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses.
22.4. Safety Tips and Best Practices
We offer practical safety tips and best practices for maximizing car seat safety, from proper harness positioning to avoiding common installation errors.
22.5. Expert Advice
Our team of experts is available to answer your questions and provide personalized advice on car seat safety.
23. Embracing the Future of Car Seat Safety
The future of car seat safety is bright, with ongoing advancements in technology and design.
23.1. Smart Car Seats
Smart car seats incorporate sensors and connectivity to provide real-time feedback on car seat usage and child well-being.
23.2. Self-Installation Systems
Self-installation systems simplify the car seat installation process, reducing the risk of errors.
23.3. Advanced Materials
Advanced materials such as energy-absorbing foams and lightweight composites are being used to enhance car seat safety performance.
23.4. Enhanced Side-Impact Protection
Enhanced side-impact protection systems are being developed to provide even greater protection in side-impact collisions.
23.5. Integration with Vehicle Systems
Integration with vehicle systems allows for seamless communication between the car seat and the vehicle, enhancing safety and convenience.
24. Statistics and Data on Child Passenger Safety
Reviewing statistics and data on child passenger safety underscores the importance of proper car seat usage.
24.1. Car Seat Effectiveness
Car seats reduce the risk of fatal injury by 71% for infants and 54% for toddlers in passenger cars.
24.2. Booster Seat Effectiveness
Booster seats reduce the risk of injury by 45% compared to seat belts alone for children ages 4 to 8.
24.3. Rear-Facing Safety
Rear-facing car seats are five times safer than forward-facing car seats for children under 2 years old.
24.4. Misuse Rates
Car seats are often misused, with an estimated 46% to 72% of car seats being installed incorrectly.
24.5. Importance of Proper Usage
Proper car seat usage is critical for reducing the risk of injury and death in car crashes.
25. Resources for Finding Certified Child Passenger Safety Technicians
Ensuring your car seat is correctly installed is crucial, and certified Child Passenger Safety Technicians (CPSTs) can provide valuable assistance.
25.1. Safe Kids Worldwide
Safe Kids Worldwide offers a search tool to find certified CPSTs in your area.
25.2. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA)
The NHTSA provides resources for locating car seat inspection stations and certified CPSTs.
25.3. Local Hospitals and Fire Departments
Local hospitals and fire departments often have certified CPSTs on staff or can provide referrals.
25.4. AAA Auto Clubs
AAA auto clubs may offer car seat inspection services and can help you find certified CPSTs.
25.5. Online Directories
Online directories such as the National Child Passenger Safety Certification Training Program provide listings of certified CPSTs.
26. Key Takeaways for Parents
Review the essential information to help parents ensure their children’s safety in the car.
26.1. Choose the Right Car Seat
Select the appropriate car seat for your child’s age, weight, and height.
26.2. Install Car Seats Correctly
Install car seats correctly using the LATCH system or the vehicle’s seat belt.
26.3. Use Harness Straps Properly
Use harness straps properly, ensuring a snug fit.
26.4. Stay Rear-Facing as Long as Possible
Keep children rear-facing as long as possible, up to the highest weight or height allowed by the car seat manufacturer.
26.5. Transition to Booster Seats When Appropriate
Transition to booster seats when children meet the age, weight, and height requirements.
26.6. Practice Safe Driving Habits
Practice safe driving habits, avoiding distractions and following traffic laws.
26.7. Stay Informed
Stay informed on car seat safety guidelines and best practices by consulting reputable resources.
27. A Call to Action for Enhanced Child Passenger Safety
Taking action to promote car seat safety can help protect more children.
27.1. Spread Awareness
Share car seat safety information with friends, family, and community members.
27.2. Support Legislation
Support legislation that promotes car seat safety.
27.3. Advocate for Resources
Advocate for increased funding and resources for car seat safety programs.
27.4. Educate Yourself and Others
Educate yourself and others on car seat safety best practices.
27.5. Get Involved
Get involved in car seat safety initiatives and programs in your community.
28. Summary of Key Recommendations
Summarize the main points to reinforce the importance of car seat safety.
28.1. Select the Right Car Seat
Ensure the car seat is appropriate for your child’s age, weight, and height.
28.2. Follow Installation Instructions
Adhere to the manufacturer’s instructions for proper installation.
28.3. Adjust Harness Straps Properly
Make sure the harness straps are snug and correctly positioned.
28.4. Keep Children Rear-Facing Longer
Extend rear-facing use as long as possible.
28.5. Transition to Booster Seats Safely
Transition to booster seats when your child meets the necessary criteria.
28.6. Practice Vigilant Driving Habits
Maintain safe driving practices at all times.
28.7. Stay Informed and Proactive
Keep up-to-date with safety guidelines and participate in community efforts to enhance child passenger safety.
29. FAQ: When Do Babies Outgrow Infant Car Seats?
29.1. What are the key indicators that my baby has outgrown their infant car seat?
The primary indicators are reaching the maximum height or weight limit specified by the manufacturer, or when the top of your baby’s head is less than one inch from the top of the seat.
29.2. What is the typical age range for babies to outgrow their infant car seats?
Most babies outgrow their infant car seats between 9 months and 2 years old, depending on their growth rate.
29.3. Can I switch to a convertible car seat before my baby reaches the maximum weight limit of the infant car seat?
Yes, you can switch to a convertible car seat as long as it is rated safe for your child’s height and weight, even if they haven’t reached the infant seat’s maximum weight limit.
29.4. What are the benefits of using a convertible car seat?
Convertible car seats offer extended rear-facing use, which is safer for young children, and can be converted to forward-facing mode as the child grows.
29.5. What is the recommended age for turning a child forward-facing in a convertible car seat?
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends keeping children rear-facing as long as possible, up to the highest weight or height allowed by the car seat manufacturer.
29.6. How do I properly install a convertible car seat?
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and use the LATCH system or the vehicle’s seat belt to securely install the convertible seat, ensuring it does not move more than one inch in any direction.
29.7. What are the key considerations when transitioning to a booster seat?
Ensure your child meets the minimum weight and height requirements, is at least 4 years old, and can sit still in the car without slumping or slouching.
29.8. What are the benefits of using a high-back booster seat?
High-back booster seats provide additional side-impact protection for the head, neck, and upper back.
29.9. When is a child ready to use the vehicle’s seat belt alone?
A child is ready to use the vehicle’s seat belt alone when they are tall enough to remain in place if the car stops suddenly, can keep their back against the vehicle seat, knees bent over the edge, and feet flat on the floor, and fit in a seat belt properly.
29.10. Where can I find more information and resources on car seat safety?
You can find more information and resources on car seat safety from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), and websites like CARS.EDU.VN.
30. Contact CARS.EDU.VN for Further Assistance
For more in-depth information and personalized assistance, reach out to CARS.EDU.VN.
30.1. Our Commitment
At CARS.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges of ensuring your child’s safety in the car. We are dedicated to providing you with the most accurate, up-to-date information and resources to help you make informed decisions.
30.2. How to Reach Us
- Address: 456 Auto Drive, Anytown, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 555-123-4567
- Website: CARS.EDU.VN
30.3. Our Services
Whether you need help choosing the right car seat, understanding state laws, or finding a certified Child Passenger Safety Technician, CARS.EDU.VN is here to support you. Visit our website or contact us today to learn more.
Understanding when babies outgrow infant car seats is crucial for ensuring your child’s safety. By following these guidelines and staying informed, you can make the best decisions for your little one.
Are you struggling to find reliable car maintenance and repair information? Do you need expert advice on choosing the right car seat or understanding vehicle safety features? Visit CARS.EDU.VN today to discover a wealth of resources and expert guidance to help you keep your family safe on the road. Our comprehensive guides, reviews, and community support will empower you to make informed decisions and protect your loved ones. Don’t wait – ensure your peace of mind by exploring cars.edu.vn now.